31% of dairy services now use beef semen. Fertility evaluations? Still pretending it’s 2005. No wonder your PTAs don’t work.
Executive Summary: If you’ve spent years selecting elite fertility bulls with zero improvement, you’re not alone—and you’re not failing. The genetic evaluation system has been broken for 20 years, inflating fertility PTAs by an estimated 25-30% based on the timing bias and management misalignment Dr. McWhorter described and costing the average 500-cow dairy $25,000 annually. Modern management broke the system: it assumes you breed at 50 days when the industry average is 67.5, can’t account for 31% of services using beef semen, and actively punishes progressive practices like extended VWP as genetic deficiencies. CDCB admits the problems and promises fixes in 2026, but smart producers aren’t waiting—they’re already discounting elite PTAs by 25-30%, trusting proven bulls with 750+ daughters, and spreading services across 8-12 sires. Your cows aren’t broken, your management isn’t failing—the measurement system just hasn’t caught up to how modern dairies actually operate.

You know, I’ve been having the same conversation at every producer meeting lately—from Wisconsin to Pennsylvania, even down in Georgia where—let’s be honest, the heat stress alone should explain everything. Folks who’ve spent five to ten years selecting top-tier fertility bulls are seeing pregnancy rates that just… aren’t budging.
Here’s what’s interesting: the disconnect between what the PTAs promise and what shows up in the tank has left many questioning their management. But after sitting through Dr. Taylor McWhorter’s presentation at World Dairy Expo this year—and digging into the research behind it—I’m convinced we’ve been measuring the wrong thing, in the wrong environment, for about two decades now.
What Dr. McWhorter laid out at Madison this October were nine major updates to fertility evaluations scheduled for 2026. And while CDCB is presenting these as routine improvements, if you read between the lines… well, they’re quietly acknowledging that our fertility evaluations have been systematically miscalculating genetic merit for herds using modern management practices.
The economic modeling CDCB has done suggests we’re looking at tens of millions in foregone genetic progress over the past decade. That’s real money left on the table.
Click the link to view the presentation. Modern Herds, Modern Hurdles: Aligning Fertility Evaluations Taylor McWhorter, Ph.D., CDCB Geneticist Slides
The Hidden Cost of Assumptions That No Longer Match Reality
So here’s how something as basic as your voluntary waiting period created this mess.
For over 20 years, the genetic evaluation system has assumed that everybody’s breeding cows at 50 days after calving. Made perfect sense back when that’s what we all did, right? I remember my dad’s operation in the ’90s—50 days was gospel.
But here’s the thing: CDCB’s own data shows that by 2020, the actual industry average VWP had crept up to 67.5 days. And I know operations pushing 80-85 days, especially those high-producing herds out West trying to let cows get their metabolic act together before breeding. Even smaller operations I work with in the Northeast are extending to 70 days based on their vets’ recommendations.
As Dr. McWhorter explained it—and this really hit home for me—the evaluation methodology was assuming all cows had the opportunity to become pregnant starting at 50 days in milk. But when you’re actually waiting 70 days, there’s this phantom 20-day window where cows physically can’t be pregnant, yet the evaluation expects them to be.
What this means for your breeding decisions is pretty straightforward, and honestly, kind of frustrating. Bulls whose daughters were in extended-VWP herds looked artificially poor for fertility. Not because the daughters weren’t getting pregnant—they just couldn’t even be bred during the timeframe the evaluation was looking for.
The economic modeling suggests this mismatch alone costs an estimated $50 per cow annually based on CDCB economic modeling of missed genetic progress in distorted selection decisions and missed genetic progress. You do the math on your herd… for a 500-cow operation, that’s $25,000 every single year. It adds up fast.
| Time Period | Industry Average VWP (Days) | Evaluation System Assumption | Timing Gap (Days) | Annual Cost Per Cow |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990s-2005 | 50 | 50 | 0 | $0 |
| 2010 | 52 | 50 | 2 | $5 |
| 2015 | 58 | 50 | 8 | $15 |
| 2020 | 67.5 | 50 | 17.5 | $50 |
| 2024 (Progressive Herds) | 75-85 | 50 | 25-35 | $75-100 |
When Beef-on-Dairy Changed Everything We Thought We Knew
But the VWP issue? That was just the warm-up act.
You probably know this already, but the beef-on-dairy explosion happened faster than anyone expected. The National Association of Animal Breeders’ data shows beef semen sales to dairy farms hit 7.9 million units in 2023—that’s 31% of all semen sold to dairies. Five years ago? That number was basically nothing.
