China’s 145M-lb whey surge masks a 39% milk powder crash—here’s why that split should terrify every dairy farmer.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: China’s August whey imports hit 145.3 million pounds—a 30-month high that most analysts are calling a recovery, but the real story lies in what they’re not buying. While raw whey surged 31.1% from the U.S., China simultaneously slashed consumer dairy purchases by 32-37% across categories, revealing a calculated strategy that’s fundamentally reshaping global dairy trade. Recent Trade Data Monitor analysis shows that China’s combined milk powder imports dropped to a decade-low level, despite a 9.2% decline in their domestic production, indicating a willingness to sacrifice short-term efficiency for long-term control over consumer-facing dairy products. This isn’t random buying—it’s surgical selection between industrial necessities they’ll import and consumer products they’re determined to control domestically, creating what industry observers now recognize as a two-tier global supplier system. The implications extend far beyond export markets, as disrupted trade flows affect regional milk pricing from California to Vermont when excess product seeks new outlets. Forward-thinking dairy operations are already adapting by building flexible processing capabilities and diversifying market relationships, recognizing that supply reliability now often trumps cost advantages in this politically sensitive landscape.

What if China’s latest trade data isn’t a recovery, but a warning? It’s the first sign that they’re no longer playing the commodity game, and that changes everything for us in the dairy industry.
Here’s what the August numbers tell us: China’s dry whey imports hit 145.3 million pounds—the highest we’ve seen in 30 months, according to Trade Data Monitor. Most analysts are calling it a seasonal bounce-back. However, when I began investigating what else they’re purchasing (and what they’re not), a different story emerges.
The whey surge shows a 4.8% increase over last year’s already strong volumes, with U.S. shipments rising 31.1% after the temporary tariff pause following the Trump-Xi TikTok negotiations. But here’s the kicker: while raw whey imports climbed, China simultaneously slashed consumer dairy purchases. Trade Data Monitor shows whey protein concentrate with at least 80% protein dropped 32%, butter fell 37%, and cheese declined 12% compared to August 2024.
This isn’t random buying. It’s surgical. China’s making calculated choices about what it’ll depend on others for and what it wants to control itself. And that selective strategy should make every dairy producer take notice.

China’s Two-Track Strategy
Looking at these patterns over the past 18 months, China’s developed what you might call a dual approach to dairy imports. Once you see the logic, it’s actually brilliant from their perspective.
Track one: They’re building an iron wall around consumer dairy—milk powders, cheese, yogurt—anything where domestic consumers care about brands and food safety stories. Complete control from farm gate to grocery shelf? That’s the goal.
Track two: They’re maintaining strategic lifelines for industrial ingredients like feed-grade whey that keep their livestock machine running. What I find particularly striking is they’re not trying to replace everything. They’re cherry-picking where they want independence versus where they’ll accept managed dependence.
The data backs this up. Trade Data Monitor reports their combined whole and skim milk powder imports through August reached just over 1 billion pounds—among the lowest January-through-August totals we’ve seen in a decade, despite a modest 1.4% increase from 2024. Meanwhile, the raw whey continues to flow because they have structural protein needs in their feed chains, especially with the ongoing rebuilding of the swine herd after African Swine Fever.
Here’s the smoking gun: China Dairy Industry Association data show that their domestic milk production actually declined 9.2% year-over-year in early 2025, with farmgate prices hitting decade lows of around $19.40 per hundredweight. Yet they’re still pushing self-sufficiency programs. This isn’t market-driven consolidation—it’s a strategic purge of smaller farms while state-connected operations get the backing they need.
The Infrastructure Arms Race Nobody Saw Coming
What surprised me most while researching this piece is the dramatic shift in the rules of export success. The old playbook—seasonal contracts, futures hedging, steady customer relationships—just got torched.
European suppliers learned this the hard way during recent trade disruptions. When Beijing needed to replace American whey volumes at lightning speed, EU exporters looked golden on paper. However, industry observers report that they couldn’t pivot their processing lines and logistics quickly enough. That’s the kind of wake-up call that costs millions and rewrites your entire export strategy.
The winners these days have built what some call flexible infrastructure. From my conversations with producers across different regions, this typically includes:
- Adaptable processing capabilities that can shift volumes and specifications on a dime—something many Midwest cooperatives are scrambling to build
- Digital contract systems that handle real-time adjustments when trade winds shift
- Multi-origin sourcing arrangements so they can blend from different locations as regulations change
- Strategic storage partnerships in key trade zones
- Risk monitoring systems that track diplomatic developments alongside milk futures
New Zealand’s the poster child for this approach. Industry reports indicate that their exporters have leveraged duty-free FTA access to command pricing premiums of 15-25%, while maintaining a consistent market share, even during the most severe U.S.-China trade disputes. But it’s not just about lower tariffs—it’s the supply guarantee that Chinese buyers will pay extra for when everything else feels like quicksand.
