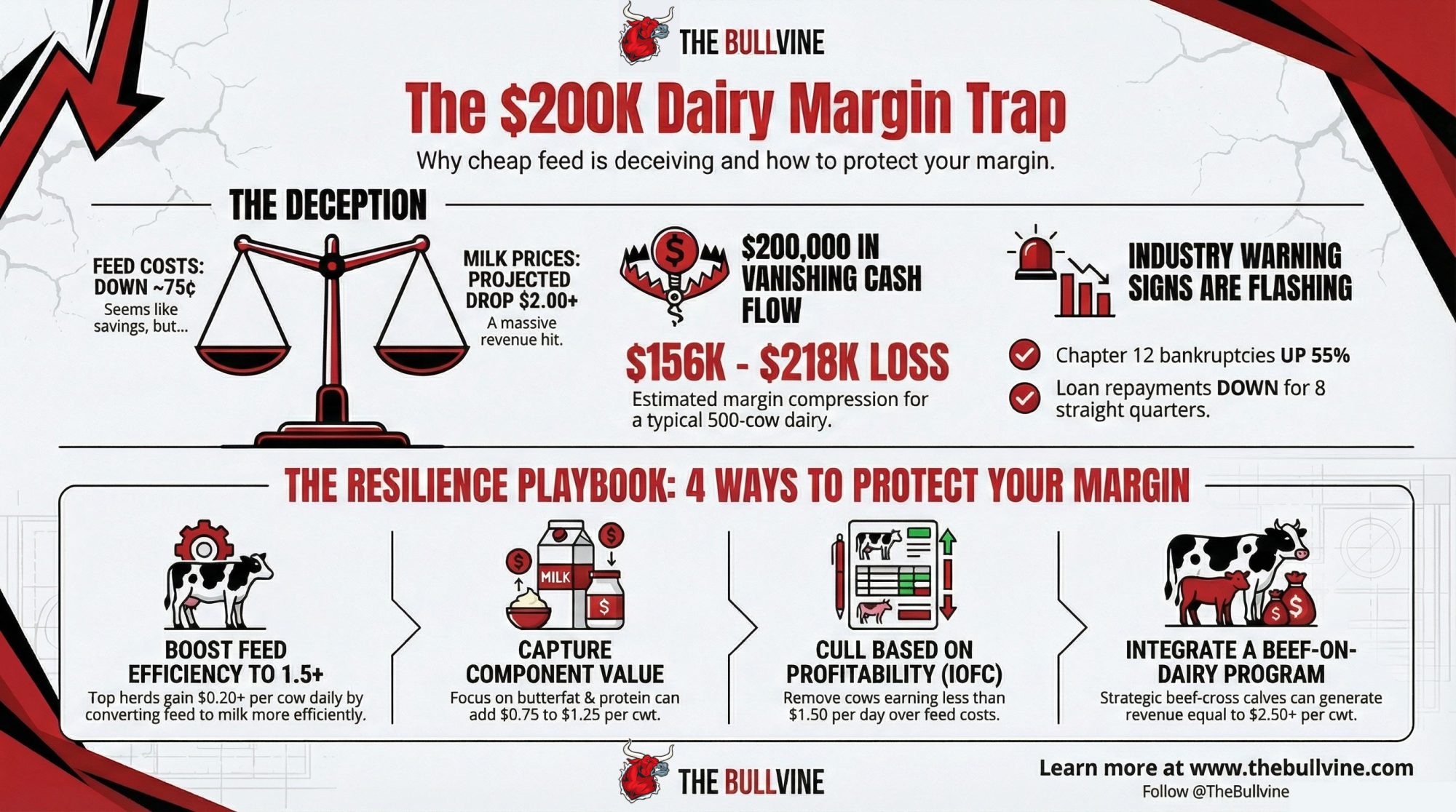
Feed dropped 75¢. Milk dropped $2. That’s not savings—that’s a $200K trap.

EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Everyone’s celebrating cheap corn—but the math tells a different story. USDA projects 2026 milk at $19.25/cwt while feed costs have dropped only modestly, creating net margin compression of $1.25-1.75/cwt—that’s $156,000 to $218,000 in lost cash flow for a 500-cow dairy. New Zealand’s lowest-cost producers see what’s coming: they paid down $1.7 billion in debt this year rather than expand. Top U.S. operators are responding with feed efficiency gains, component optimization, IOFC-based culling, and beef-on-dairy programs that can protect $1.50+ per cow daily. With Chapter 12 bankruptcies up 55% and ag lenders reporting eight straight quarters of declining repayment rates, the window for strategic positioning is narrowing. The question isn’t whether margins compress in 2026—it’s whether you’ll position your operation before they do.
You know that feeling when everything looks fine on paper, but something in your gut says otherwise?
It’s the kind of conversation happening at kitchen tables across dairy country right now. The milk check looks okay—maybe even decent by recent standards. Feed costs have come down. The cows are milking well.
And yet something feels off.
That instinct isn’t wrong.
The FAO has been tracking global food prices for decades, and its November numbers tell an interesting story. The overall Food Price Index has dropped for three consecutive months, and the dairy sub-index has declined for five straight months.
New Zealand just posted a 17.8% production surge in their early season, according to their Dairy Companies Association data. U.S. milk output keeps climbing, too.

What’s worth understanding—and this is something many of us tend to underestimate—is the timeline between when these global signals show up and when they hit our milk checks.
Generally speaking, we’re looking at about six to eight months.
So the softening that started this fall? It’s likely showing up in Q2 and Q3 2026 checks.
Mark Stephenson, who spent years as Director of Dairy Policy Analysis at the University of Wisconsin-Madison before his recent retirement, studied these price transmission patterns extensively throughout his career. His research documented this lag across multiple market cycles.
The movement in international powder and butter prices isn’t really a question of whether it affects domestic markets—it’s more about when and how much.
USDA’s November World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates projects the all-milk price at $19.25 per hundredweight for 2026. That’s a meaningful change from the $22-24 range that many operations built their budgets around during stronger periods.
So what are the producers who’ve navigated these cycles before actually doing about it?
The Feed Cost Conversation That’s Missing Something
Walk into any farm supply store or dairy meeting right now, and you’ll hear some version of the same reassurance: “At least feed costs are down.”
And that’s true.
Corn is trading around $4.37 per bushel on the Chicago Board of Trade as of early December. Soybean meal is running around $310-$315 per ton. The DMC feed cost calculation is in a favorable territory compared to recent years—no question about that.
But here’s what that conversation often leaves out.

When milk prices were $22.75, and feed costs were about $11.00 per hundredweight, producers captured roughly $11.75 in income over feed costs.
Run the same math with 2026 projections—$19.25 milk and lower feed costs—and that margin still compresses to around $9.00.
Feed improved by maybe seventy-five cents. Milk dropped by more than two dollars.
The net effect is still a $1.25 to $1.75 per hundredweight margin compression for most operations.

On a 500-cow dairy producing 125,000 hundredweight annually, that’s $156,000 to $218,000 in reduced cash flow. Real money that has to come from somewhere—whether that’s reduced family living, deferred maintenance, or tighter input decisions.
Michael Dykes, who leads the International Dairy Foods Association as their President and CEO, put it well in a recent industry briefing. Lower feed costs are helpful, no question, but they’re best understood as breathing room to make strategic moves—not as a solution to margin pressure.
I recently spoke with an Upper Midwest nutritionist who put it more directly:
“I’ve got producers telling me they’re holding off on decisions because corn is cheap. That’s exactly backwards. Cheap corn is the opportunity to lock in favorable feed contracts and build some cushion—not permission to wait and see what happens.”
The timing matters here.
Producers who lock in Q1 and Q2 2026 feed contracts now, while basis levels remain favorable, capture that advantage regardless of what happens to spot markets later. Those who wait may find the window has closed.
It’s worth running the numbers with your feed supplier at a minimum.
What’s Actually Happening in Export Markets
The China situation deserves more attention than it typically gets in domestic dairy discussions, even for producers who don’t think of themselves as export-dependent.
Why does this matter to all of us? The economics tell the story.
The current reality is pretty stark.
U.S. dairy products face total tariffs of 84 to 125 percent in China following the trade escalation that peaked in April 2025—China’s Ministry of Finance and Reuters covered this extensively at the time.
