Wisconsin trial: 47% fewer deaths, 70% less leakage, $640 more per cow. The dry-off method? Backwards from everything you know.

I recently spoke with a producer from central Wisconsin who asked me something that really made me think: “What if everything we’ve accepted about dry-off losses is actually preventable?”
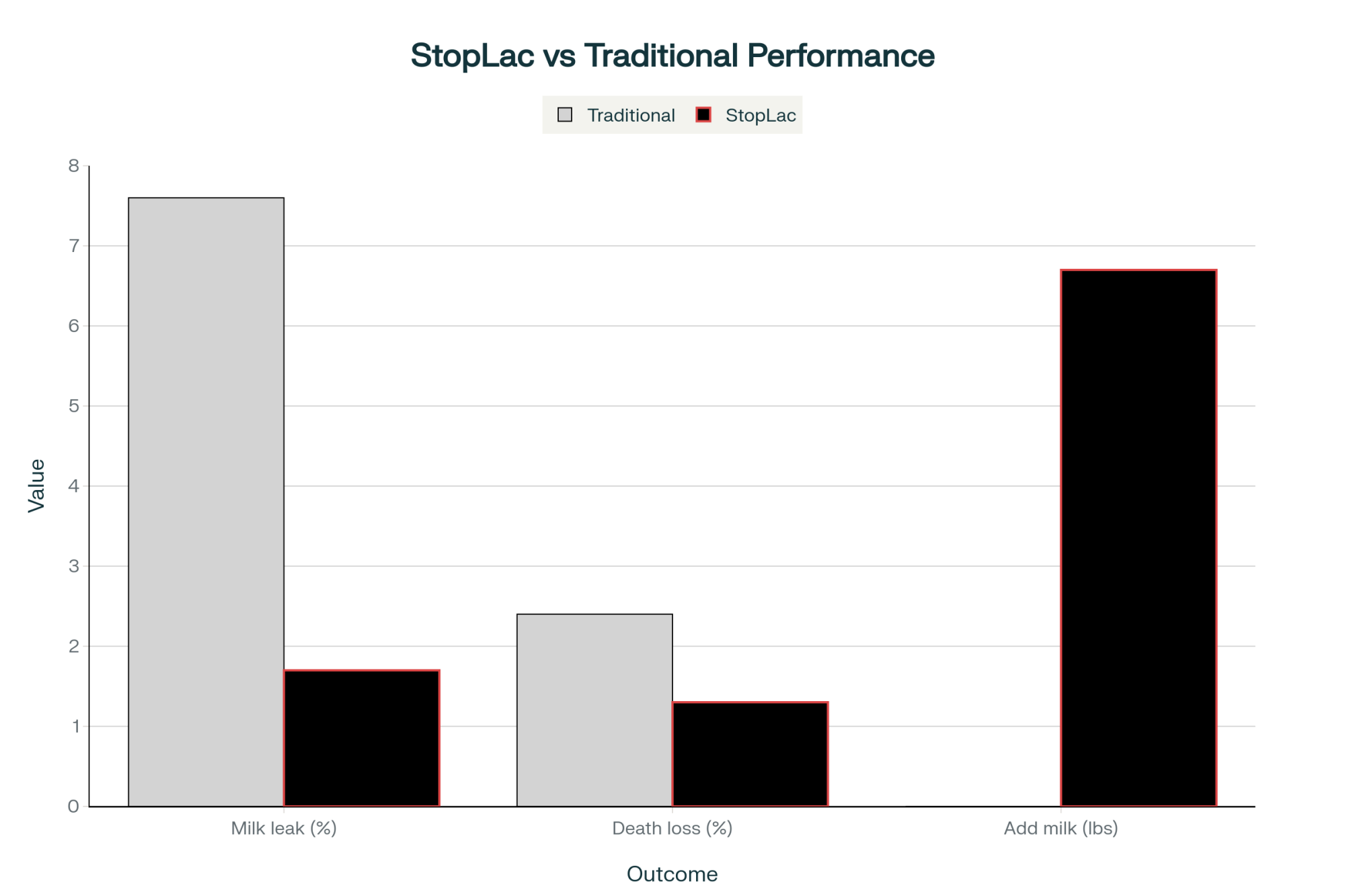
Looking at what’s happening on Wisconsin farms this past year, I’m starting to believe he’s onto something. Here’s what caught my attention—across two dairies with 404 cows total, the ones using StopLac had 70% less milk leakage and nearly half the death losses in the first 60 days after calving. And get this—they’re producing 6.7 pounds more milk daily during their first 100 days in milk. That’s data from AHV International’s trials, and honestly, it’s making me rethink a lot of assumptions.
