Your grandfather milked 50. You milk 500. China milks 500,000. This ends one of three ways.
Having spent the better part of two decades analyzing dairy production trends, I can tell you that what we’re witnessing today represents a fundamental shift in how milk is produced globally. The International Farm Comparison Network’s latest 2024 data reveals something remarkable: five of the world’s ten largest dairy operations are now Chinese-owned. Modern Dairy, for instance, manages nearly half a million cows across 47 farms—a scale that would have been unimaginable just a generation ago.
What’s particularly noteworthy is Almarai’s achievement in Saudi Arabia. They’re consistently hitting 14 tonnes of milk per cow annually in desert conditions where summer temperatures routinely exceed 50°C. That level of production in such challenging conditions offers valuable lessons for operations everywhere, from California’s Central Valley to the arid regions of Arizona and even parts of Texas experiencing increasing drought pressure.
This transformation comes at a time when mid-sized dairy operations across North America are evaluating their strategic options. The conversations happening at farm meetings and extension workshops reflect genuine uncertainty about the path forward. Should an 800-cow operation expand to 2,500? Can family farms find sustainable niches in this changing landscape? These aren’t abstract questions—they’re daily realities for thousands of producers.
The Geographic Realignment of Global Dairy Production
Looking at this trend, what strikes me most is how quickly the center of gravity has shifted eastward. The 2024 data from IFCN paints a clear picture: China’s five largest operations—Modern Dairy with 472,480 cows, China Shengmu with 256,650, Yili Youran with 246,000, and Huishan with 200,000—represent impressive numbers. They reflect a deliberate national strategy.
Dr. Jiaqi Wang at the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences provides important context here. Following the 2008 melamine incident that affected hundreds of thousands of infants, Chinese dairy companies fundamentally restructured their approach to prioritize supply chain control. This builds on what we’ve seen in other industries where food safety crises prompted systemic changes.
| Metric | China Elite | China Avg | US Midwest | US Mega |
| Herd Size | 472k (Modern) | 8k-15k | 1k-5k | 10k-30k |
| Yield/Cow (t) | 9.5-12.0 | 9.6 | 11.0-13.0 | 11.8-13.4 |
| Feed Conv Ratio | 1.4:1 | 1.6:1 | 1.5:1 | 1.4:1 |
| Self-Suffic | 85% (170%) | 73% | 100% | 100% |
| Tech Invest Lvl | Very High | High | Moderate | Very High |
China’s agricultural policy documents outline ambitious targets: achieving 70% milk self-sufficiency by 2030, with intermediate goals potentially pushing toward 75-85% over time. They’re also targeting annual yields exceeding 10 tonnes per cow—a significant leap from current averages. This aligns with their broader strategy of reducing import dependence across agricultural commodities.
Why does this matter for North American and European producers? Well, the USDA Foreign Agricultural Service reports that China’s dairy imports have exceeded $10 billion annually in recent years. As Rabobank’s 2024 quarterly analysis shows, China added 11 million metric tons of production between 2018 and 2023, already displacing approximately 240,000 tonnes of whole milk powder imports. For regions that have counted on Chinese demand as a growth driver—particularly New Zealand and Australia—this represents a significant market shift requiring strategic recalibration.
Understanding Productivity Variations Across Mega-Dairies

One of the most intriguing findings from analyzing global mega-dairy performance is the substantial productivity variation even among the largest operations. Consider the range based on 2024-2025 company data: Almarai achieves 14.00 tonnes per cow annually; Rockview Dairies in California produces 11.80 tonnes; Modern Dairy in China averages 9.53 tonnes; and Huishan manages 7.70 tonnes.
This 82% productivity gap between the highest and lowest performers—both operating at massive scale with significant capital resources—challenges assumptions that scale automatically drives efficiency. What accounts for these differences?
Anthony King, who oversees operations at Almarai’s Al Badiah facility, shared insights at the International Dairy Federation’s 2024 World Dairy Summit about their management approach. The attention to detail is extraordinary: maintaining barn temperatures at 21-23°C year-round despite extreme external heat, providing 300 liters of water per cow daily, and implementing precision feeding protocols that optimize every nutritional variable.