New Zealand, by contrast, completed their Free Trade Agreement phase-in on January 1, 2024, and now ships dairy to China at zero percent tariff.
The market share shift has been significant.
While exact percentages shift quarter to quarter, the direction is clear: New Zealand has captured the lion’s share of China’s powder imports while U.S. product faces what amounts to a prohibitive tariff wall.
That displaced volume didn’t disappear—it backed up into domestic markets.
Even producers selling exclusively to domestic processors feel this effect, as Mary Ledman at Rabobank has pointed out in her global dairy market analysis. She’s been tracking these patterns as their Global Dairy Strategist for years now.
When export channels close, that milk has to go somewhere. It adds supply pressure that affects everyone, even if indirectly.
The regional effects aren’t uniform, though.
California and Idaho operations—traditionally more export-oriented through Pacific Rim trade—feel this more acutely than Upper Midwest producers whose milk flows primarily into domestic cheese markets.
I spoke with a Wisconsin cheesemaker recently who said his plant’s order book looks fine through mid-2026, but he’s watching West Coast capacity closely because displaced milk eventually tends to find its way east.
What’s particularly noteworthy is how New Zealand producers are responding to their advantageous position.
Despite favorable prices and strong production conditions, Kiwi farmers repaid NZ$1.7 billion in debt in the six months through March 2025 rather than expanding. ANZ Bank and New Zealand’s rural news outlets have been tracking this closely.
When the world’s lowest-cost producers choose balance sheet repair over growth during historically good times… well, it suggests they’re preparing for extended market softness.
That’s a signal worth paying attention to.
Reading the Financial Signals
Several data points help distinguish what’s happening now from typical cyclical patterns.

Chapter 12 farm bankruptcy filings—the specialized bankruptcy provision for family farmers—hit 216 cases in 2024, up 55 percent from the prior year. The American Farm Bureau Federation has been tracking federal court records on this, and the first half of 2025 saw additional filings running well ahead of 2024’s pace.
Context matters here. Bankruptcy filings alone don’t tell the whole story—they can reflect access to legal resources, regional legal practices, and individual circumstances as much as broad economic conditions.
But the trend is notable.
Geographic patterns show particular stress in California, Iowa, Michigan, Kansas, and Wisconsin—a mix of traditional dairy regions and areas affected by specific challenges, such as avian influenza and water constraints.
Debt service coverage ratios tell a related story.
Farm Progress recently reported on data from the Minnesota FINBIN farm financial database showing that the average producer had a concerning coverage ratio of around 85 percent in 2024—meaning operations were generating only 85 cents for every dollar of debt service obligation.
The remaining gap has to come from equity drawdown, off-farm income, or loan restructuring.
What concerns many lenders is the compounding effect.
Interest costs have roughly doubled over the past three years as rates have reset. An operation that was comfortable at 3.5 percent interest faces a completely different equation at 7.5 percent—as many of us have experienced firsthand.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago’s Q3 2025 agricultural credit survey found 38 percent of banks reporting lower repayment rates—the eighth consecutive quarter of deterioration. More than two-thirds of lenders expect farmland values to flatten or decline in 2026.
None of this predicts any individual operation’s future—every farm has its own circumstances, strengths, and challenges.
But it does suggest the industry overall is experiencing stress levels that reward careful financial planning over optimistic assumptions.
The Expansion Paradox
One of the more counterintuitive aspects of current markets—and something I find genuinely interesting to think through—is why production keeps growing despite weakening price signals.
The biological reality is that dairy expansion decisions made two to three years ago are just now showing up in production numbers.
Heifers conceived in early 2023 are entering milking strings in late 2025. Facilities that broke ground during strong margins in 2023 and 2024 are now completing and being populated.
Once those commitments are made—once the cows are bred, raised, and the facilities built—the production is essentially locked in.
Debt service creates similar momentum.
Operations carrying expansion loans need to maintain production to meet their obligations. Reducing herd size often costs more than continuing to milk at marginal profitability, especially when the alternative is triggering loan covenant violations.
Christopher Wolf, the E.V. Baker Professor of Agricultural Economics at Cornell, has written thoughtfully about this dynamic. The economics of stopping are often worse than the economics of continuing.
