Uncover the transformative power of AI in dairy farming. Explore advancements in efficiency, early disease detection, and sustainability. Are you prepared to elevate your farm’s operations through AI integration?

Imagine a period when farming only used human effort and crude instruments. Now, fast ahead, the agricultural scene has changed throughout many revolutions. Every step, from domestication to crop rotations, has changed farming. The entry of artificial intelligence (AI) into dairy production marks the most recent phase. Through better efficiency, animal health, and sustainability promotion, artificial intelligence has significant power to transform dairy production. Integration of artificial intelligence marks early illness diagnosis and better decision-making. The dairy business is at a pivotal junction as climate change strains food systems and global population increases call for change. Artificial intelligence presents a light of hope by streamlining processes, lowering waste, guaranteeing cattle well-being, and thus enabling a robust and forward-looking agricultural industry.
The Brain Behind the Machines: Understanding AI in Dairy Farming
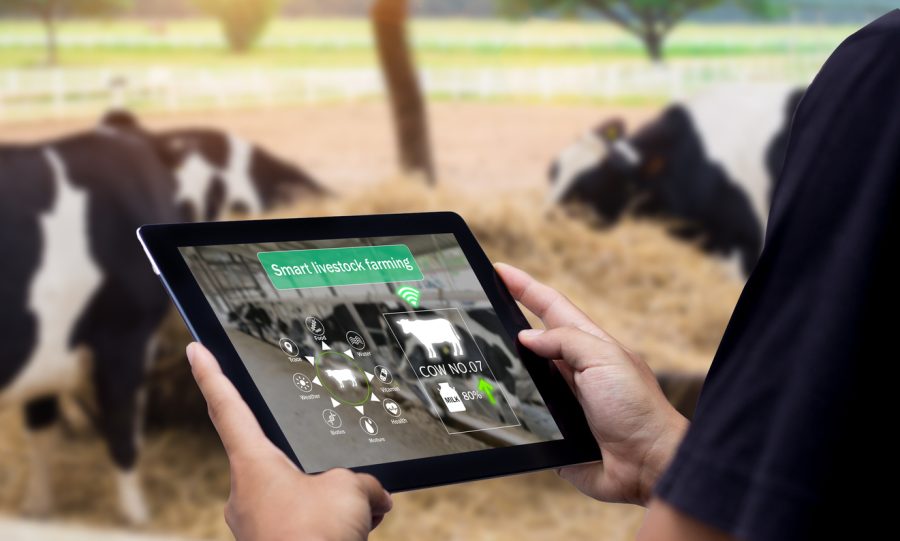
Within computer science, artificial intelligence (AI) studies creating systems capable of doing tasks requiring human intellect, like natural language understanding, decision-making, and pattern recognition. AI lets robots observe, interpret, and respond to challenging stimuli, enabling them to replicate human intellect. From sophisticated benchtop equipment to smartphone applications, the range of artificial intelligence technologies is broad and includes camera systems, milk meters, ear tags, boluses, and many sensors. These instruments complement specialist software by analyzing data to provide practical insights, revolutionizing sectors such as dairy farming.
Embarking on AI Integration: A Practical Guide for Dairy Farmers
Starting artificial intelligence integration into dairy production calls for a thorough strategy. Farmers should consider elements such as farm size and money, as smaller farms need reasonably priced solutions while bigger ones might choose complete systems. Ensuring that it fits with the current infrastructure helps to smooth the change.
New technologies have a high learning curve that takes time and money for successful training. Data outputs must be understood by farmers and turned into workable plans for maximum yield and efficiency. Starting small-scale trial initiatives and consulting peers who use these tools will enable one to evaluate effects without committing to significant changes. This careful approach finally results in effective and long-lasting integration of artificial intelligence in dairy production.
Initiating AI Integration through Pilot Projects: A Pragmatic Approach for Farmers
Starting artificial intelligence integration via pilot projects gives farmers a low-risk approach to assessing new technologies on a smaller scale. This method lets one test and evaluate performance without endangering the whole operations of the farm. Farmers should prioritize sustainability and the long-term viability of AI technologies. Critical elements in keeping these systems valuable over time include regular upgrades, possible obsolescence, and an economy of cost-effectiveness. Maintaining current with industry standards usually calls for these upgrades; the long-term worth of these technologies depends much on the dependability of AI suppliers.
Achieving Balance: Navigating the Challenge of False-Positive Alerts in AI Systems
Managing false-positive alarms is one of the most challenging obstacles in introducing artificial intelligence technologies into dairy production. False alarms waste time as they force farmers to address non-existent problems, which results in pointless interventions stressing animals and upsetting daily operations. False positives at high frequency might undermine the device’s confidence, reducing its general value. Crucially, sensitivity and accuracy must be balanced. While accuracy guarantees proper notifications by reducing false positives, sensitivity recognizes actual problems. A system that is too sensitive flags numerous fake concerns but captures all possible faults. On the other hand, a system focused only on accuracy might overlook essential warning signals. Successful artificial intelligence integration depends on finding harmony between many elements.