Holstein semen dropped from complete market dominance to just 43% of cow services by 2024, with Angus alone accounting for nearly 29% according to CDCB’s April evaluation summary. I mean, that’s a fundamental shift in what we’re doing reproductively.

And it’s not just a market trend—it’s changed what “fertility” even means in a modern breeding program.
The research McWhorter presented from her University of Georgia work shows Angus semen produces slightly different conception rates than Holstein semen—we’re talking 33.8% versus 34.3% in lactating cows. But here’s what really matters: beef semen gets used strategically on problem breeders, averaging a service number of 3.04, compared to Holstein’s 2.13.
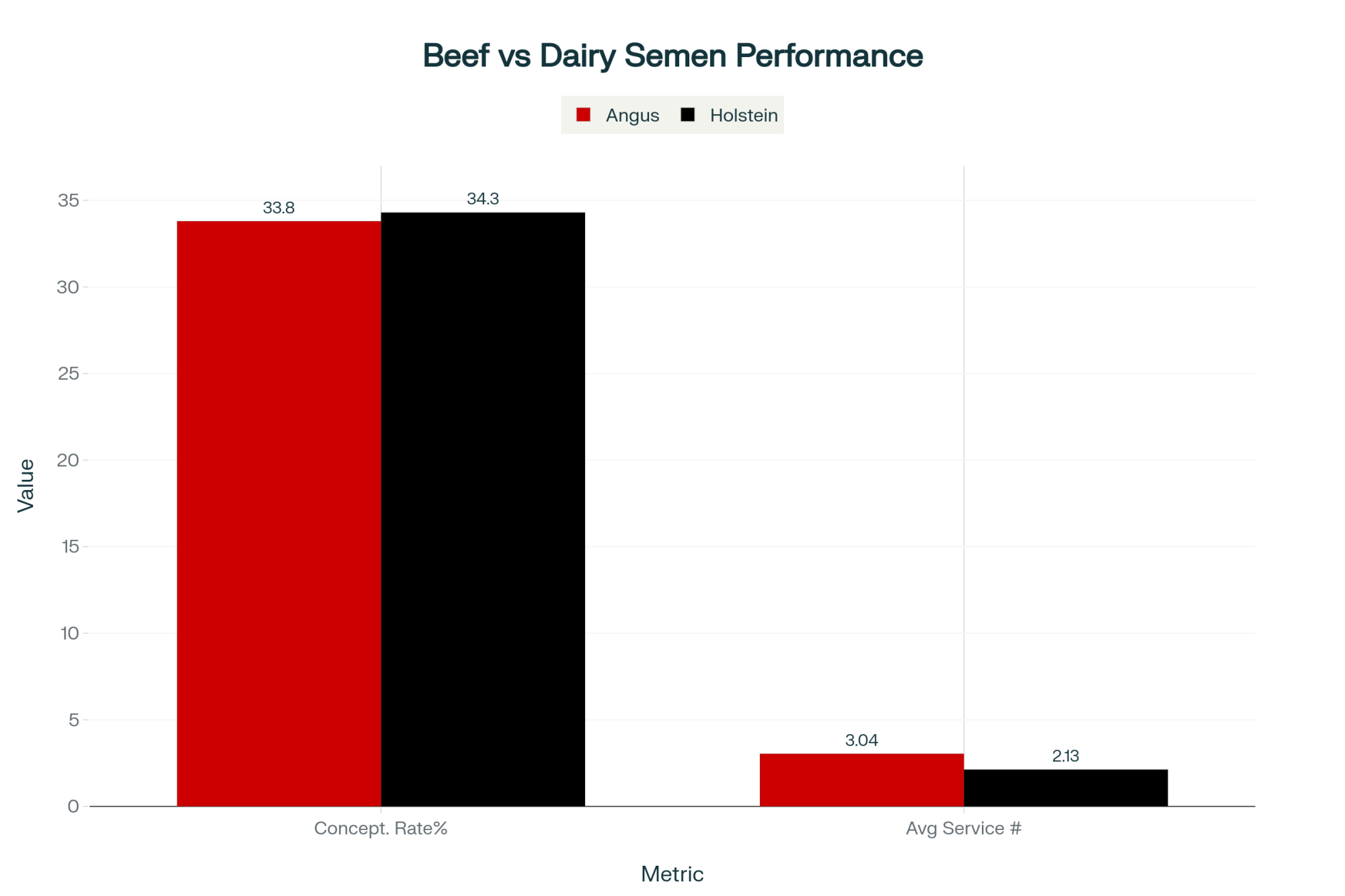
What I’ve found is that when 40-50% of services in a herd use beef semen—and those services concentrate on cows that already struggled with dairy breeding—the evaluation system can’t tell the difference. It attributes all of that to the dairy bull’s genetics.
