The surprising market shift that’s making component quality more valuable than volume—and what producers are learning about the 3-5 year window ahead
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: China’s premium dairy surge is handing component-focused producers $150,000-$200,000 in extra annual revenue—no expansion required. While premium imports rocket up 18%, commodity imports are tanking 12%, creating a historic quality-over-quantity shift driven by 670 million Chinese middle-class consumers who prioritize safety and nutrition over price. Here’s the critical part: the 3-5 year window to lock in premium supplier status is already 40% gone, with October 2025 marking a crucial decision point. Producers implementing targeted nutrition changes see results in 12-18 months, while genomic improvements take 36-48 months—both achievable before the 2027 market saturation deadline. Right now, component-optimized milk commands $24/cwt versus $18 for commodity, a $6 gap that represents survival versus thriving. Bottom line: farms that pivot to components this winter will count premium checks in 2026, while volume-chasers will still be wondering what happened when the window slams shut.

You know, last week I was going through Chinese customs data, and something really caught my attention. China’s economy is slowing down to 4.6% GDP growth—we all know that story. But here’s what’s interesting… their dairy import patterns are telling a completely different tale, one that’s got progressive American producers rethinking how they value every pound of milk in the bulk tank.
So the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service released its May 2025 report, showing that China’s overall dairy imports grew by about 6% through September. Not bad, nothing spectacular. But when you dig into the specific categories—and this is where it gets really fascinating—premium dairy products are advancing nearly 18% year-over-year while commodity products are retreating around 12%, based on what we’re seeing in Chinese customs data and the latest Tridge market analysis. For those of us who’ve built our operations around maximizing volume for generations, well… this divergence is something we need to talk about.

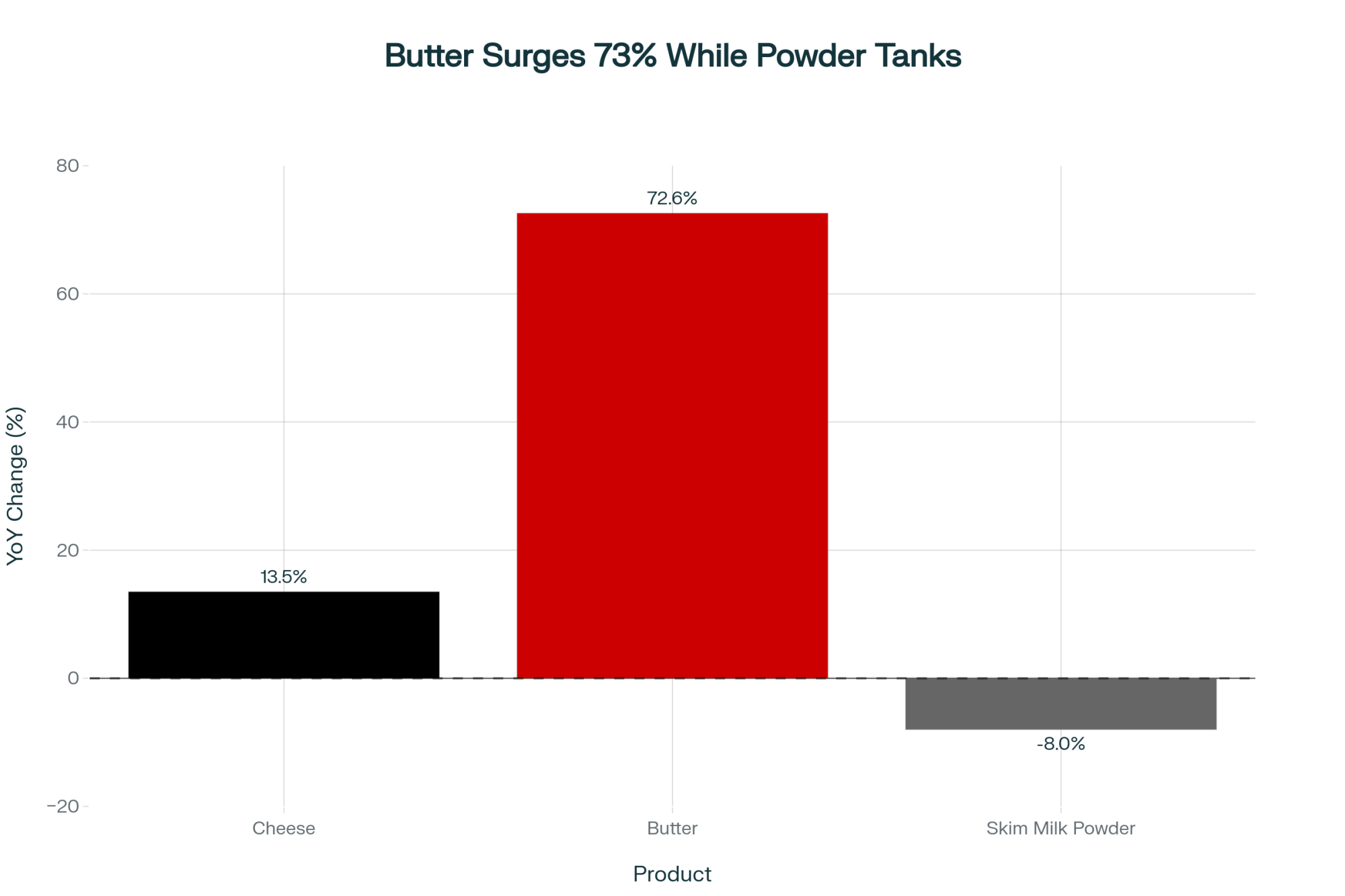
What the latest customs reports are showing is cheese imports rising 13.5% and butter—get this—surging 72.6% year-over-year. Meanwhile, skim milk powder? That’s heading the other direction. I’ve been talking with dairy market analysts who’ve tracked this stuff for the past decade, and they’re telling me this isn’t just another market fluctuation. It looks like we’re seeing a fundamental shift in what the world’s largest dairy import market actually values.