Farmers should assess the usefulness of these tools and discuss false alert management with artificial intelligence companies. Investigating customizing choices also helps satisfy specific operating requirements. By weighing these elements and reducing adverse effects, dairy producers may maximize the advantages of artificial intelligence.
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security: A Critical Aspect of AI Integration in Dairy Farming
One cannot emphasize the need for data privacy and security in artificial intelligence systems. Dairy farms create vast volumes of sensitive information, from operational measures to animal health records. First, this data must be safe and free from illegal access. Farmers must aggressively interact with artificial intelligence companies to determine how their data will be kept, accessed, and utilized.
Unambiguous agreements covering data use, access policies, and continuous cybersecurity initiatives are essential. Adopting strict data privacy policies goes beyond mere compliance; it’s about establishing confidence and ensuring AI technologies help the farm without sacrificing its ethical values. Farmers who prioritize these factors will confidently embrace AI developments, knowing their data is safe.
AI’s Role Transcends Theory: Practical Applications Enhancing Precision and Effectiveness in Dairy Farming
AI’s role in dairy farming is more than theoretical; it delivers real-world applications to enhance farm management.
Lameness Detection: AI analyzes video and accelerometer data to spot lameness through walking patterns with 75% to 85% accuracy. Early intervention boosts animal welfare, though false positives do occur.
Mastitis Monitoring: AI detects mastitis by examining udder temperature, milk composition, and herd data. False alerts complicate practical use and offset high predictive power.
Reproductive Health: AI tools analyze sensors and visual cues to detect estrus, matching veterinarians in accuracy. However, predicting conception rates and calving events remains less reliable, with a 60% to 80% accuracy.
Feed Intake Monitoring: AI uses cameras and machine learning to measure individual feed intake. It shows promise with an error margin of under 200 grams per meal. This could revolutionize health and nutritional management.
Despite advancements, minimizing false positives remains a crucial challenge. Ongoing refinement and testing are essential to ensure these technologies provide reliable insights.
The Bottom Line
Artificial intelligence in dairy production offers advantages like early disease diagnosis and higher efficiency. Four main things to consider are mastering the learning curve, guaranteeing sustainability, safeguarding data privacy, and controlling false-positive alarms. Early detection of health problems like lameness and mastitis, improved operational efficiency, and better reproductive management—all of which help to save money and increase animal welfare—all of which AI can do. But it’s important to proceed carefully, beginning with pilot programs to lower risks and evaluate effects on everyday operations and farm management. Considering the changing character of artificial intelligence, assessing continuous upgrades and obsolescence risk becomes crucial. Equally vital is knowing the data privacy and security policies of AI vendors. Controlling false alarms guarantees systems find actual issues without needless interruptions. Strategically approaching AI integration, farmers should do extensive study, speak with colleagues, and start small-scale projects. Effective artificial intelligence integration in dairy production may usher in a new age of animal health and efficiency. This technology’s mastery will help farmers utilize its advantages and create sustainable and efficient farm surroundings. Accepting this change requires a careful balance between a rigorous adoption plan and excitement for innovation so that agricultural methods develop with increasing technology.
Key Takeaways:
- The integration of AI into dairy farming can enhance efficiency and early disease detection, but adoption requires careful consideration of learning curves, sustainability, data privacy, and false-positive alerts.
- AI can mimic human intelligence-related skills, using a diverse array of technologies such as smartphone apps, camera systems, and milk meters, often requiring substantial investment in training and adaptation.
- Farmers should evaluate the time, cost, and potential disruptions involved in implementing AI technologies, preferably starting with small-scale pilot projects.
- Sustainability and long-term viability are critical, as AI tools may become obsolete, necessitating continuous updates and cost assessments.
- Effective AI systems must achieve a balance between sensitivity and minimizing false alerts to avoid unnecessary interventions and maintain farmer trust.
- Data privacy and security are paramount, requiring clear agreements with AI providers on data ownership and usage terms.
- AI applications in dairy farming, such as detecting lameness, mastitis, estrus, calving, and feed intake, show promising potential but need further refinement to reduce false positives.
- The integration of AI in dairy farming offers significant opportunities but must be approached cautiously, emphasizing the need for thorough planning and evaluation.