So bulls in herds doing extensive beef-on-dairy look artificially poor for fertility, even when their actual dairy-breeding daughters are doing just fine.
The Five Games: When One Size Doesn’t Fit Anyone
Here’s what’s become crystal clear from analyzing all that data in the National Cooperator Database—you know, that massive collection of over 100 million lactation records we all contribute to…
“Fertility” has basically fragmented into at least five distinct biological processes. And each one selects for different genetic capacities.

Think about it this way:
The elite replacement game. These are your nucleus herds using sexed Holstein semen on high-merit heifers and first-lactation cows at optimal timing. They’re pushing for maximum conception rates to produce superior replacements. Based on DHI participation patterns, about 20% of herds operate primarily this way.
You know the type—those big registered operations in Wisconsin and New York.
Commercial dairy breeding. Your typical commercial operation using conventional semen on mid-tier cows after standard VWP. This probably represents 35% or so of operations, based on what CDCB sees in their herd management surveys. Most of the 200-500 cow herds across the Midwest fall here.
Problem breeder salvage. We’ve all been there—service number four or five, just trying to get that cow pregnant before you have to cull her.
The Wisconsin research suggests this affects about 30% of the breeding-eligible population at any given time.
Beef-on-dairy terminal breeding. Strategic use of beef genetics on lower-genetic-merit cows to maximize calf value. NAAB data shows this grew from basically zero to representing 15-20% of breeding decisions in just five years. And it’s still growing.
The ET programs. Elite genetics multiplied through embryo transfer, bypassing natural breeding entirely. Small percentage overall, but concentrated in high-value genetics.
Now, current evaluations average performance across all five of these “games” into a single Daughter Pregnancy Rate or Cow Conception Rate score. But—and this is where it gets really interesting—the genetic correlations between these management systems have dropped to 0.65-0.75, based on recent genotype-by-environment research.
What’s that mean in plain English? A bull ranking in the top 10% for elite replacement production might rank in the bottom 30% for problem breeder management. Same genetics, completely different outcomes depending on which game you’re playing.
What Progressive Producers Are Learning the Hard Way
I was talking with a producer managing about 1,800 cows in Wisconsin—he’d been selecting exclusively on top-tier genomic bulls for fertility since 2019. His pregnancy rate? Still stuck around 28%.
He told me, “I kept thinking we were screwing something up with our management. We extended VWP to 72 days based on the University of Wisconsin recommendations for better first-service conception. We adopted beef-on-dairy for inventory control—now using about 35% beef semen. Everything the consultants said should help.”
What he didn’t realize—and what nobody was really talking about clearly—was that his progressive management practices were systematically penalized by the evaluation methodology.
Here’s the kicker that CDCB research has shown: high-fertility daughters enter genetic databases 6-12 months before low-fertility daughters. It’s this timing bias thing. Young bulls get their first evaluations based predominantly on their best-performing daughters. The PTAs look fantastic initially, then drift downward as more complete data rolls in.

Kind of like judging a pitcher’s ERA after only counting the scoreless innings, you know?
And it’s not just one or two operations seeing this. I’ve heard similar stories from California to Idaho—producers who thought they were doing something wrong when, in reality, the evaluation system wasn’t capturing what they were doing right.
One producer near Boise who made the shift told me his pregnancy rates reportedly improved notably after he started ignoring genomic fertility PTAs and selecting more on within-herd performance. Sometimes going backwards is actually going forwards.
Practical Steps for Managing Through the Uncertainty
What I’ve noticed is that savvy producers aren’t waiting for the 2026 updates. They’re already adjusting their selection strategies based on what they’re seeing in their own barns.
After talking with consultants and progressive producers across the country, several strategies keep coming up.
First, you’ve got to discount those sky-high PTAs. Many consultants I work with are recommending haircuts of 25-30%on top-ranked fertility PTAs. A large-herd manager I know in Idaho put it pretty bluntly: “A bull showing +3.0 DPR? We treat him like he’s maybe a +2.0, +2.2 at best for our operation.” It’s not perfect, but it’s more realistic.
Trust proven bulls for fertility. Dr. Kent Weigel at Wisconsin-Madison has published extensively on this—progeny-proven bulls with 750+ daughters have already been through the timing bias wringer. While their genetics may be a generation older, their fertility predictions have proven more reliable in field conditions.