“The premium shift isn’t temporary—it’s structural. Producers who position themselves now will capture long-term value that commodity markets simply can’t match.”
And here’s what really makes you think… China’s middle class is continuing to expand—the USDA projects they’ll add 80 million people by 2030—and we’re observing similar patterns across Southeast Asia, India, and parts of Africa, according to Rabobank’s December 2024 analysis. What I’ve found is this could represent the most meaningful value shift in global dairy markets we’ve seen in decades.

Understanding What’s Really Driving This Premium Shift
When you look at the forces reshaping China’s dairy demand, they actually make a lot of sense—wealth creation, food safety consciousness, evolving consumer preferences. Understanding these drivers helps explain why this shift feels different from the usual market cycles we’ve all ridden out before.
The Food Safety Factor That Won’t Go Away
It’s been seventeen years since that 2008 melamine incident—the World Health Organization reports documented six infant deaths and 300,000 illnesses. Yet Chinese consumers still show a strong preference for imported dairy products, especially when it comes to their kids. The China Dairy Industry Association’s data shows imports of infant formula increased from 28% of dairy imports in 2008 to 45% by 2019.
What’s particularly telling—and this surprised me—is that premium infant formula now represents 37% of market share, up from 32.8% just a year ago, according to July 2025 market research from Innova. The Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences recently published consumer research showing Chinese consumers prioritize nutritional value at 59%, quality at 45%, and safety at 39%. Price? That ranks at just 6% when they’re selecting a formula. That preference hierarchy creates real pricing opportunities for suppliers who can demonstrate superior quality and traceability.
How Middle Class Growth Changes Everything
The scale here is… well, it’s something else. China’s middle class expanded from 3.1% of the population in 2000 to 50.8% in 2018, according to McKinsey Global Institute data. We’re talking about roughly 670 million people joining the ranks of consumers with discretionary income. The National Bureau of Statistics of China reports per capita income grew at a 6.1% compound annual rate from 2019 to 2024, reaching 41,300 RMB—that’s about $5,792 annually.