Summary:
Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly impacted the dairy industry, especially in response to climate change and population growth. AI systems, like camera systems, milk meters, and sensors, can perform tasks requiring human intelligence, such as natural language understanding and pattern recognition. However, integrating AI into dairy production requires a strategic approach considering factors like farm size and budget. Farmers should understand data outputs, develop plans for maximum yield and efficiency, and prioritize sustainability and long-term viability of AI technologies. Balancing sensitivity and accuracy is crucial, and successful AI integration depends on finding harmony between these elements. Data privacy and security are also critical aspects of AI integration in dairy farming, with farmers interacting with AI companies to determine data storage, access, and utilization.








 Discover how Blockchain technology can revolutionize your dairy farming business. Learn to streamline operations, enhance traceability, and boost profits. Dive in now.
Discover how Blockchain technology can revolutionize your dairy farming business. Learn to streamline operations, enhance traceability, and boost profits. Dive in now. Today, Lely is launching the improved mixing and feeding robot (MFR) for the Lely Vector feeding system. The system is now even more focused on improving animal health. Reliability and service life have also been increased through upgrading to even more durable components, such as stainless steel for the mixing bin and auger.
Today, Lely is launching the improved mixing and feeding robot (MFR) for the Lely Vector feeding system. The system is now even more focused on improving animal health. Reliability and service life have also been increased through upgrading to even more durable components, such as stainless steel for the mixing bin and auger.
 You can now get a text message sent to your phone about an hour before your cow gives birth.
You can now get a text message sent to your phone about an hour before your cow gives birth. An enterprising Taranaki farmer isn’t following the herd when it comes to innovation – he’s flying above it instead thanks to a $1000 drone aircraft.
An enterprising Taranaki farmer isn’t following the herd when it comes to innovation – he’s flying above it instead thanks to a $1000 drone aircraft. A Canadian startup company whose invention lets dairy farmers check the quality of milk from individual cows is getting $1 million to set up shop in Buffalo.
A Canadian startup company whose invention lets dairy farmers check the quality of milk from individual cows is getting $1 million to set up shop in Buffalo.
 Imagine if you could understand what cows are trying to say when they moo, bawl or bellow.
Imagine if you could understand what cows are trying to say when they moo, bawl or bellow. Ms Green said that understanding what cows were saying could change the way dairy farmers managed their herds.
Ms Green said that understanding what cows were saying could change the way dairy farmers managed their herds. Vickie Baker is a farm consultant in southwestern Pennsylvania who sees dairies struggling to find workers all the time. It’s hard to attract people to physically demanding, dirty farm work. That’s especially true at dairies, where cows need to be milked year-round, several times a day, including the middle of the night.
Vickie Baker is a farm consultant in southwestern Pennsylvania who sees dairies struggling to find workers all the time. It’s hard to attract people to physically demanding, dirty farm work. That’s especially true at dairies, where cows need to be milked year-round, several times a day, including the middle of the night.
 DeLaval has released the Rotary E100 at Fieldays. The new dairy system has a cockpit within arms length of the cow bales.
DeLaval has released the Rotary E100 at Fieldays. The new dairy system has a cockpit within arms length of the cow bales. CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology has been used for the first time to successfully produce live cows with increased resistance to bovine tuberculosis, reports new research published in the open access journal Genome Biology.
CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology has been used for the first time to successfully produce live cows with increased resistance to bovine tuberculosis, reports new research published in the open access journal Genome Biology. Siri and Alexa already help you find your keys and remember friends’ birthdays. So maybe it’s not such a stretch that they could also also manage a few hundred cattle.
Siri and Alexa already help you find your keys and remember friends’ birthdays. So maybe it’s not such a stretch that they could also also manage a few hundred cattle. VIRTUAL fencing for cattle is set to be commercially available later this year, following Melbourne-based agri-tech company Agersens’ success in raising $2 million.
VIRTUAL fencing for cattle is set to be commercially available later this year, following Melbourne-based agri-tech company Agersens’ success in raising $2 million. A dairy industry supplier says technology is helping producers monitor more of their cow’s activities.
A dairy industry supplier says technology is helping producers monitor more of their cow’s activities. Gene editing can complement traditional breeding in enhancing food sustainability and animal health and welfare, according to a renowned animal geneticist.
Gene editing can complement traditional breeding in enhancing food sustainability and animal health and welfare, according to a renowned animal geneticist. These are exciting days for agri technology companies as they bring new concepts to the market to help farmers increase productivity.
These are exciting days for agri technology companies as they bring new concepts to the market to help farmers increase productivity. The market for agricultural robots is developing at a rapid pace, with a large number of established and startup agricultural technology companies developing, piloting, and launching an innovative range of robotic systems to tackle a wide variety of tasks. Key application areas for agricultural robots include driverless tractors, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), material management, field crops and forest management, soil management, dairy management, and animal management, with a diverse set of subcategories emerging within each of those areas.