Match your bulls to your management. If you’re running an extended VWP with substantial beef-on-dairy, bulls evaluated in traditional 50-day VWP environments may underperform pretty dramatically. With those genetic correlations of 0.65-0.75 between evaluation and deployment environments, you’re looking at only 65-75% of predicted gains actually showing up.
And don’t ignore your own data. For herds that are substantially different from national averages, selecting replacement heifers based on actual performance in your environment may outperform genomic predictions. A heifer that conceives on first service in your system? She’s carrying genetics that work for you, regardless of what her genomic PTA says.
I know one producer in Pennsylvania who’s been tracking this meticulously—he’s seen better results selecting on within-herd performance than chasing high genomic PTAs for fertility. Sometimes the old ways still work.
They’re also diversifying bull selection. Rather than putting all their eggs in 3-5 elite bull baskets, they’re spreading services across 8-12 sires. When top-ranked bulls prove overestimated—which history suggests some will—the damage is contained.
Many are building custom indices, creating herd-specific selection criteria that weight production traits (where evaluations remain pretty accurate) more heavily than fertility traits (where accuracy has… degraded).
Producer networks are sharing real outcome data. “This bull delivered, that one didn’t”—the kind of real-world validation that matters more than PTAs sometimes.
Keep in mind, with generation intervals what they are, you’re looking at 2-3 years before these breeding strategy adjustments really show up in your pregnancy rates. It’s a marathon, not a sprint.
| Selection Strategy | Old Approach (Pre-2024) | New Reality (2024+) | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trust Top Genomic PTAs | Use +3.0 DPR at face value | Treat +3.0 as +2.0-2.2 | 25-30% inflation risk |
| Apply 25-30% Discount | Not applied | Applied to all elite PTAs | More realistic expectations |
| Young Bulls (<750 daughters) | Primary selection pool | High risk for inflation | Timing bias exposure |
| Proven Bulls (750+ daughters) | Considered “”outdated genetics”” | More reliable predictions | Already corrected |
| Bull Diversification | 3-5 elite bulls | 8-12 bulls minimum | Risk mitigation |
| Selection Weight on Fertility | 35-40% of TPI weight | 15-20% of custom index | Reduce unreliable traits |
| Custom Index Approach | Standard TPI/NM$ | Production-heavy weighting | Weight what works |
Industry Trends Reshaping How We Think About Fertility
The changes coming in 2026 aren’t happening in a vacuum. They’re responses to massive shifts that caught the evaluation system flat-footed:
You’ve got management fragmentation—DHI data shows VWP now ranges from 50 to 85+ days across herds, compared to that narrow 45-55 day range we had two decades ago.
The beef integration explosion is real. NAAB reports show that 7.9 million units of beef semen were produced in 2023, up from 7.6 million the previous year. That’s not a trend anymore—it’s the new normal.
Then there’s the problem of missing data. CDCB estimates that about 6.6% of breedings have unknown or unrecorded service sires. Hard to evaluate what you can’t even identify, right?
Technology adoption is huge, too. The 2024 National Dairy FARM Program data suggests that around 68% of herds with 500 or more cows now use some form of automated heat detection. That’s creating management variation that the evaluations just can’t capture yet.
And here’s what really accelerates everything: generation intervals have collapsed from about 7 years pre-genomics to 2.5 years now, according to Holstein Association USA genetic trend reports. So evaluation errors multiply through breeding pyramids faster than… well, faster than the system can correct them.
What’s Actually Changing in 2026 (If Everything Goes Through)
Dr. McWhorter outlined nine specific updates at World Dairy Expo, pending Interbull validation this January. Let me break down what actually matters for us:
They’re finally going to adjust for variable VWP, accounting for herd-specific waiting periods from 50 to 85 days. About time, right?
Service sire breed effects will be adjusted for differences in conception rates between dairy and beef semen. That should help with the beef-on-dairy distortion.
There’s a 36-month age restriction coming to prevent that timing bias from early-reporting daughters I mentioned.
They’re introducing First Service to Conception as a new trait that measures only the post-breeding interval. That’s actually pretty clever—sidesteps a lot of the VWP confusion.
The variance components are being updated using the most recent 10 years of data rather than… well, let’s just say, much older averages.
Plus improvements to genomic validation, methods for handling those unknown service sires, some tweaks to the Early First Calving trait, and better modeling across multiple lactations.
If these pass Interbull validation in January, we’ll see implementation in April 2026 evaluations at the earliest. Miss that window? Add another 6-12 months minimum. So don’t hold your breath.
The Bigger Picture: Why Change Takes Forever
You might wonder why it takes 20 years to fix problems everyone can see. I’ve been asking the same question for… well, a long time.
