Two identical farms. One gets $17.81/cwt today. The other? $13.75. The ONLY difference: where their milk truck goes.
Executive Summary: Today’s dairy market delivered a brutal verdict: if your milk goes to cheese, you’re winning at $17.81/cwt – but if it’s heading to powder, you’re bleeding money at $13.75. This historic $4 gap means identical farms are now separated by $3,800 per 100 cows per month, and NDM’s collapse today (seven sellers, zero buyers) signals it’s getting worse. While cheese held firm above $1.82, powder crashed by 2.25 cents amid intensifying European competition and weakening global demand. Feed costs keep climbing – corn hit $4.35/bu, soybean meal $308/ton – squeezing everyone’s margins, but only cheese producers have the pricing power to survive. The industry’s geographic revolution accelerates as Texas adds 50,000 cows and builds massive new plants while California and Wisconsin struggle with regulations and aging infrastructure. Smart operators are locking in Q1 2026 Class III near $18 and making hard decisions about their future – because in this market, standing still means falling behind.

Let me tell you what’s happening in the dairy markets today —and, more importantly, what it means for your next milk check. We saw cheese prices hold steady above $1.82, which is good news if you’re shipping to a cheese plant. But if your milk’s going into powder? That 2.25-cent drop in NDM to $1.14 is going to sting. This growing divergence between Class III and Class IV prices — now nearly $4 per hundredweight — is creating clear winners and losers depending on where your tanker is unloaded.
Looking at today’s trading, what’s interesting here is the complete absence of action in cheese despite decent bid support. No trades in blocks or barrels isn’t unusual after a week-long rally, but the seven offers stacked up against zero bids in NDM? That tells you everything about where sentiment is heading for powder markets.

Today’s Price Action — What These Numbers Mean for Your Farm
| Product | Price | Today’s Move | Weekly Trend | Real Impact on Your Farm |
| Cheese Blocks | $1.8250/lb | Unchanged | Up 1.4% | Holding firm above $1.82 keeps Class III near $17.80 |