A perfect example is a Wisconsin cooperative that partnered with processing facilities in three different states, enabling them to blend products to meet shifting regulatory requirements. When one plant faced inspection delays, they pivoted production seamlessly. That kind of flexibility was unthinkable in our industry five years ago, but it’s now table stakes for anyone serious about export markets.
When Politics Hijacked Commodity Trading
| Risk Category | Traditional Dairy Trading | Political-Aware Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Concerns | Weather, Feed Costs, Milk Prices | Tariff Changes, Trade Wars |
| Contract Length | 90+ days standard | 30-60 days maximum |
| Price Volatility | ±15% seasonal variation | ±40% political swings |
| Success Metrics | Lowest cost per unit | Supply guarantee premiums |
| Infrastructure Investment | $50K-100K processing focus | $150K-400K political hedging |
| Market Response Time | 30-60 days planning cycles | 24-48 hour pivot capability |
Here’s something that would’ve sounded like science fiction five years ago: major Chinese importing companies now run specialized war rooms that monitor diplomatic developments 24/7. These aren’t your grandfather’s commodity desks—they’re designed to pounce when political windows crack open.
Early intelligence suggests that when Trump and Xi reached a preliminary agreement on TikTok in September, some buyers responded with remarkable speed to secure additional whey contracts. That response time has forced exporters to tear up their traditional playbooks entirely.
Many are now offering what amounts to “political insurance policies” instead of standard long-term contracts:
- Rapid-response rolling contracts that buyers can adjust monthly rather than seasonally
- Price adjustment clauses that activate automatically when trade conditions shift
- Option-style agreements that give buyers escape hatches without firm commitments
- Risk-tiered payment structures that fluctuate with political temperature
Bottom line? Supply certainty now trumps rock-bottom pricing. If you can guarantee delivery when the diplomatic weather turns nasty, buyers will pay handsomely for that insurance.
Decoding the Import Data Tea Leaves
China’s buying patterns reveal its master plan, and understanding it matters because these ripple effects also impact domestic markets. You’ve got falling production while farmgate prices crater, yet they’re doubling down on self-sufficiency. Seems backwards until you realize their endgame isn’t maximizing every gallon—it’s owning the consumer narrative while keeping industrial lifelines they can’t easily replace.
This creates genuine opportunities if you can read between the lines. Many exporters are pivoting heavily toward industrial ingredients, such as feed-grade whey, lactose, and protein isolates. These products typically dodge political crossfire and show steadier demand patterns than consumer brands caught in the culture wars.
For most family dairies, you’re not cutting deals with Beijing directly. But grasping these dynamics helps you evaluate your cooperative’s chess moves and ask the right questions about where your milk premiums really come from. When major export channels get choked off, that milk needs somewhere to go, and it usually lands in regional markets at prices you feel.
The milk powder market tells the flip side of this story. Ever.Ag analysis shows skim milk powder imports crashed to an 11-month low at 21.8 million pounds in August—down 39% from last year. This tracks with USDA forecasts as China builds domestic capacity to strangle consumer product imports. For U.S. producers, that means excess powder that used to flow east needs new homes, creating pricing pressure from California to Vermont.
The New Geography of Dairy Power
What’s crystallizing—and the data’s still developing—is a complete redraw of the dairy trade map. The old model, based on production costs and shipping rates, has been replaced by something that resembles geopolitical chess more closely.
You’re seeing the emergence of what might be called preferred suppliers versus spot market survivors. Preferred suppliers build fortress-like relationships for essential industrial ingredients. New Zealand, with its FTA armor, select Canadian operations, and some U.S. cooperatives with the right infrastructure, earns this status. They command premium pricing and steady volumes even when diplomatic storms rage.
Everyone else is relegated to spot markets that surge and crash with the flow of political headlines. U.S. whey shipments exploded 31.1% in August, but that could evaporate overnight if negotiations derail.
This forces brutal choices for cooperatives and larger operations. Either invest heavily in the infrastructure and relationships necessary for preferred supplier status, or accept the rollercoaster ride that comes with opportunistic trading.
Even smaller operations focused on domestic markets can’t ignore these shifts. When export channels slam shut, that milk floods back into regional markets, affecting pricing and cooperative strategies across the board. Northeast operations, for instance, are finding that disrupted export flows from larger processors can create unexpected opportunities in regional specialty markets, but also pricing volatility they hadn’t planned for.