That’s not irrational behavior—it’s responding logically to the debt structure and fixed-cost reality that exist in most operations.
Processing capacity investment adds another layer.
More than $11 billion in new U.S. dairy processing capacity is under construction or recently completed—IDFA released a detailed report in October covering 50-plus projects across 19 states.
That processing investment creates a regional demand pull that can support local expansion even when broader markets are oversupplied. A producer within hauling distance of a new plant in Dodge City or along the I-29 corridor faces different economics than one in a region without recent processing investment.
I’ve been hearing about this regional divide increasingly this season.
In Texas and New Mexico, where several major cheese and powder facilities have opened or expanded, local producers report being actively recruited with multi-year contracts.
Meanwhile, some Northeast producers describe tighter relationships with their cooperatives—fewer premium opportunities and more pressure on base pricing.
Same industry, very different regional realities.
What Successful Producers Are Doing Differently
Conversations with producers navigating current conditions successfully reveal consistent patterns. These aren’t revolutionary changes requiring massive capital—they’re an intensified focus on fundamentals.
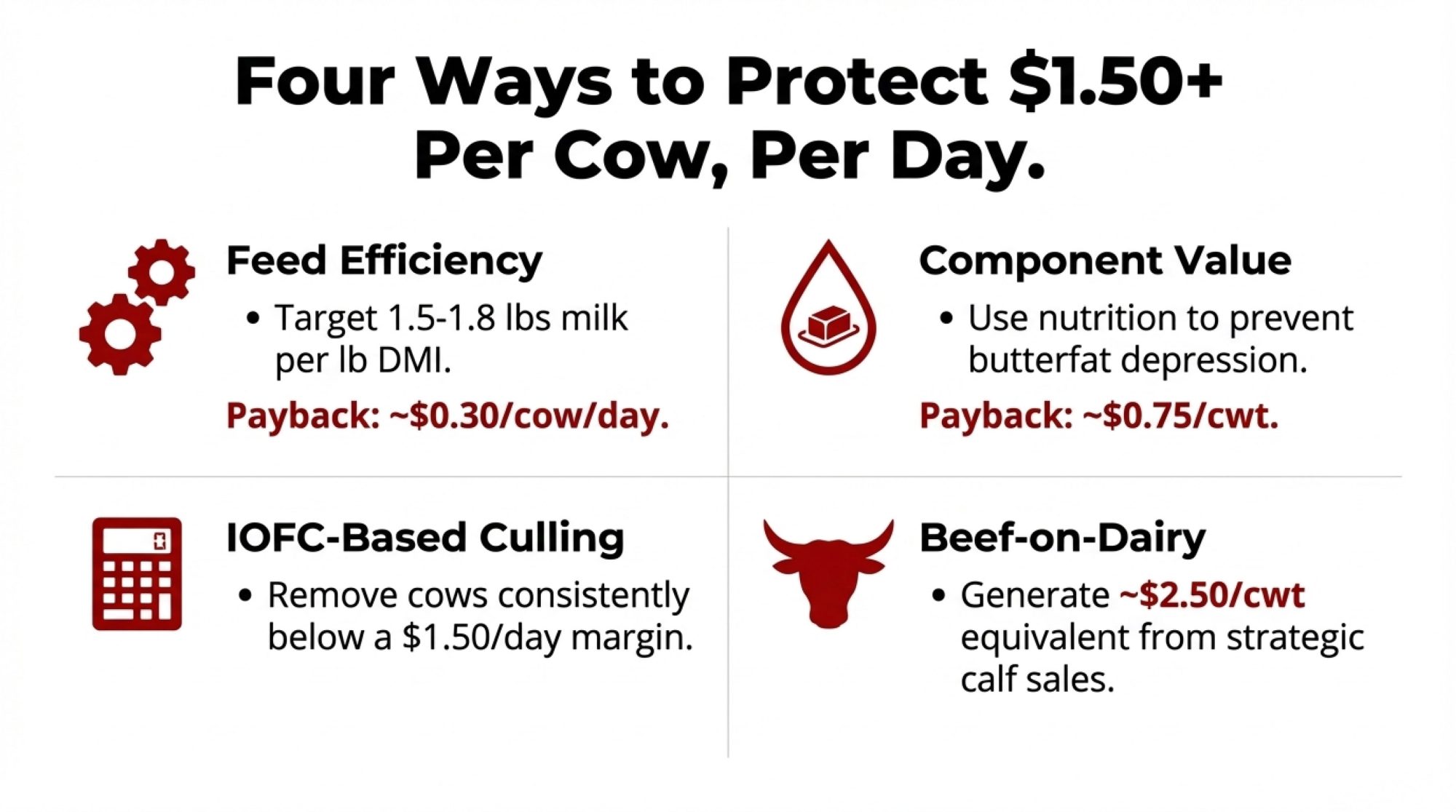
1. Feed Efficiency Optimization
Top-performing herds are achieving feed efficiency ratios of 1.5 to 1.8 pounds of milk per pound of dry matter intake. The industry average sits around 1.4.
