For years the topic of Supply Management has been a hot button issue for dairy producers around the world. Those who operate under a supply management system, such as the one in Canada, are strong advocates for the program. While those that do not, such as New Zealand, Australia, and the US, tend to look at it with envy and even disdain. Recently there has been a lot of international talk about supplying of the supply management in the dairy sector. The EU is removing supply management and the US government, who was proposing a supply management system, removed it in their most recent farm bill (Read more: Dairy Farmers from Across the Nation Oppose Supply Management and Compromise Reached: Supply Management OUT of Dairy Policy in Farm Bill). With world trade becoming a greater and greater reality for all countries, it is only a matter of time before supply management, as we know it, no longer exists.
With that in mind we decided to take a look at the Canadian Supply Management System and the resulting impact, if it were removed. Canada’s Milk Supply Management System was created to solve milk surpluses and low returns to farmers. Understanding how this policy originally came into practice helps explain its longevity. And understanding how the system works in practice points to the pressures it faces today. These include astronomical quota costs, unanticipated dairy imports and globally uncompetitive pricing. The system has had to evolve to address a range of domestic and trade changes. The current milk supply management operates under three “pillars”: production controls (quota), administered pricing, and import controls. As conditions have changed, regulations under supply management have changed. It has been broadly successful in doing so, but its complexity has created operating costs and burdens for government and the dairy industry. Furthermore, with a more global economy, it has recently become a stumbling block in Canadian government world trade talks. (Read more: Are We Playing Hide and Seek With Supply Management? and Why the Future of the North American Dairy Industry Depends on Supply And Demand).
What’s the Story around the World?
Comparing Canada to the rest of the world, we find that New Zealand and Australia are at the highly market-oriented end of the continuum. Canada is at the highly protectionist end. The U.S. and Netherlands/EU are in between.
Canadian milk production has been essentially constant since the mid-1970s and is actually down compared with the early 1960s. At the same time, milk production in the U.S. has increased steadily. In Australia, it has increased markedly following policy changes, prior to recent years when widespread drought limited production. Netherlands dairy production increased steadily before quota controls were imposed in the 1980s and it has been relatively steady since, with a recent increasing trend. New Zealand’s milk production is significantly up.
And what about milk pricing? The national patterns diverge to a degree. The available data suggests that prior to the mid-1980s, milk prices in the countries considered here broadly increased. Canadian milk prices have continued to increase since the 1980s. In the U.S. prices abandoned their trend of increases in the 1980s and have since become more volatile, consistent with the reduction in support pricing. Similarly, in the Netherlands, the increasing price trend ended in the late 1980s. Milk prices in Australia increased through the 1980s and plateaued in the 1990s. However, with the recent super market price wars, the price for milk in Australia has been extremely volatile. New Zealand has seen a trend of higher prices and increased volatility, with some similarity to Australia.
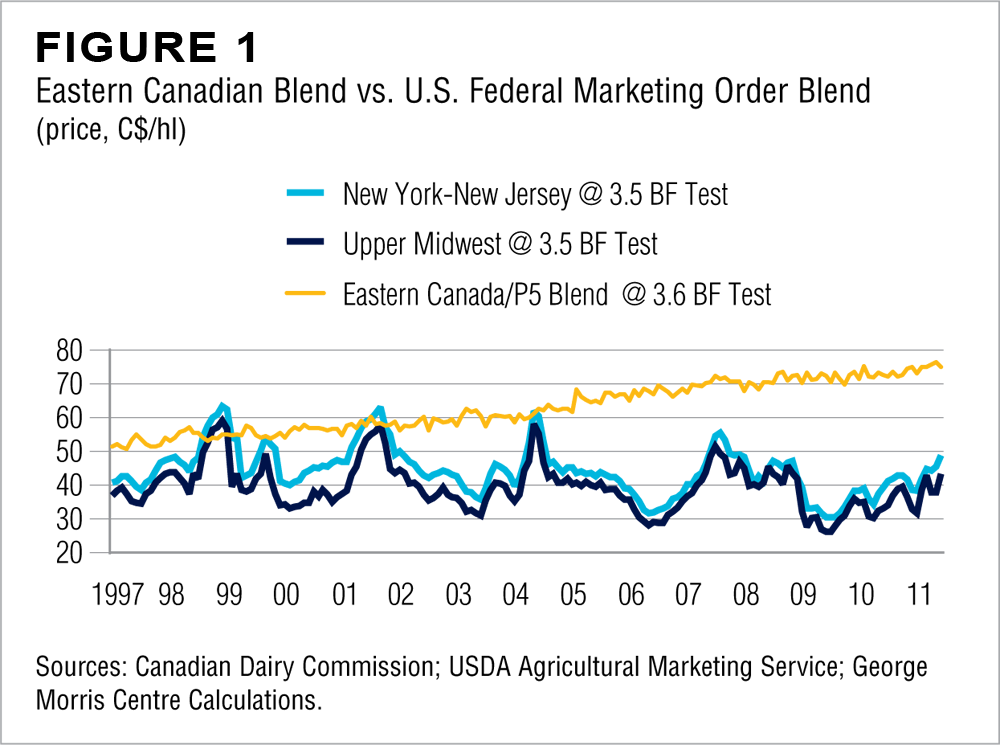
Figure 1 presents divergences in milk pricing, using the U.S. as a reference. The chart plots monthly P5 Eastern Milk Pool27 (Canada) blend milk prices versus U.S. Federal Order blend prices for New York/New Jersey and for the Upper Midwest since 1997. Milk prices in Canada are generally much higher than those in the U.S. Over that period, the eastern Canadian price averaged $C63.05/hl, while the U.S. Midwest price averaged $C39.42/hl and New York/New Jersey averaged $C44.31/hl. Moreover, because U.S. milk prices are much more volatile than those in Canada, the price differential is commonly wider than these averages suggest. For example, the price spread between eastern Canada and the Upper Midwest U.S. has frequently exceeded $C40/hl— more than the average value of the Upper Midwest price itself. (Read more: Canada’s Supply-Managed Dairy Policy: How Do We Compare?)