Technology as the Great Leveler
Here’s the silver lining for smaller players: technology and transparency can help narrow the gap. Digital platforms that provide real-time supply chain visibility, inventory tracking, and bulletproof quality documentation help build trust with buyers, thereby managing political risk.
Some forward-thinking operations now offer enhanced traceability using blockchain verification—not just for exports, but also for domestic premium markets. Others have built systems giving buyers instant access to shipment tracking and quality data when their primary channels face disruption.
One development that has caught my attention is that several regional cooperatives are pooling resources to create shared digital documentation systems. Instead of each co-op burning cash on expensive individual platforms, they’re creating shared systems that deliver the transparency buyers demand at a fraction of the cost. A group of Northeast cooperatives recently launched this approach, and early reports suggest it’s opening doors to specialty contracts they couldn’t access before.
Technology investments vary wildly depending on scale and ambition. But producers across different regions tell me better documentation systems help with everything from organic certification to regional branding, not just export markets.
Different Operations, Different Survival Strategies
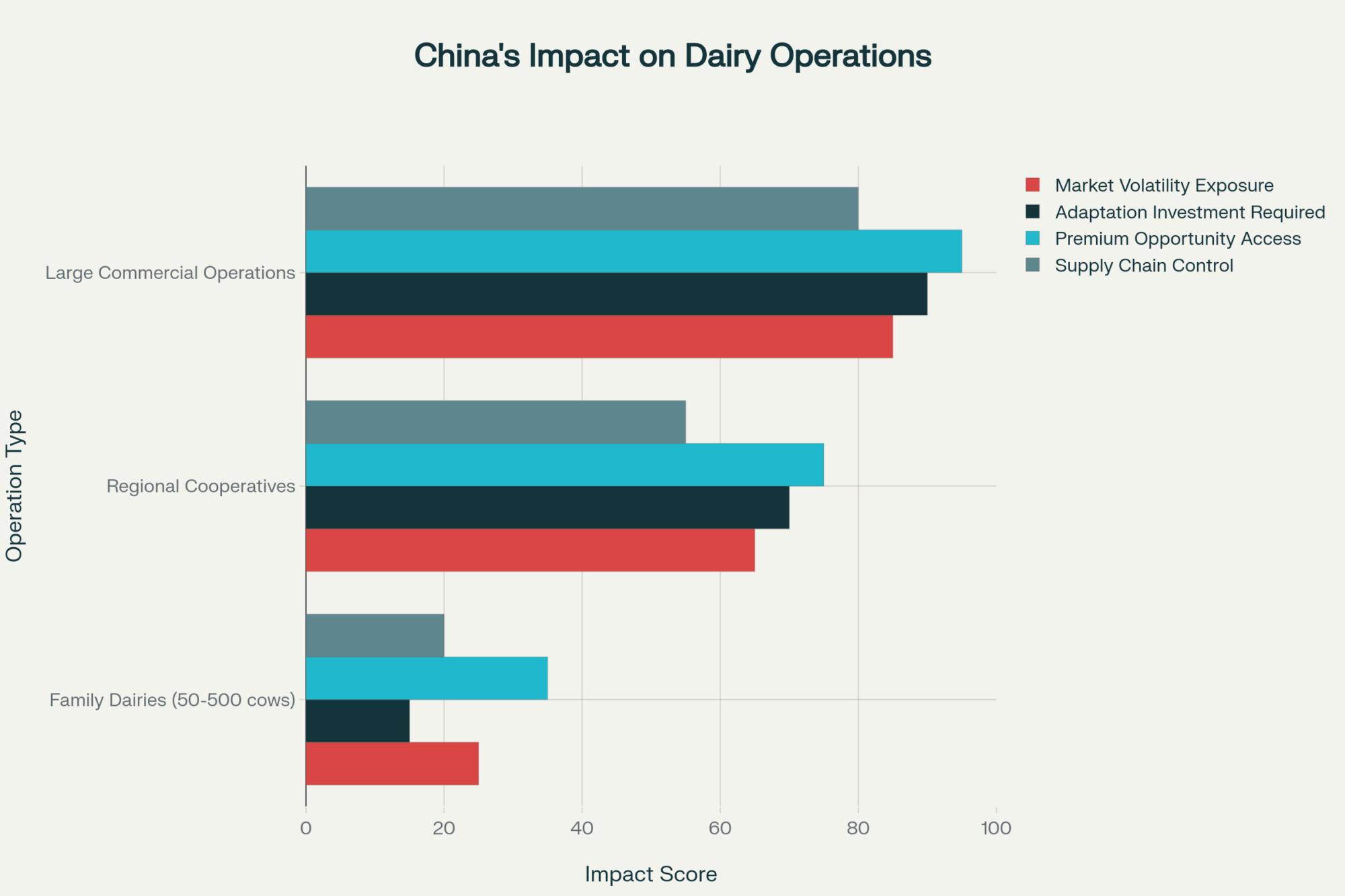
These seismic shifts hit different dairy operations in unique ways:
For family dairies (50-500 cows): You probably aren’t cutting export deals directly, but understanding these currents helps you evaluate your cooperative’s strategic positioning. When co-op leadership talks about export market development, you’ll know what hard questions to ask about infrastructure investments and political risk management.