The Impact: Each tenth of a point improvement translates to roughly $0.20 to $0.30 per cow/day in margin enhancement.
The Tactic: Weekly NIR analysis on forages (~$15/sample) allows for immediate ration adjustments, rather than guessing between monthly tests.
I recently spoke with a Wisconsin producer who started as a custom heifer raiser before transitioning to his own milking herd. He described implementing weekly NIR testing on every forage load.
“The payback is maybe ten to one in ration accuracy,” he said. “We were basically guessing before.”
Most producers I’ve talked with see measurable results within 45 to 60 days—though individual results vary based on starting point and forage variability.
2. Component Value Capture
Producers focusing on butterfat performance and protein levels report capturing an additional $0.75 to $1.25 per hundredweight compared to volume-focused approaches.
The Tactic: Using rumen-protected choline during transition periods and summer heat stress (~$0.08/cow/day) to prevent butterfat depression.
The genetic piece is a longer-term play—daughters of high-component sires won’t hit the milking string for two-plus years—but the nutritional interventions can show results within a milk test cycle or two.
Worth having a conversation with your nutritionist about current ration fatty acid profiles and where component optimization opportunities might exist for your herd.
3. Strategic Culling Based on IOFC
Rather than culling primarily based on age, reproduction metrics, or production levels, progressive operations calculate income over feed cost for each cow and move out animals that are consistently below $1.50 per cow daily.
The Shift: “A seven-year-old cow giving 60 pounds might look fine on paper,” one herd manager at a 1,200-cow Minnesota dairy told me. “But when you run her actual IOFC with her feed intake and health costs, she’s sometimes underwater. We’re making decisions on math now, not sentiment.”
For operations without individual cow feed intake data (which is most of us), pen-level IOFC calculations still identify which groups are carrying the herd versus dragging it down.
Most herd management software can generate these reports with minimal setup.
4. Beef-on-Dairy Integration
Producers systematically breeding bottom-tier genetics to beef sires report equivalent revenue of $2.50+ per hundredweight from crossbred calf sales.
The Math: A straight Holstein bull calf might bring $150. A beef-cross brings $1,000 or more based on current USDA feeder cattle reports.
The Genetics Play: Use genomic testing or breeding values to identify the bottom 20-30% of your herd’s genetic merit. Breed those animals to proven beef sires with good calving ease scores, and establish buyer relationships before calves hit the ground.
This is where your genomic data becomes a direct revenue driver—not just a breeding tool.
Operations that treat beef-on-dairy as an afterthought leave money on the table compared to those who plan the program strategically.
The Emerging Structure: Two Viable Paths
Looking at where the industry appears headed over the next three to five years, a structural pattern is emerging that’s worth understanding—even if it raises uncomfortable questions.