What I’m seeing in the consumption data is these folks aren’t looking for the cheapest option on the shelf. They want Western-style products with clear quality differentiation. USDA estimates show cheese consumption alone could hit 495,000 metric tons by 2030, growing at a 9.1% compound annual rate. And here’s the kicker—60 to 75% is being consumed in foodservice settings like Western restaurants and pizza chains.
Why China Can’t Make These Premium Products Themselves
This caught me off guard when I first looked into it. China aims to achieve 75% dairy self-sufficiency under its 14th Five-Year Plan, but its domestic production focuses mainly on fluid milk and basic dairy products. The USDA’s May 2025 China dairy report shows Chinese farms are actually reducing output—down 0.5% in 2024 with another 1.5% decline forecast for 2025—as farmgate prices hit decade lows around 3.20 RMB per kilogram.
But here’s the real issue… China lacks the processing infrastructure for specialty cheese production, premium protein concentrates, and other high-value categories. The USDA report notes that while “domestic cheese production will increase gradually, with growing investment in natural cheese capacity,” current production is just 30,000 MT, compared to 178,000 MT imported.
Dr. Leonard Polzin from the University of Wisconsin’s Center for Dairy Profitability calls this “structural import dependency” for premium products—and it’s likely to persist given the technical expertise and infrastructure requirements. Makes sense when you think about it.
How Payment Systems Shape Who Wins in Export Markets
What’s really revealing about the competition between major dairy exporters is how payment structures influence what farmers produce, which ultimately determines export success. New Zealand is capturing 46% of China’s dairy imports? That’s not luck—it’s directly tied to how they pay farmers.
The Fonterra Approach Makes You Think
So Fonterra pays farmers solely on the basis of kilograms of milk solids—butterfat plus protein. Water? Doesn’t matter. Lactose? Not counted. Their 2025/26 forecast, announced in May, stands at $10.00 NZD per kilogram of milk solids.
Research published this year by dairy economics specialists shows the New Zealand payment system essentially discourages chasing volume. When volume isn’t the main metric, farmers naturally optimize for component density instead of pushing cows for maximum daily production. It’s a different mindset entirely.
What I find interesting is how this payment structure aligns farmer incentives with premium market demand almost automatically. When Chinese buyers want high-protein cheese or concentrated dairy ingredients, New Zealand farmers are already producing that milk profile—not specifically for exports, but because that’s what their payment system rewards.
Where American Payment Systems Create Challenges
And this is where it gets tricky for us. Most American cooperatives still use volume-focused payment systems with base prices per hundredweight, treating component premiums as add-ons rather than the main event. This creates an interesting situation—we’re optimizing for volume because that’s what payment systems reward most directly, even as global markets increasingly value component density.
Cornell University’s 2020 research on payment structures, led by Dr. Chris Wolf, found something eye-opening: non-cooperative handlers allocated 37% of premiums to quality incentives, while cooperatives allocated just 18% to quality. As the research shows, some cooperatives reward production excellence while others… well, they basically reward showing up.
“We spent decades asking, ‘How much milk can we ship?’ Now we ask, ‘How much value can we create?’ That change in thinking transformed everything about our operation—and our future.”
Learning from European Approaches
What’s interesting is looking at how European producers handle this. In the Netherlands, FrieslandCampina’s payment system includes substantial sustainability and quality bonuses that can add up to 15% to the base price. German cooperatives like DMK have shifted toward value-based pricing models that reward both components and environmental metrics. These systems took years to implement, but they’re now seeing the payoff in premium export markets.
What Progressive Producers Are Learning
I’ve been talking with forward-thinking dairy operations across the country, and many aren’t waiting around for payment system reform. They’re discovering that transitioning from volume to value can happen faster than we’ve traditionally thought—often with pretty encouraging financial results.
The Nutrition Strategy That Works Right Now
A Wisconsin producer I spoke with recently—runs about 500 cows near Eau Claire—told me something interesting: “We figured component improvement would take years, but our nutritionist showed us we could see real changes within a single lactation cycle.”