The Story Behind the Science
Sometimes the best innovations come from people who just can’t accept “that’s how it’s always been done.” There’s this veterinarian in the eastern Netherlands, Dr. Gertjan Streefland, who kept running into cows that wouldn’t respond to antibiotics the way they should. As Jan de Rooy—he runs AHV International now—tells it, Streefland didn’t just throw more drugs at the problem. He started asking different questions.
Now here’s where it gets interesting. The Dutch couldn’t just expand when they hit problems—land costs were astronomical, and they had production quotas limiting them until 2015. So they had to get smarter with what they had. Traditional dry-off had worked fine for decades, but when you can’t add cows, you’ve got to make every single one count.
The breakthrough came around 2010, when de Rooy attended a university course on bacterial communication—something called quorum sensing. Basically, bacteria can coordinate their attacks through chemical signals. When de Rooy and Streefland connected after that course, they began wondering whether bacteria in udder tissue were essentially organizing themselves into a coordinated army rather than random raiders.
What they found aligns with research from places like Cornell’s Quality Milk Production Services—these bacterial communication patterns are real, and they’re a big part of why some infections are so hard to beat. Similar work from the University of Minnesota’s veterinary diagnostic lab has shown that mastitis pathogens exhibit comparable biofilm resistance patterns.
Understanding What Really Happens at Dry-Off
Let me walk you through what happens when we dry off a cow the traditional way. You’ve got a cow making 60, maybe 80 pounds of milk daily, and we just… stop. That udder pressure doesn’t magically disappear. Research from AHV’s work with Utrecht University shows it stays elevated for several days—creating stress we’re only now starting to understand.
Dr. Geoff Ackaert, who’s the Technical Director at AHV, has presented some fascinating evidence about this. Those stress hormones from the abrupt dry-off? They actually wake up dormant bacteria that have been hiding in what we call biofilms—think of them like bacterial apartment buildings where they protect each other and wait out the tough times.
And here’s the kicker—bacteria protected in these biofilms can be 10 times, sometimes much more, resistant to antibiotics in experimental settings. Even on the low end, that’s a huge problem. The National Mastitis Council has documented similar patterns, and independent research from institutions like Ohio State’s veterinary college confirms these biofilm resistance levels.
How This New Approach Actually Works
StopLac takes a completely different approach. Instead of that sudden stop, which creates all that pressure, it helps the cow naturally wind down production—basically a guided shift in how her body manages the transition. It’s different from selective therapy or just using teat sealants, and it’s also distinct from gradual cessation protocols that some farms have tried.
The Utrecht collaboration documented a 56% drop in milk production within 24 hours, but here’s the important part—it’s due to physiological changes, not pressure building up. Jon Beller, who runs about 2,400 cows in Wisconsin, told me something that really stuck: “A lot less vocalization during the dry-off period. The cows cease production almost instantly with no more milk secretion after dry-up.”

Steve Jaeger shared something similar that really caught my attention. “On Friday morning, when I do my walk through and I walk past the dry pen, in the past, after dry off, there were always cows screaming. I mean, just screaming. You could tell the udders were full. They were uncomfortable,” he told me. “Since May 15, I barely had a, you know, you want to say a murmur? The barn was quiet. I just couldn’t believe it.”
You probably know this already—when cows are quieter during dry-off, that tells you everything. They’re not stressed.
What’s happening in the udder is pretty clever, too. The pH shifts so bacteria don’t thrive. Lactose is reabsorbed instead of being fermented by bacteria. Calcium stays balanced—and anyone who’s dealt with milk fever knows how crucial that is. The liver keeps functioning properly instead of getting overwhelmed.

The Numbers That Matter
Let’s talk about what this means in real numbers. In those Wisconsin trials with 404 cows, only four cows—about 1.7%—in the StopLac group had milk leakage issues. The control group? Thirteen cows, or 7.6%. Death losses within 60 days were 1.3% versus 2.4%.
That 6.7-pound daily production advantage during the first 100 days? If that holds even partially through the full lactation, you’re looking at substantial gains. Many producers are reporting the improved start carries through, though individual results vary.
During that H5N1 outbreak at Joe Soares Farms—nobody wants to deal with that kind of crisis, but it gave us a valuable comparison. Their Turlock facility, with 2,500 cows using the AHV protocol, maintained about 88 pounds per cow daily, with monthly losses of around 40-60 cows. Their Chowchilla facility with 5,500 cows on traditional protocols? They dropped to 77 pounds per day and were losing over 100 cows per month. The comparison is eye-opening.