| Cheese Barrels | $1.8200/lb | Unchanged | Up 1.4% | Steady demand supporting the cheese complex strength |
| Butter | $1.5725/lb | +1.75¢ | Down 0.1% | Small bounce won’t offset NDM weakness for Class IV |
| NDM Grade A | $1.1400/lb | -2.25¢ | Up 3.4% | Sharp drop pulls November Class IV below $14 |
| Dry Whey | $0.7000/lb | Unchanged | Up 3.2% | Steady support for Class III other solids value |
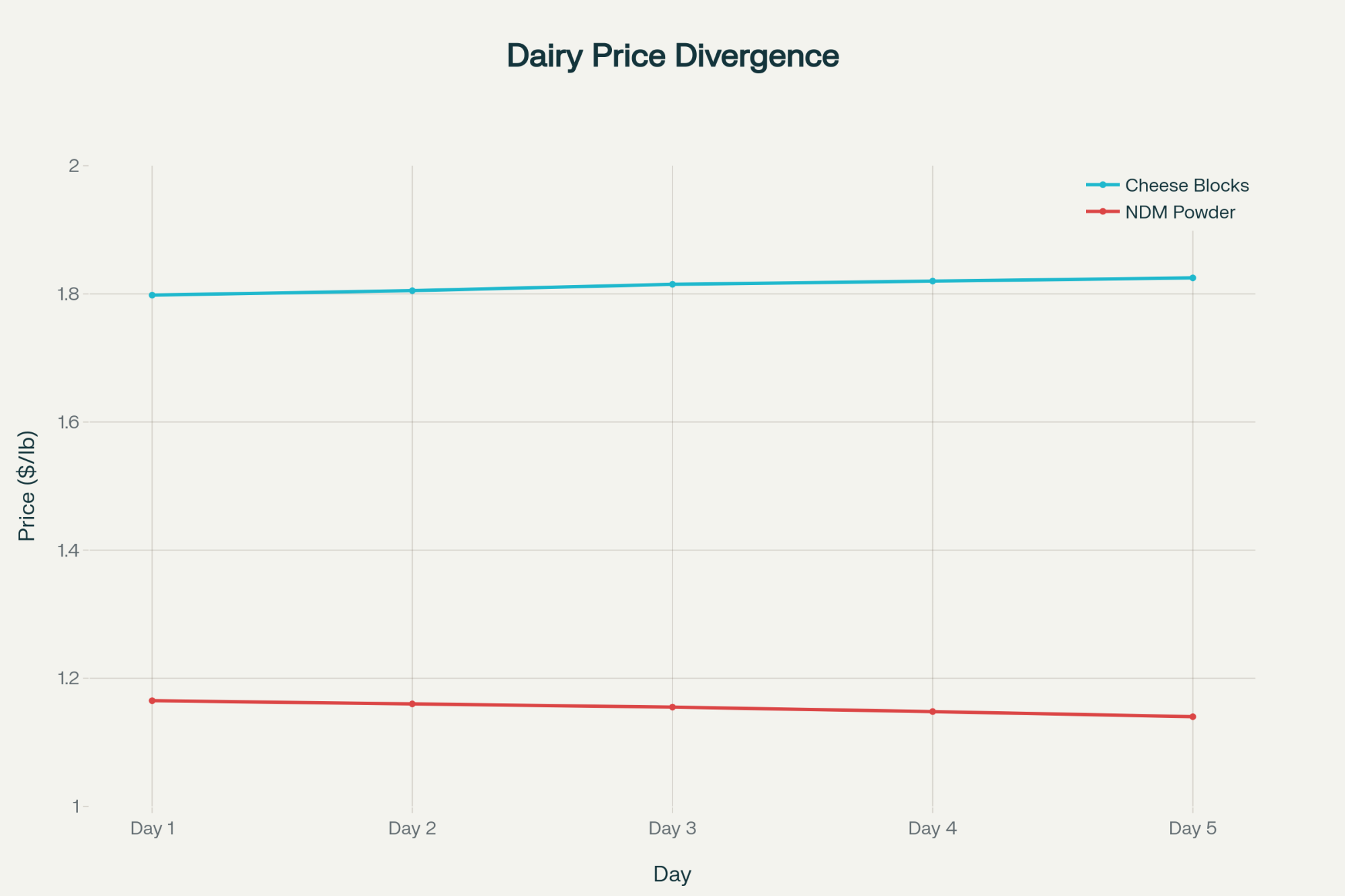
The cheese market’s taking a breather after climbing steadily all week. With blocks and barrels both parked above $1.82, processors seem content with their inventory levels heading into the November holiday demand. That’s actually constructive for maintaining these price levels.
But here’s where it gets concerning — NDM dropping 2.25 cents on heavy offers and absolutely no buying interest. When you see seven sellers trying to unload product with no takers, that’s a market looking for a floor. This weakness directly hits anyone shipping to butter-powder plants, pulling that November Class IV price down toward $14 or potentially lower.
From the Trading Floor — Reading Between the Lines
Bid/Ask Dynamics Tell the Story
The order book today painted two very different pictures. Cheese showed balance with just two bids and two offers on blocks, nothing on barrels — that’s a market comfortable with current levels. But NDM? Zero bids against seven offers is about as bearish as it gets. As one Chicago floor trader told me this morning, “Nobody wants to catch a falling knife in powder right now.”
Trading volumes stayed extremely light — only two loads of butter actually changed hands. The lack of cheese trades doesn’t worry me; it’s normal consolidation. But NDM’s inability to attract even a single bid at progressively lower prices? That suggests we haven’t found the bottom yet.
Volume Patterns and Market Mechanics
What caught my attention was the timing of those NDM offers. They started appearing early and kept building throughout the session, with sellers growing increasingly anxious as the day wore on. The price had to drop 2.25 cents just to clear the board, and even then, no actual trades occurred — just a lower posted price trying to entice buyers who weren’t there.