The USDA Economic Research Service’s comprehensive 2023 analyses (their most recent full report) support what many progressive producers have long suspected: management sophistication and technological integration matter more than scale alone. Well-managed 500-cow operations implementing advanced protocols often outperform poorly-managed facilities ten times their size.
In Idaho, a 600-cow dairy was achieving 13,000 kilograms per cow through exceptional management, while a nearby 5,000-cow facility struggled to reach 11,000 kilograms. The difference? Attention to transition cow management, consistent fresh cow protocols, and meticulous record-keeping at the smaller operation.
The Economics Driving Industry Consolidation
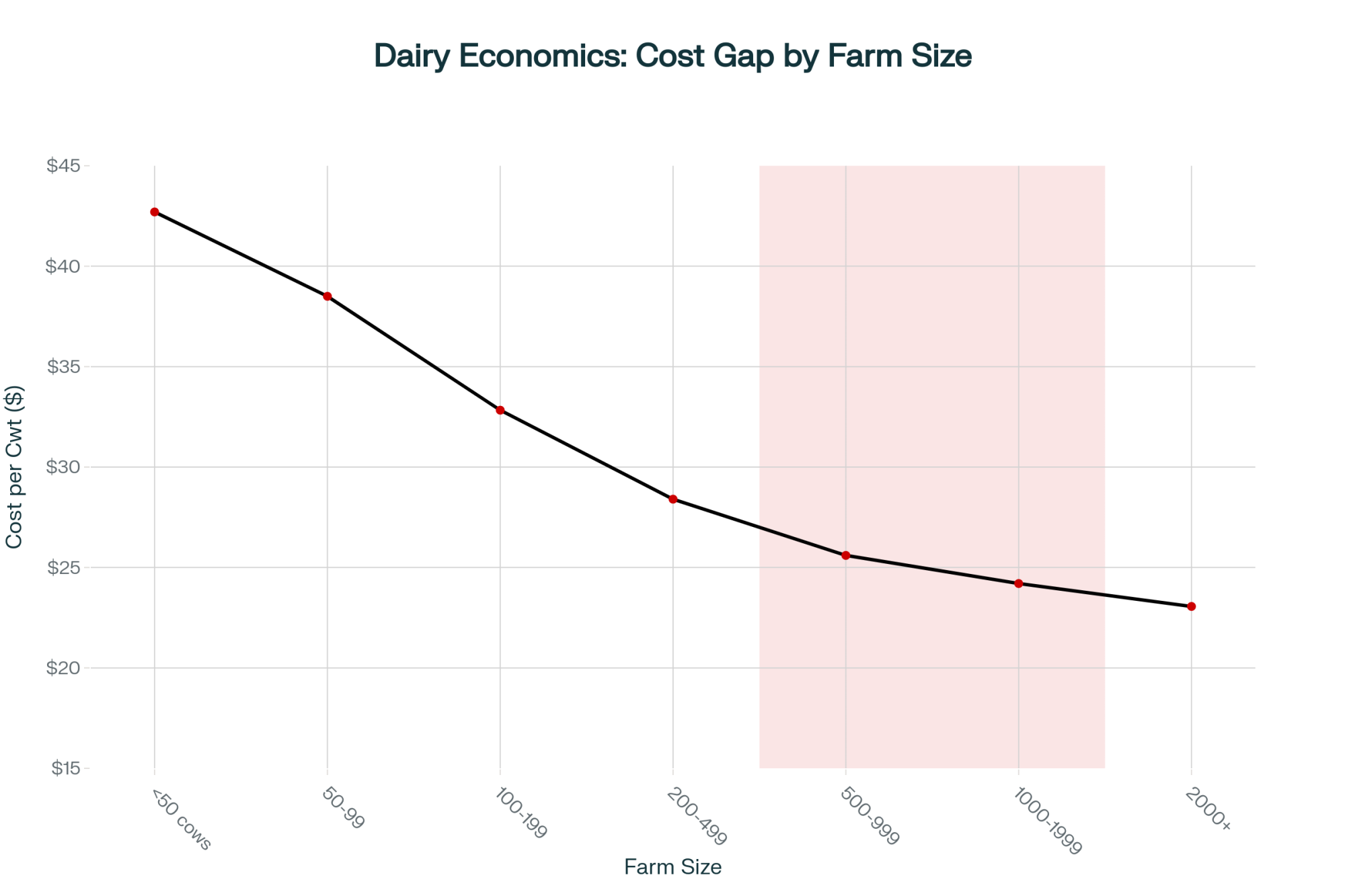
What farmers are finding is that consolidation isn’t really about wanting to get bigger—it’s about the relentless mathematics of fixed costs. USDA’s 2024 cost of production data reveals the economics clearly: operations with 2,000+ cows average $23.06 per hundredweight in total costs, while farms with 100-199 cows face costs of $32.83—a difference of $9.77 per hundredweight.