The answer lies in how genetic evaluation governance works. CDCB operates through consensus among groups with very different priorities. Breed associations worry about the continuity of genetic trends. AI studs are protecting bull valuations. Data providers are managing costs. Getting them all to agree? It’s challenging, to put it mildly.
As Dr. Paul VanRaden explained at his retirement seminar last year, the system is designed for stability and credibility, not rapid adaptation. That served us well when management practices changed slowly. But when beef-on-dairy transforms the industry in 5 years, our 15-20 year update cycle just can’t keep pace.
What’s fascinating—and maybe a bit frustrating—is that this governance structure is working exactly as designed. It just wasn’t designed for the pace of modern dairy innovation.
Looking Ahead: What This Means for Different Operations
The impact varies quite a bit depending on your operation. And our friends north of the border in Canada are dealing with similar challenges through their own evaluation system—affecting international semen trade in ways we’re just starting to understand.
Smaller herds—say, under 200 cows—are often less affected because many still operate closer to traditional management. But those adopting beef-on-dairy to capture calf premiums? They face the same evaluation distortions as anyone.
Large Western dairies have been hit hardest. They led beef-on-dairy adoption and VWP extension. Their progressive management gets penalized most severely by these outdated evaluation assumptions.
In the Southeast, heat stress complicates everything, making it harder to separate management effects from genetic merit. The evaluation updates may actually help these herds most by reducing some of those confounding factors.
And grazing operations? That’s a different ballgame entirely. Seasonal breeding and pasture-based systems create genotype-by-environment interactions that the evaluation system barely acknowledges. Many have already moved to within-herd selection just out of necessity.
For seasonal calving systems in places like New Zealand or Ireland? They’re playing an entirely different game that the evaluation system barely recognizes.
Key Takeaways for Your Breeding Program
After all this, several lessons really stand out:
- Your management wasn’t failing—the measurement was. If fertility hasn’t improved despite selecting high-PTA bulls for years, evaluation bias likely explains most of that gap. So you can stop second-guessing yourself.
- Progressive practices have been getting penalized. Extended VWP, beef-on-dairy integration, those individualized strategies that actually improve fertility? They can make genetic evaluations look worse. The system has been interpreting sophistication as genetic failure.
- Production traits remain reliable, thankfully. Milk yield, components, and type evaluations maintain high accuracy with genetic correlations above 0.90 across different management systems, according to recent published research. So focus your genetic selection firepower there.
- For fertility specifically? Proven beats potential right now. Young bulls’ fertility PTAs are most inflated. Bulls with large progeny groups provide predictions you can actually bank on.
- And honestly? Local performance beats global predictions. For traits with high management sensitivity, your herd’s actual outcomes predict future performance better than national evaluations that measure different environments.
- Change is coming—slowly. The 2026 updates will help, but won’t fully resolve the fragmentation across management systems or the historical bias already baked into current breeding pyramids.
Fertility by the Numbers: A Quick Review
- Discount elite fertility PTAs by 25-30%
- Prefer bulls with 750+ daughters for fertility
- Spread services across 8-12 bulls
- Genetic correlation between evaluation and your environment: 0.65-0.75
- Cost of VWP mismatch: $50/cow annually
For now, those of us who understand these limitations can make smarter breeding decisions: discounting inflated predictions, preferring proven performance, and trusting our own herds’ outcomes when genomic promises don’t match what we see in the barn.
The evaluation system is adapting, just at a pace that ensures progressive producers will keep operating at least one management revolution ahead of the genetic measurements trying to catch up. But that’s not necessarily a crisis; it’s just the new reality we need to factor into our breeding decisions.
After all, we’ve been dealing with the difference between promise and performance since the first bull stud opened, and we’ll figure it out, like we always do.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Revolutionizing Dairy Reproduction: Why Your Outdated Protocols Are Costing You Thousands – This article provides the tactical “how-to” for overcoming stagnant fertility, detailing modern synchronization protocols like Double-Ovsynch and the proper implementation of Milk PAG testing to improve pregnancy rates right now.
- The Holstein Genetics War: What Every Producer Needs to Know About the Battle for Our Breed’s Future – This strategic analysis reveals the economic and genetic consequences of industry trends. It provides an action plan for managing inbreeding, diversifying genetics, and maximizing the ROI of beef-on-dairy.
- The UK’s Sexed Semen Playbook: How UK Dairies Hit 84% While You’re Still Stuck at 50/50 – This piece explores the successful adoption of new fertility technology. It demonstrates how UK producers overcame old fertility penalties to leverage modern sexed semen, providing a clear case study on boosting heifer inventory.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!