The key advantage that Canadian producers have enjoyed over its peer countries is that fluid milk markets are characterized by seasonality that creates surpluses, which are diverted to industrial milk markets and thus result in lower industrial milk prices. Sudden losses of export markets exacerbate domestic surpluses and depress milk prices. Under persistent surpluses, with their associated inequities and low returns to farmers, the initial response is to mitigate adjustment through 27 The P5 Eastern Milk Pool is an interprovincial pooling agreement among Canada’s eastern provinces (Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Prince Edward Island) mandated pooling systems and more interventionist policies, such as price supports, product surplus removal programs, and production quotas. These are eventually reduced or eliminated due to their cost burden. The industry then adjusts, resulting in market growth. Canada has not experienced the same pressures to reduce or eliminate interventionist policy that its peer countries have, so Canada continues to use certain approaches that its peers have dropped. Nevertheless, industry adjustment has occurred in Canada, but without the market growth seen elsewhere.
Therefore, while Canada has not seen the growth that other world markets have, it also has not seen the extreme volatility that those other markets experience. This stability is very much appreciated by Canadian milk producers, despite the high cost of entry and production (Quota, and Quota financing costs).
The World is Changing!
After 30 years in a supply management system the UK has now abandoned it. Moreover, the EU as a whole is pushing for other countries to remove supply management as well. (Read more: Canada May Drop Cheese Tariffs to Access EU Beef Market and Canada’s dairy farmers ‘angered and disappointed’ by EU trade deal that would double cheese imports). This is causing great pressure for Canada to follow suit. As the Canadian government seeks to open trade for all industries, especially Oil, Lumber and Beef, that access often comes at a cost. In Canada’s case that cost is opening up the Canadian dairy market. More competition will mean that Canada’s high milk costs will have to go down thus decreasing the net return to producers. While I don’t foresee the abolishment of the quota system immediately, it will happen. As Canada opens up its markets to the world, that means that the Canadian government will have to further subsidize the milk price or allow the milk price to drop. As the Canadian government is already running tight on its fiscal position, they are not likely to subsidize this system for very long.
While no one is arguing the benefits that supply management has had for the Canadian dairy farmer, that protection has come at a cost. One of the greatest costs that I don’t think many realize is that it has allowed many producers to become complacent about their operations. They have not been forced to be as efficient as possible. Those that have been the most complacent are the ones who are going to feel the greatest hurt as Canada continues to open up access to world markets. For those Canadian dairy farmers who think that the Canadian government will protect them till the end….what about the beef farmers, lumber and oil industry? How can the Canadian government afford to protect and grow the market for all of them? Everything has a price. (Read more: Save Frank & Marjorie Meyers Farm – The Army Is At The Gate & This Farmers Number Is Up!)
As a clarification point, while supply management as we know it is threatened, there is no question that the Canadian government is committed to a strong domestic agricultural industry. Many other countries, including the European Union and the United States enact policies that subsidize (directly or indirectly) domestic production. This is something Canada does not currently do. As the world market evolves, the Canadian system may have to move toward global markets and away from supply management. It is also important to note that Canada gives more access to imported products than many other countries give in any single sector. Canada currently imports over 6% of the market for dairy products and more than 7.5% for poultry. In contrast, the United States gives only 2.75% access to their market for dairy products and Europe offers a mere 0.5% for poultry. These will all be areas that will be addressed as world trade evolves.
The Bullvine Bottom Line
The world is rapidly moving to a free market economy. This highly market oriented system will mean that those producers who can produce milk the most cost effectively will excel and those that are not efficient will perish. Canada and its quota system that has done an amazing job at protecting its producers are most likely to be the hardest hit by these global forces. Producers that are looking to the next generation need to seriously evaluate their operations and become as efficient as possible as fast as possible. The message is clear. Canada will be saying goodbye to the current supply management system.
Get original “Bullvine” content sent straight to your email inbox for free.