For regional cooperatives, these changes highlight the critical importance of processing agility and market diversification. The ability to pivot between consumer products and industrial ingredients becomes a survival skill when export channels face political headwinds. The cooperatives weathering this storm best seem to be those that can dance between markets when one door slams shut but another cracks open.
For larger commercial operations, direct export opportunities exist, but they require significant infrastructure investment and sophisticated risk management. The fundamental question becomes whether you want to build those capabilities or double down on domestic market strength where you control more variables.
Early signals suggest that operations with bulletproof domestic market positions—through organic premiums, regional branding, or lean cost structures—may weather export market volatility better than those reliant on commodity export pricing.
Seasonal Rhythms and Market Timing
These trade dynamics interact with our production cycles in ways that amplify their impact. When export markets get strangled during flush season, the pricing pain cuts deeper than during lower production periods. Spring 2025 was particularly brutal when trade tensions peaked just as production ramped up across most regions.
Regional timing differences matter more than ever. California’s steadier year-round flow doesn’t face the same vulnerability to flush season as Wisconsin operations, where peak production typically occurs from April through June. Vermont and other northeastern states often peak later, from May through July, while some southern operations surge earlier. These regional patterns affect how export market disruptions ripple through local pricing.
The August whey surge hit during the sweet spot when many operations plan fall feeding programs and evaluate protein ingredient needs for the coming year. That timing likely amplified the volume response once buyers could reaccess U.S. products.
The Bottom Line
China’s whey surge isn’t just about seasonal recovery—it’s a preview of how agricultural trade has evolved into a landscape where political alliances and supply guarantees often outweigh traditional cost advantages. The old dairy trade model—built on seasonal patterns, cost advantages, and handshake relationships—has evolved into something where political awareness and supply chain agility separate winners from losers.
Those who recognize this shift and adapt accordingly will find tomorrow’s opportunities. Those waiting for yesterday’s patterns to return may find themselves managing more volatility than they bargained for. This season’s whey market performance offers a crystal ball into this transformed landscape—the key question each of us must answer is which changes actually affect our specific operation, and which ones we can safely ignore while focusing on what we do best.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Processing flexibility pays premiums: Operations that can pivot between consumer products and industrial ingredients are commanding 15-25% higher margins during trade disruptions, as buyers prioritize supply certainty over rock-bottom pricing.
- Infrastructure investment separates winners from survivors: Cooperatives building shared digital documentation systems and multi-origin blending capabilities are accessing specialty contracts worth $0.50-$1.20 per hundredweight above commodity rates while reducing political risk exposure.
- Regional market diversification protects against export volatility: Dairy operations with strong domestic positions, achieved through organic premiums or regional branding, weather export market swings 40% better than those dependent on commodity export pricing.
- Technology levels the playing field for smaller players: Shared blockchain traceability systems among regional cooperatives are opening doors to premium markets that were previously accessible only to large-scale exporters, while providing the transparency that buyers now demand.
- Political awareness becomes essential business intelligence: Understanding diplomatic developments alongside traditional market fundamentals is helping progressive operations time contract negotiations and inventory decisions to capture opportunities when political windows open.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Why This Dairy Market Correction Feels Different – and What It Means for Our Farms – This strategic analysis reveals that the current dairy market correction is unlike previous cycles, driven by a global confluence of factors like surging New Zealand production and plummeting Chinese imports. It provides essential context on why commodity prices are so volatile and offers insights on diversification to survive this extended period of pressure.
- The $8 Billion Infrastructure Trap: Why America’s Dairy Boom Could Become Its Biggest Bust – This article directly addresses the processing flexibility challenge raised in the main piece, arguing that the U.S. dairy industry’s massive infrastructure investment is a risky bet. It provides a tactical checklist for producers to evaluate their own exposure and prepare for a potential oversupply crisis.
- Tech Reality Check: The Farm Technologies That Delivered ROI in 2024 (And Those That Failed) – This piece complements the discussion on technology as a leveler by providing a practical, data-driven look at which farm technologies are delivering real returns. It helps progressive producers justify investments in adaptable systems by highlighting which innovations are genuinely reducing costs and which are falling short on their promises.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!