Breaking Down the Economics
Here’s how the money actually works out. Traditional dry-off has all these hidden costs that add up:
You’ve got milk leakage at about $11.55 per cow. New infections run around $94. Death losses within 60 days average $66. Extra culling adds $120. Antibiotics and withdrawal time, another $32.90. Extra labor dealing with problems, at least $16.
Add it all up—that’s $340.45 per cow for each dry-off when things go relatively well.
Now, with an investment of roughly $40 per cow, plus implementation costs, you’re looking at a total investment of $55-60 per cow. The measured benefits in improved production during early lactation, reduced health events, and lower death losses average over $400 according to the trial data. When you stack the $340 in avoided costs on top of the $400+ in production/health gains, and subtract the investment, you are looking at a net economic benefit of $640 per cow.
For a 1,000-cow dairy, that’s significant annual savings. Even if you’re milking 200-300 cows, the proportional benefits are worth looking at. Actually, I talked to a producer in Vermont with 180 cows who started with just his repeat offenders—the cows that always seemed to have issues. He’s now using it across the whole herd because the results on those problem cows were so clear.
It’s important to note that individual results depend on current management practices, facility design, and local conditions. The $640 benefit represents best-case scenarios from trial data—your actual results may vary based on factors like current dry-off success rates, labor efficiency, and herd health status
For comparison, other dry-off innovations typically show different returns. Selective dry cow therapy can reduce antibiotic costs by about 50% while maintaining udder health, according to University of Wisconsin extension research. Internal teat sealants alone generally show ROI in the 200-300% range based on Cornell studies.

Sponsored Post
Who’s Ready for This (And Who Isn’t)
Not every farm is ready to make this change immediately, and that’s fine. The operations I’ve seen succeed with this usually have a few things in common. They’re closely tracking individual cow data. Their teams actually follow protocols—you know how that goes. They think in full lactations, not just quarterly numbers. And they see change as an opportunity, not a threat.
Of course, not everyone’s convinced yet. As one Pennsylvania dairyman told me, ‘I’ll wait to see three-year data before switching my whole herd.’ That’s fair—major management changes deserve careful consideration.

David Goodrich at Goodrich-Cylon Dairy really exemplifies this approach. He’s been using StopLac since early December and tells me, “I have no difference in cell count or fresh cows with mastitis. I find it works really well on the farm, and I have no plans of going back to using tubes and sealants and all that stuff anymore.”
What’s interesting is his observation about implementation: “I don’t think it takes really any more time than putting tubes and sealants in every cow. I actually think it might cut a step out… the employees have really liked that they don’t have to handle the cows twice in the parlor.”
I should mention—some farms in the trials did hit bumps initially, mostly around training staff and getting protocols consistent. One producer said it took about three weeks for his team to really get comfortable with the new approach, but the results made it worthwhile. Another operation struggled initially because it tried to implement during its busiest season—timing matters.
If you’re not tracking individual cows well yet, or if you’re managing finances month-to-month, you might want to build those systems first. There’s no shame in that—recognizing what you need before jumping into new technology is actually smart management.
What to Expect Month by Month
Based on what producers have told AHV during their follow-ups, here’s the typical timeline:
First couple of months: Your milking crew notices cows are calmer at dry-off. No udder engorgement. Staff finds it easier. As Steve Jaeger noted, “It’s obvious that pressure isn’t there, that the AHV StopLac is doing what we need it to do.”
Months 3-4: Hospital pen has fewer cows. The Giacomini trial showed conception rates improving by several percentage points—that’s meaningful progress.
Months 6-8: Treatment costs drop noticeably. Those first StopLac cows are milking better than expected in their new lactation. Jaeger is particularly excited about this: “If we can shrink that udder faster and give that udder more time to regenerate, those cows are going to take off, I hope, a lot faster and perform a little better.”
By month 12: Everything compounds. Better production, fewer deaths, less culling—your banker notices the improved cash flow.
Regional Differences to Consider
It’s worth noting that results might vary depending on where you are and how you manage. Operations in hot, humid areas might encounter different bacterial pressures than those in drier regions. Down in the Southeast, where heat stress is a constant battle, producers report that the reduced metabolic stress during dry-off seems especially beneficial. Meanwhile, Southwest producers dealing with dust and environmental challenges say the stronger immune response helps their cows better handle those conditions.
Grazing dairies could see variations compared to confinement. Organic producers—who can’t use many traditional treatments anyway—might find this particularly useful.
Spring and fall transitions might show different responses, too. Some producers report better results during cooler months, though the trials didn’t show major seasonal variations.