Where We Stand Globally — And Why It Matters
You want to know why NDM’s struggling? Look at global prices. U.S. NDM at $1.14 per pound is now squeezed between New Zealand at roughly $1.15 and Europe, sitting around $1.00 (based on current exchange rates). That 14-cent premium over European powder is killing our competitiveness in key export markets like Mexico and Southeast Asia.
The real opportunity — and I’ve been saying this for weeks — is in butter. At $1.5725, we’re trading at a massive discount: 89 cents below Europe and $1.40 below New Zealand. Yet nobody’s stepping up to arbitrage this gap. Either U.S. butter is about to rally hard, or global prices are set for a major correction. Something’s got to give.

According to Rick Naerebout, CEO of the Idaho Dairymen’s Association, “We’re seeing strong interest from international buyers for U.S. butter at these levels, but the logistics of securing a consistent supply through Q1 2026 is holding back larger commitments.”
Feed Costs Keep Creeping Higher
Your feed bills aren’t doing you any favors right now. December corn futures closed at $4.3450 per bushel, up 6.5 cents this week. December soybean meal hit $308.70 per ton, gaining $11.
For a typical Upper Midwest dairy running a standard TMR, you’re looking at an extra $0.15-0.25 per cow per day in feed costs from this week’s rally alone. With the milk-to-feed ratio barely treading water, these incremental cost increases are directly eating into your already thin margins.
Dr. Bill Weiss from Ohio State’s dairy nutrition program notes, “The projected feed cost index for 2025 sits at 92, suggesting an 8% decrease from 2024 levels, but current futures pricing indicates that relief may not materialize until late Q1 2026.”
Production Reality Check — Where the Milk’s Coming From
USDA’s latest projections have milk production at 230.0 billion pounds in 2025 and 231.3 billion pounds in 2026 — both revised upward from previous estimates. But here’s what matters: where that milk’s being produced and who’s got the processing capacity to handle it.
The geographic shift is striking. Texas posted a jaw-dropping 10.6% surge in April 2025, hitting 1.511 billion pounds. Idaho’s up 4.2% at 1.471 billion pounds. Meanwhile, California’s still recovering from H5N1 impacts, down 1.4%, and Wisconsin — the traditional dairy heartland — barely grew at 0.1%.
This isn’t just statistics; it’s a fundamental realignment of the U.S. dairy industry. Texas added 50,000 cows in the past year. Idaho gained 28,000. Kansas jumped 16,000. These states are building new processing capacity to match — Leprino’s massive cheese plant in Lubbock will process a million pounds daily when it opens in 2025.

What’s Really Driving These Markets
Domestic Demand Dynamics
Holiday cheese demand is providing the floor under current prices. Retailers are actively building inventory for Thanksgiving promotions, keeping both block and barrel prices well-supported above $1.82. Food service demand remains steady, according to several major processors I spoke with this week.
But butter’s a different story. Inventories appear more than adequate for holiday baking needs. As one major retailer’s dairy buyer put it, “We’re covered through New Year’s at current consumption rates. No need to chase prices higher.”
Export Markets — The Pressure Points
U.S. Dairy Export Council data shows we’re in a knife fight with the EU for market share in Mexico. Today’s NDM price drop was necessary to stay competitive. But the bigger story is Southeast Asia, where demand continues to grow at 4-6% annually, according to recent USDEC reports.
The massive butter discount to global prices should be creating export opportunities, but logistics remain challenging. “We need consistent supply commitments through Q2 2026 to make these international contracts work,” notes a major exporter who requested anonymity.
Forward Markets and What They’re Telling Us
November Class III futures settled at $17.81 yesterday — today’s stable cheese market keeps that outlook intact. November Class IV at $14.02 faces more downward pressure after today’s NDM drop, potentially testing below $14.
Looking ahead, markets are pricing Class III around $17.30 for Q4 2025 and $16.85 for the first half of 2026. Class IV projections sit at $16.00 for Q4 and $15.75 for H1 2026. This persistent $1.50+ spread between Class III and Class IV isn’t going away anytime soon.
USDA’s all-milk price forecast for 2025 sits at $21.35 per hundredweight, with 2026 projected at $20.40 — both recently revised downward due to growing milk supplies and moderate demand growth.