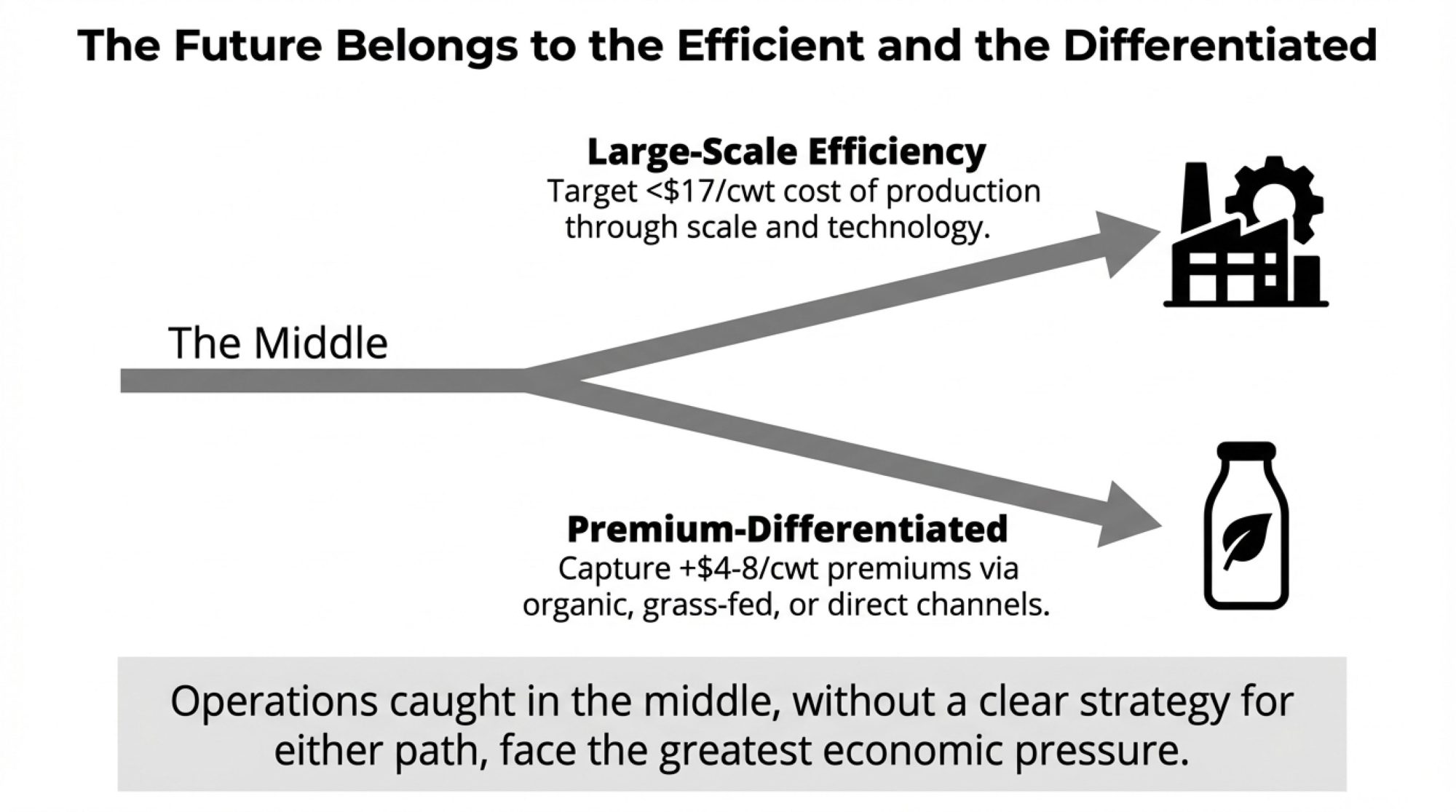
The data increasingly suggests two economically viable models:
Large-scale efficiency operations—generally 1,500 cows and above—achieving production costs in the $14 to $17 per hundredweight range through scale economics, technology adoption, and processing relationships.
USDA’s Economic Research Service cost-of-production data confirms that this scale advantage has widened over the past decade. Many of these operations use dry-lot systems or hybrid facilities to maximize throughput efficiency.
Premium-differentiated operations—typically 50 to 500 cows—capturing $4 to $8 per hundredweight premiums through organic certification, grass-fed positioning, or direct-to-consumer channels.
These require proximity to metro markets and significant transition investment, but create a margin cushion independent of commodity prices.
Operations in the middle face the most challenging economics under the current market structure.
This isn’t a judgment about the value of family-scale dairy farming or the communities these farms anchor. It’s an observation about where the current market structure creates clearer paths forward.
Regional variation matters significantly.
A 300-cow dairy in Vermont with Boston market access faces different options than a similar-sized operation in central Wisconsin without nearby premium channels.
A Framework for Evaluation
For producers working through these questions—and most of us are—several considerations help clarify the path forward.