Based on Penn State Extension research and field trials across the Midwest, here’s what’s delivering results:
- Amino acid balancing targeting 6.5-7.2% lysine and 2.4-2.6% methionine in metabolizable protein: University of Wisconsin trials show 0.1-0.2% protein increases are worth approximately $71,000 annually for a 500-cow operation
- Fatty acid supplementation using rumen-protected fats: Michigan State research demonstrates 0.2-0.3% butterfat increases valued at $98,000+ annually
- Forage quality optimization, maintaining 26-32% neutral detergent fiber: Cornell studies confirm this supports efficient rumen fermentation for better component production
Dr. Mike Hutjens, Professor Emeritus of Animal Sciences at the University of Illinois—he’s worked with dozens of component-focused operations—tells me farms are capturing $150,000 to $200,000 in additional annual revenuethrough nutrition changes alone, before even touching genetics.
How Genomics Accelerates the Timeline
The genomic testing revolution has really changed the game here. Chad Ryan, genetic programs manager at Select Sires, puts it this way: “What used to take 6-7 years now happens in 36-48 months for herds committed to change.”
The Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding reports that as of April 2025, the average Holstein heifer calf produces 45 more pounds of butterfat and 30 more pounds of protein annually compared to one born in 2015—purely through genetic selection. That’s progress.
Strategic Approaches by Farm Size
Through conversations with producers nationwide, it’s becoming clear that farms of every size can access premium value—though the best strategies vary quite a bit based on scale, location, and market access. Now, not every region has equal access to premium processors—let’s be honest about that—but opportunities are expanding faster than many folks realize.
Mid-Size Operations (300-800 cows): Finding the Balance
These operations often have that nice combination of enough scale for efficiency while maintaining flexibility to adapt. A producer milking 550 cows near Green Bay shared this with me: “We’re big enough to matter to processors but small enough to pivot when we need to.”
Wisconsin’s Department of Agriculture reports that operations focusing on cheese-quality milk are seeing annual revenue increases of $150,000-$200,000 through component optimization. You know what’s interesting about this size operation? They can often implement changes faster than larger dairies while still having enough volume to negotiate favorable terms with processors.
Large Operations (1,500+ cows): Leveraging Scale
California’s larger dairies are taking a different approach. A manager running a 2,100-cow operation in Tulare County explained their strategy: “We provide consistent, high-volume premium supply for export contracts.”
What I’ve noticed with these larger operations is that they’re often dealing with tighter margins per cow, so even small percentage improvements in components can make a huge difference to the bottom line. And with California’s ongoing water challenges and environmental regulations, maximizing value per gallon of water used is becoming critical.
Small Family Farms (Under 200 cows): The Niche Advantage
What’s been really encouraging—and honestly, kind of surprising—is how smaller farms are finding lucrative opportunities in specialty markets. A Pennsylvania family running 165 cows who switched to A2 production three years ago now gets $24 per hundredweight. “Would’ve seemed impossible five years ago,” they told me.
Penn State Extension specialist Lisa Holden confirms what we’re seeing: “Small farms using modern management systems are proving that farmstead-scale operations can achieve competitive margins. The key is identifying and serving premium niches that value authenticity and story alongside quality.”
The Window of Opportunity—And Its Limits
Dr. Mary Ledman, global dairy strategist at Rabobank, sees a clear but limited window here. “Producers have about 3-5 years to establish themselves as premium suppliers before market saturation occurs,” she explained at a recent industry conference. “China’s premium import growth won’t stay at 18% forever.”
What makes this particularly compelling is that nine out of ten emerging markets—Southeast Asia, India, Africa—are reporting double-digit gains in premium dairy demand according to IFCN Dairy Research Network data. Southeast Asia’s dairy market alone is projected to grow at 7-8% annually through 2030, according to FAO projections.
But let’s be realistic here. Not every producer has convenient access to premium processors. Transition costs can be substantial upfront. And yeah, there’s risk in shifting away from what’s worked for generations. Plus, with the way weather patterns have been changing—we all saw what happened with the flooding in California’s Central Valley last spring—maintaining consistent component levels through environmental challenges adds another layer of complexity.