From the Farm — Producer Perspectives
“We’re holding our own with these cheese prices, but barely,” says Jim Henderson, who milks 450 cows near New Glarus, Wisconsin. “Feed costs keep nibbling away at margins. If Class III drops below $17.50, we’ll have to make some hard decisions about culling.”
Down in Texas, the mood’s different. “We’re expanding,” states Maria Rodriguez, managing a 2,500-cow operation outside Dalhart. “With Leprino coming online next year, we need the milk ready. These prices work for us with our cost structure.”
In Pennsylvania, third-generation dairyman Tom Mitchell is more cautious: “I’m locking in 30% of my Q1 2026 milk at $18.85 Class III. After what we went through in 2023, I’m not taking chances. Better to know your margin than hope for higher prices.”
Regional Spotlight: The Changing Landscape
Wisconsin and Minnesota — The traditional dairy heartland is holding steady but not growing. Corn harvest is complete with good yields, helping stabilize the local feed basis. Cheese plants are operating at capacity due to holiday orders. Spot milk premiums remain steady, reflecting balanced supply-demand dynamics. The real concern? Younger producers are questioning long-term viability with these margins.
Texas and the Southwest — This is where the action is. With Cacique’s Amarillo facility now operational and Leprino’s Lubbock plant set to come online in 2025, processing capacity is finally catching up with production growth. Land values of $6,000-$8,000 per acre remain reasonable compared to traditional dairy regions. Water availability varies by location, but it hasn’t yet constrained growth.
California — Still recovering from H5N1 impacts and facing ongoing water challenges. The proposed Dairy Order requiring nitrogen discharge limits of 10 milligrams per liter will add costs. As dairy farmer John Silva near Tulare explains, “Between water regulations, air quality rules, and labor laws, it’s getting harder to compete. Some neighbors are selling to almond growers.”
Idaho — Continuing its steady expansion, with milk production up 4.2% year-over-year. The state now ranks fourth nationally, accounting for 7.5% of total U.S. production. Processing capacity remains the constraint, but several expansion projects are in the planning stages.
Three Market Scenarios for Next Week
Bull Case (25% probability): Cheese breaks above $1.85 on strong holiday orders, pulling Class III toward $18.50. Export buyers finally move on discounted butter, sparking a rally above $1.65. This scenario requires an unexpected surge in demand or a production disruption.
Base Case (60% probability): Cheese consolidates between $1.80 and $1.85. NDM continues sliding toward $1.10. Butter stays range-bound $1.55-1.60. Class III pays $17.50-18.00, while Class IV pays $13.75. Feed costs remain elevated.
Bear Case (15% probability): Cheese breaks below $1.80 on profit-taking. NDM accelerates decline toward $1.05. Growing milk supplies overwhelm demand. Class III drops toward $17, Class IV toward $13.50. This requires significant demand destruction or a major production surge.
What Farmers Should Do Now
Price Risk Management Lock in 25-30% of Q1 2026 milk production through Class III futures near $18. Use Dairy Revenue Protection for catastrophic coverage below $16. Consider collar strategies to maintain upside while protecting downside — buying $17 puts while selling $19 calls, for instance.
Feed Strategy Book 40-50% of Q1 2026 corn needs at current levels. Soybean meal showing concerning strength — if you lack coverage through winter, act before it breaks $320/ton. Watch South American weather closely; any production issues there will drive prices higher.
Operational Decisions With the massive Class III/IV spread, every percentage point of protein and fat matters. Work with your nutritionist to fine-tune rations. Consider genomic testing to identify your highest component producers. Cull decisions should factor in not just production but component quality.
Cash Flow Planning. That gap between Class III and Class IV means uneven milk checks depending on your plant’s utilization. Budget conservatively. Build working capital while cheese prices hold. Consider equipment purchases now rather than waiting for potentially tighter margins in 2026.