The market for agricultural robots is developing at a rapid pace, with a large number of established and startup agricultural technology companies developing, piloting, and launching an innovative range of robotic systems to tackle a wide variety of tasks. Key application areas for agricultural robots include driverless tractors, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), material management, field crops and forest management, soil management, dairy management, and animal management, with a diverse set of subcategories emerging within each of those areas. Knowing when a cow is going to calve can improve calf survivability as assistance can be provided during difficult calvings and colostrum can be fed promptly after birth. Dystocia is defined as delayed or difficult parturition and is a major cause of weakness, morbidity, and mortality in calves and increases the incidence of postpartum disorders in cows. A prolonged and difficult calving may cause acidosis and hypoxia in the calf, which can negatively affect immunoglobulin G absorption and influence calf health and future production. Providing calves with high quality colostrum immediately after calving will increase calf survival by protecting the calf against diseases. Inadequate colostrum consumption shortly after birth can result in reduced growth rates, increased risk of disease and death, increased risk of being culled, and decreased milk production in their first lactation.
Knowing when a cow is going to calve can improve calf survivability as assistance can be provided during difficult calvings and colostrum can be fed promptly after birth. Dystocia is defined as delayed or difficult parturition and is a major cause of weakness, morbidity, and mortality in calves and increases the incidence of postpartum disorders in cows. A prolonged and difficult calving may cause acidosis and hypoxia in the calf, which can negatively affect immunoglobulin G absorption and influence calf health and future production. Providing calves with high quality colostrum immediately after calving will increase calf survival by protecting the calf against diseases. Inadequate colostrum consumption shortly after birth can result in reduced growth rates, increased risk of disease and death, increased risk of being culled, and decreased milk production in their first lactation. BEEF producers have launched high level legal proceedings to halt a brazen bid by North American giants Cargill USA and Branhaven LLC to patent established cattle genetic selection techniques.
BEEF producers have launched high level legal proceedings to halt a brazen bid by North American giants Cargill USA and Branhaven LLC to patent established cattle genetic selection techniques. For thousands of years, farmers have been choosing which traits their crops and livestock carry by using selective breeding. The first genetically modified crops were commercialized in the 1990s. In 2012, a huge scientific breakthrough changed what is possible yet again.
For thousands of years, farmers have been choosing which traits their crops and livestock carry by using selective breeding. The first genetically modified crops were commercialized in the 1990s. In 2012, a huge scientific breakthrough changed what is possible yet again.


 vetMEDRIA SENSOR – Cow Monitoring System is Dedicated to Reliable Real-Time Data
vetMEDRIA SENSOR – Cow Monitoring System is Dedicated to Reliable Real-Time Data In July of 2016, GEA introduced the Wireless Integrated Control (WIC) system which is an intelligent software for its proven MixFeeder. The new system ensures that every performance group receives the optimal mix ration of raw feed, concentrated feed and minerals in the right volumes at the most appropriate intervals. The WIC delivers the feed precisely and reliably around the clock. This benefits milk producers and herd managers as it ensures that their cows are always performing at their full potential, thereby improving milk volumes and quality and reducing workload and costs.
In July of 2016, GEA introduced the Wireless Integrated Control (WIC) system which is an intelligent software for its proven MixFeeder. The new system ensures that every performance group receives the optimal mix ration of raw feed, concentrated feed and minerals in the right volumes at the most appropriate intervals. The WIC delivers the feed precisely and reliably around the clock. This benefits milk producers and herd managers as it ensures that their cows are always performing at their full potential, thereby improving milk volumes and quality and reducing workload and costs. Introducing the Robot Named, “ROVER!”
Introducing the Robot Named, “ROVER!”
 A dairy equipment specialist says farms are continuing a transition to robotics despite the current milk price environment.
A dairy equipment specialist says farms are continuing a transition to robotics despite the current milk price environment. At the farm level, producers have long capitalized on making genetic progress through sire selection. The importance of using the best sires possible stems from the fact that over 90% of the genetic progress realized in most dairy herds results from sire selection. In herds that have the highest rates of genetic gain, importance is also placed on the selection of cows as dams of the next generation of replacement heifers.
At the farm level, producers have long capitalized on making genetic progress through sire selection. The importance of using the best sires possible stems from the fact that over 90% of the genetic progress realized in most dairy herds results from sire selection. In herds that have the highest rates of genetic gain, importance is also placed on the selection of cows as dams of the next generation of replacement heifers..JPG)

 Do cows get seasick? It’s not a question farmers often ask, except in the Dutch city of Rotterdam where a team of developers plans to build a
Do cows get seasick? It’s not a question farmers often ask, except in the Dutch city of Rotterdam where a team of developers plans to build a 


 Brian T. Horowitz is an editor for Dell’s technology news website,
Brian T. Horowitz is an editor for Dell’s technology news website, 