Practical First Steps You Can Take
Based on everything I’ve learned researching this shift, here’s what I’d suggest doing in the next 30 days:
Week 1: Figure Out Where You Stand
- Calculate your average components from the past year (and compare them seasonally—summer depression is real)
- Compare your payment structure to what others in your region are getting
- Identify processors in your area who pay component premiums
Week 2: Look at Nutrition Options
- Set up a meeting with your nutritionist about amino acid balancing
- Get quotes for rumen-protected fat supplements
- Test your current forage quality—NDF digestibility, particle size, the works
Week 3: Explore Your Market
- Call three specialty processors or cheese makers within reasonable hauling distance
- Research what certifications the premium markets in your area require
- Talk with your cooperative about their export programs and premium opportunities
Week 4: Build Your Plan
- Set component targets for the next 12 months
- Budget for genomic testing of heifer calves
- Pick your first step—nutrition usually offers the quickest payback
Where This All Leads—And Why Time Matters Now
Looking at everything together—the data, what producers are experiencing, where markets are heading—this shift from volume to value in global dairy markets isn’t just talk anymore. It’s happening right now, and we’re seeing clear differences between those adapting and those holding steady.
What really strikes me is how China’s market is basically showing us the future. That surge of nearly 18% in premium dairy imports, while commodity products decline around 12%? That’s not just noise. We’re seeing similar patterns across emerging markets—FAO, Rabobank, and IFCN are all documenting this—which creates multiple opportunities for well-positioned suppliers.
I’ll be straight with you—the window for action feels tighter than many producers might expect. Those who establish premium positioning in the next 3-5 years will likely lock in long-term contracts and relationships. If we look at historical patterns in agricultural markets, waiting for others to prove the model usually means competing for whatever’s left in increasingly crowded markets.
And here’s the thing that should really get your attention: we’re already ten months into 2025. If that 3-5 year window started when these trends became clear in early 2024, we’re already approaching the halfway point of year two. The producers making moves now—this fall, this winter—are the ones who’ll be established when the real competition for premium contracts heats up in 2026 and 2027.
What gives me hope is that farms of every size genuinely have pathways forward. From 150-cow family operations I’ve visited who’re targeting local specialty markets to 2,000-cow enterprises supplying export containers, there are viable strategies across the board.
The window’s open right now—but with 2025 nearly in the books and premium market competition accelerating, every month of hesitation means watching another competitor lock in the contracts and relationships that could’ve been yours. Based on everything I’m seeing and hearing, by the time the 2026 harvest rolls around, the early movers will already be counting their premium checks while others are still debating whether to make the shift.
The clock is ticking. The question isn’t whether this shift will happen—it’s whether you’ll be part of it.
Key Takeaways:
- The Opportunity: Premium dairy imports to China up 18% while commodity down 12%—this isn’t temporary
- The Timeline: 3-5 year window to establish premium positioning before market saturation
- The Money: $150,000-$200,000 potential annual revenue increase for 500-cow operations through component optimization
- The Path: Nutrition changes deliver results in 12-18 months; genetic improvements in 36-48 months
- The Reality: Not every producer has equal access to premium markets, but opportunities are expanding rapidly
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Seizing the Moment: Maximizing Milk Solids Output Through Strategic Nutrition and Genetics – This article provides a tactical playbook for implementing the component-focused strategy discussed in the main piece. It details specific nutritional targets, supplement strategies, and breeding advice to help you start boosting your milk solids and revenue right away.
- 2025 Dairy Market Reality Check: Why Everything You Think You Know About This Year’s Outlook is Wrong– For a deeper strategic dive, this piece analyzes the powerful economic forces behind the component revolution. It validates the main article’s premise with hard data on market volatility, export opportunities, and why traditional milk pricing models are breaking down.
- Genetic Revolution: How Record-Breaking Milk Components Are Reshaping Dairy’s Future – Looking at innovation, this article explores how genomics is the engine driving the industry’s shift to high-component cows. It reveals how DNA testing accelerates genetic progress and why the latest 2025 genetic updates prioritize butterfat and feed efficiency.
 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
Every week, thousands of producers, breeders, and industry insiders open Bullvine Weekly for genetics insights, market shifts, and profit strategies they won’t find anywhere else. One email. Five minutes. Smarter decisions all week.






 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.