Industry Intelligence — What’s Coming Down the Pike
Federal Order Reform Impact The comment period for FMMO reform closes soon. Key proposals include updating milk component values, revising Class I pricing, and adjusting make allowances. “These changes could shift milk values by $1-2 per hundredweight once implemented,” notes Dr. Marin Bozic, dairy economist at the University of Minnesota.
Processing Capacity Expansion Beyond Leprino: In Texas, significant capacity is coming online. Chobani’s $500 million Idaho expansion, Select Milk’s powder facility upgrades, and multiple smaller cheese plants across the Midwest. The industry’s investing over $11 billion in new capacity through 2026, according to the International Dairy Foods Association.
Technology Adoption: Robotic milking systems are no longer just for small farms. Several 1,000+ cow operations are installing robots, citing labor savings and improved cow health. “The payback’s under five years at current milk prices,” reports one Wisconsin producer who installed 24 robots last year.

The Bottom Line — Context for Today’s Market
Today was a pause day after cheese’s weeklong rally. That’s normal, healthy even. The stability above $1.82 suggests these levels are sustainable through holiday demand.
But NDM’s accelerating weakness is concerning. This isn’t just market noise — it reflects fundamental oversupply in global powder markets and weak demand from key importers. When you can’t find a single bid at progressively lower prices, more downside usually follows.
The growing spread between Class III and Class IV — now approaching $4 per hundredweight — creates distinct winners and losers. If you’re shipping to a cheese plant, you’re in decent shape. Butter-powder plants? That’s a different story entirely.
Compared to last October, we’re in a better position on cheese but significantly worse on powder and butter. This divergence isn’t resolving anytime soon. Success in this environment requires active management — of price risk, feed costs, and operational efficiency. The days of riding market waves without a strategy are over.
What’s clear is that the U.S. dairy industry is undergoing fundamental restructuring. Production is shifting to states with fewer regulatory constraints and newer infrastructure. Traditional dairy regions face mounting challenges. Processing capacity is playing catch-up to this geographic realignment.
Smart money’s positioning for this new reality. The question is: are you adapting fast enough to thrive in tomorrow’s dairy industry, or are you hoping yesterday’s strategies will somehow work in tomorrow’s markets?
Key Takeaways:
- The $45,600 Question: Same milk, same work, but cheese-bound farms earn $17.81/cwt while powder operations bleed at $13.75 – your plant relationship now matters more than your production efficiency
- NDM’s Zero-Bid Disaster: Today’s seven sellers vs zero buyers signals something darker – U.S. powder can’t compete with Europe’s $1.00/lb pricing, and the gap’s widening
- Geographic Exodus Accelerates: Texas added 50,000 cows while California lost 8,000 – follow the milk to states with water rights, sane regulations, and new $11B in processing capacity
- Feed Math That Kills: At $4.35 corn and $308 soy meal, you need $18+ milk to maintain 2019 margins – only cheese producers have a shot
- Your 72-Hour Decision: Lock in 30% of Q1 2026 at $18+ Class III before smart money takes it all – standing still in this market means falling behind
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- 11 Proven Strategies to Lower Feed Costs and Boost Efficiency on Your Dairy – This guide provides tactical methods for optimizing TMR and herd nutrition. It reveals actionable strategies to improve feed conversion, manage rumen health, and reduce waste, directly addressing the margin pressures from rising feed costs mentioned in our market report.
- Who Speaks for Your Milk Check? The Push to Reform Dairy’s Voting Power – Delve into the high-stakes issue of Federal Order reform. This article explains how recent changes to make allowances impact your farm’s bottom line and outlines the critical debate around producer voting rights that will shape future milk pricing policy.
- Tech Reality Check: The Farm Technologies That Delivered ROI in 2024 (And Those That Failed) – Before investing in automation, read this critical analysis. It breaks down the real-world payback periods for robotic milkers, health sensors, and automated feeders, demonstrating how strong management—not just the machinery—is the key to achieving a positive return.
 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
Every week, thousands of producers, breeders, and industry insiders open Bullvine Weekly for genetics insights, market shifts, and profit strategies they won’t find anywhere else. One email. Five minutes. Smarter decisions all week.






 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.