For operations considering expansion:
- Is there processing capacity within 200-300 miles actively seeking suppliers?
- Is replacement heifer availability realistic? National inventory sits at roughly 3.9 million dairy replacement heifers 500 pounds and over—the lowest absolute level since 1978, according to USDA’s January 2025 Cattle report. The heifer-to-cow ratio of 41.9% is the lowest since 1991.
- Can production costs realistically reach sub-$17 per hundredweight at expanded scale?
- What do debt service requirements look like at current interest rates, not 2021 rates?
For operations considering premium positioning:
- Is there a metro market within a reasonable distance with demonstrated premium demand?
- What’s the realistic timeline? Organic certification alone typically takes three years under USDA National Organic Program rules.
- Does the land base and climate support pasture-based systems?
- Is there family interest in direct marketing relationships?
For operations evaluating the current position:
- What’s the actual debt service coverage ratio at projected 2026 milk prices?
- When do loans mature, and at what interest rate reset?
- Has the processor offered multi-year supply contracts?
- What’s the true breakeven with full cost accounting—including family labor and reasonable return on equity?
These aren’t comfortable questions.
But they’re better asked now than answered by circumstances later.
The Timing Reality
One thread runs through conversations with producers, lenders, and analysts who’ve navigated previous downturns: timing matters more than most people acknowledge.
Producers who assess their position and make strategic decisions during 2025 and early 2026—while milk prices are still serviceable, while cull cow prices remain historically strong—retain meaningfully more options than those who wait.

December through February: Run your real numbers. Calculate the actual DSCR at $19.25 milk. Have the honest conversation with your lender—most good lenders appreciate proactive communication.
This is also the window for DMC enrollment decisions. If you haven’t reviewed your coverage levels against projected margins, now’s the time. LGM-Dairy is worth a conversation with your insurance agent, too, especially for operations wanting more flexible coverage options.
February through April: Make feed decisions. Lock contracts if the math works. Implement efficiency improvements that deliver results by summer.
Spring 2026: Evaluate first-quarter performance against projections. Adjust culling strategy based on actual margins. Make the bigger strategic calls with real data rather than hope.
The Bottom Line
The dairy industry has navigated challenging transitions before, and it will again.
The producers who came through previous cycles strongest were generally those who saw conditions clearly, made decisions based on their specific circumstances, and acted while they still had choices.
That window is open now.
The question is what each of us does with it.
The Bullvine provides market analysis and industry perspective for dairy producers worldwide. This article reflects conditions and data available as of early December 2025. Individuals should consult their own financial advisors, lenders, and Extension specialists when making significant business decisions. Every farm’s situation is unique, and the right path forward depends on factors only you and your advisors can fully evaluate.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- The Trap: Feed dropped 75¢. Milk dropped $2. That’s not savings—that’s $200K in vanishing cash flow for a 500-cow dairy.
- The Global Signal: NZ farmers paid down $1.7 billion in debt instead of expanding. The world’s lowest-cost producers expect extended softness.
- The Warning Signs: Chapter 12 bankruptcies up 55%. Ag loan repayments have been declining for 8 quarters straight. Financial stress is accelerating.
- What Top Producers Are Doing: Capturing $1.50+/cow/day through feed efficiency, component optimization, IOFC-based culling, and beef-on-dairy integration.
- The Window Is Now: Cull values are strong. Milk checks are still serviceable. Lenders are still flexible. Make strategic decisions while you still have options.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- The $700 Truth: Your Best Milkers Are Your Worst Investment – Reveals why high-volume cows often lose $3/day in actual margin and demonstrates how to use Residual Feed Intake (RFI) data to identify the true profit-drivers in your herd.
- The $228,000 Exit Strategy Reshaping Dairy – Uncovers the “Section 1232” tax provision behind the recent surge in Chapter 12 filings, explaining how strategic bankruptcy is helping retiring producers preserve equity rather than losing it in traditional sales.
- Robot Revolution: Why Smart Dairy Farmers Are Winning – Analyzes the 2025 ROI of automated milking systems beyond simple labor savings, providing a blueprint for the “efficiency-at-scale” model that allows family operations to compete with larger consolidators.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.






 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!