The Regulatory Picture
The regulatory landscape keeps evolving, as we all know. The EU’s Regulation 2019/6 took effect on January 28, 2022, basically ending blanket dry cow therapy as we knew it. Canada’s national framework includes clear objectives to reduce agricultural antibiotic use. And let’s be honest—consumers increasingly want products from farms using antibiotics responsibly.
According to AHV’s specifications, StopLac has a zero withdrawal time—something to consider as regulations continue to tighten.
The Bottom Line
We’re seeing an interesting split in our industry: some operations are questioning old assumptions, while others are sticking with tradition. The Dutch example shows what happens when you can’t just expand your way out of problems—you innovate.
AHV reports over 2,650 farms are now using StopLac, with more than a million tablets distributed since last June. Industry trends suggest these approaches will likely become more common, though nobody can predict exactly how fast things will change.
Questions worth asking yourself: How do your current dry-off results compare to what’s possible now? What happens when neighbors cut their fresh cow losses in half? How might evolving market preferences affect your opportunities?
What started as one vet’s frustration with antibiotic failures has become a documented opportunity for real economic improvement. Each dry-off cycle represents biological potential—once it’s lost, you can’t get it back. Wisconsin producers in these trials aren’t just saving money today; they’re building advantages that compound with each lactation.
The most successful farms I’ve seen treat this as fundamental management evolution, not just buying a new product. Maybe that’s the real lesson—when you can’t expand, innovation becomes essential.
| Metric | Traditional Dry-Off | StopLac |
| Milk leakage (%) | 7.6 | 1.7 |
| Death loss (%) | 2.4 | 1.3 |
| Daily milk increase (lbs) | 0 | 6.7 |
| Withdrawal time (days) | 3-6 | 0 |
| Annual cost per cow ($) | 340 | 55-60 |
| ROI per cow ($) | 0 | 640 |
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The $640/cow revelation: Traditional dry-off creates $340 in preventable losses (mastitis, deaths, culling)—a $55 StopLac investment returns $640 through prevention plus 6.7 lbs more daily milk in early lactation
- Your barn doesn’t lie: Screaming dry cows = tissue damage and bacterial activation. Silent cows = healthy metabolic transition. Wisconsin trials proved the difference: 47% fewer deaths, 70% less mastitis
- Implementation roadmap: Start with repeat offenders; implement during calmer seasons; expect a 3-week staff adjustment. Month 1: quieter barns. Month 3: fewer hospital cows. Month 12: banker notices cash flow improvement
- The regulatory advantage: Zero withdrawal time positions you ahead of tightening regulations (EU already banned blanket dry therapy in 2022, North America following)
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY:
Wisconsin data just proved the unthinkable: traditional dry-off costs you $640 per cow annually in completely preventable losses. In trials with 404 cows, StopLac achieved what tubes and sealants never could—70% less milk leakage, 47% fewer deaths, and 6.7 pounds more daily milk during the first 100 days. The breakthrough came when Dutch farmers, unable to expand due to land constraints, discovered that helping cows metabolically wind down production prevents the pressure that awakens biofilm-protected bacteria.
Steve Jaeger describes the transformation: “After traditional dry-off, cows were screaming… now with StopLac, the barn is silent.” With an investment of roughly $40 per dose and zero withdrawal time, the economics are undeniable—invest $55-60 total, recover $640 in reduced deaths, mastitis, culling, and improved production. With 2,650 farms already switched and testimonials like David Goodrich’s (“tubes may have caused MORE mastitis”), for many producers, the question isn’t just whether to change—it’s whether they can afford not to.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Transition Cow Success: Winning The High-Stakes Game That Makes or Breaks Your Dairy’s Profit Margin – Expands on the dry-off conversation by detailing the “Vital 90 Days” framework. This guide provides specific nutritional and management protocols to reduce metabolic disasters like ketosis, protecting the investment you make during the dry period.
- Dairy Profit Squeeze 2025: Why Your Margins Are About to Collapse (And What to Do About It) – Analyzes the current economic landscape where income-over-feed costs are dropping below $12/cwt. This strategic analysis validates why capturing the $640 per cow advantage highlighted above is critical for survival in the 2025 market.
- Abandon Your ‘Wait and Treat’ Mastitis Strategy Before It Bankrupts Your Operation – Demonstrates how shifting from reactive treatment to proactive biomarker monitoring can cut antibiotic use by 31%. This piece perfectly complements the StopLac prevention approach by offering a technological roadmap for eliminating mastitis costs.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!