What’s revealing here is the breakdown. The University of Wisconsin’s Center for Dairy Profitability research, led by Dr. Mark Stephenson, indicates that feed cost differences account for only about $2.50 of that gap. The remaining differential? It stems from spreading fixed infrastructure investments across production volume.
As Dr. Stephenson articulated in his January 2024 market outlook presentation: when fixed costs exceed variable costs in a commodity market, smaller operations face structural disadvantages regardless of management quality. For a representative 1,000-cow Upper Midwest operation producing 23 million pounds annually, this translates to $690,000 to $920,000 in additional costs compared to larger competitors—often exceeding total profit margins.
This economic reality helps explain why we’re seeing continued consolidation despite many producers’ preference for maintaining traditional farm sizes. The economics are pushing the industry in one direction, even as community ties, lifestyle preferences, and succession-planning challenges pull it in another.
Technology Adoption: Promise and Complexity
This development suggests that technology alone won’t solve dairy’s challenges—it’s how that technology is managed that matters. Beijing SanYuan exemplifies what’s possible, achieving 11,500+ kg per cow annually—matching Israel’s national average—through systematic adoption of Israeli dairy management systems since 2001, according to their published operational data.
But here’s the challenge. Professor Li Shengli at China Agricultural University identifies a critical constraint in his 2024 research published in the Journal of Dairy Science China: human capital. Chinese Ministry of Human Resources data from 2024 indicates that only about 7% of the country’s 200 million skilled workers possess the high-level capabilities needed to manage complex dairy systems effectively.
This creates an interesting paradox we see globally. Operations with capital for advanced technology often lack the expertise to optimize it, while highly skilled managers at smaller operations can’t access these tools. I know a manager in Pennsylvania running 600 cows who could likely double productivity with access to advanced monitoring systems and automated feeding technology. Meanwhile, I’ve toured 5,000-cow facilities with million-dollar technology packages operating well below potential due to management constraints.
Environmental Management: Challenges and Opportunities
The environmental dimension presents both challenges and unexpected opportunities—and it’s more nuanced than many discussions suggest. EPA calculations show that a 2,000-cow operation generates approximately 87.6 million pounds of manure annually—that’s 240,000 pounds daily, which require sophisticated management.
The World Resources Institute’s 2024 analysis highlights how scale affects these choices. Larger operations typically implement liquid storage systems for operational efficiency, but these generate substantially more methane than the daily-spread approaches common on smaller farms. This creates environmental trade-offs worth considering.
What’s encouraging is that at sufficient scale—typically around 5,000+ cows based on current feasibility analyses—biogas digesters become economically viable. These systems, which require investments of $2-5 million, can generate 5 million cubic meters of biogas annually. Youran Dairy in China operates nine such facilities, each producing approximately this volume according to their 2024 sustainability reports.
These operations are transforming waste management from a cost center into revenue through electricity generation, fertilizer sales, and carbon credit programs. The capital requirements mean this solution remains out of reach for most mid-sized operations, though, creating another scale-dependent advantage.
It’s worth noting explicitly that while larger farms may achieve better emissions intensity per unit of milk produced, smaller farms often have lower absolute emissions overall—a nuance that deserves more attention in environmental policy discussions. A 200-cow grass-based operation in Vermont creates different environmental impacts than a 10,000-cow facility in New Mexico, even if the per-gallon metrics favor the larger operation.
Strategic Options for Mid-Sized Operations
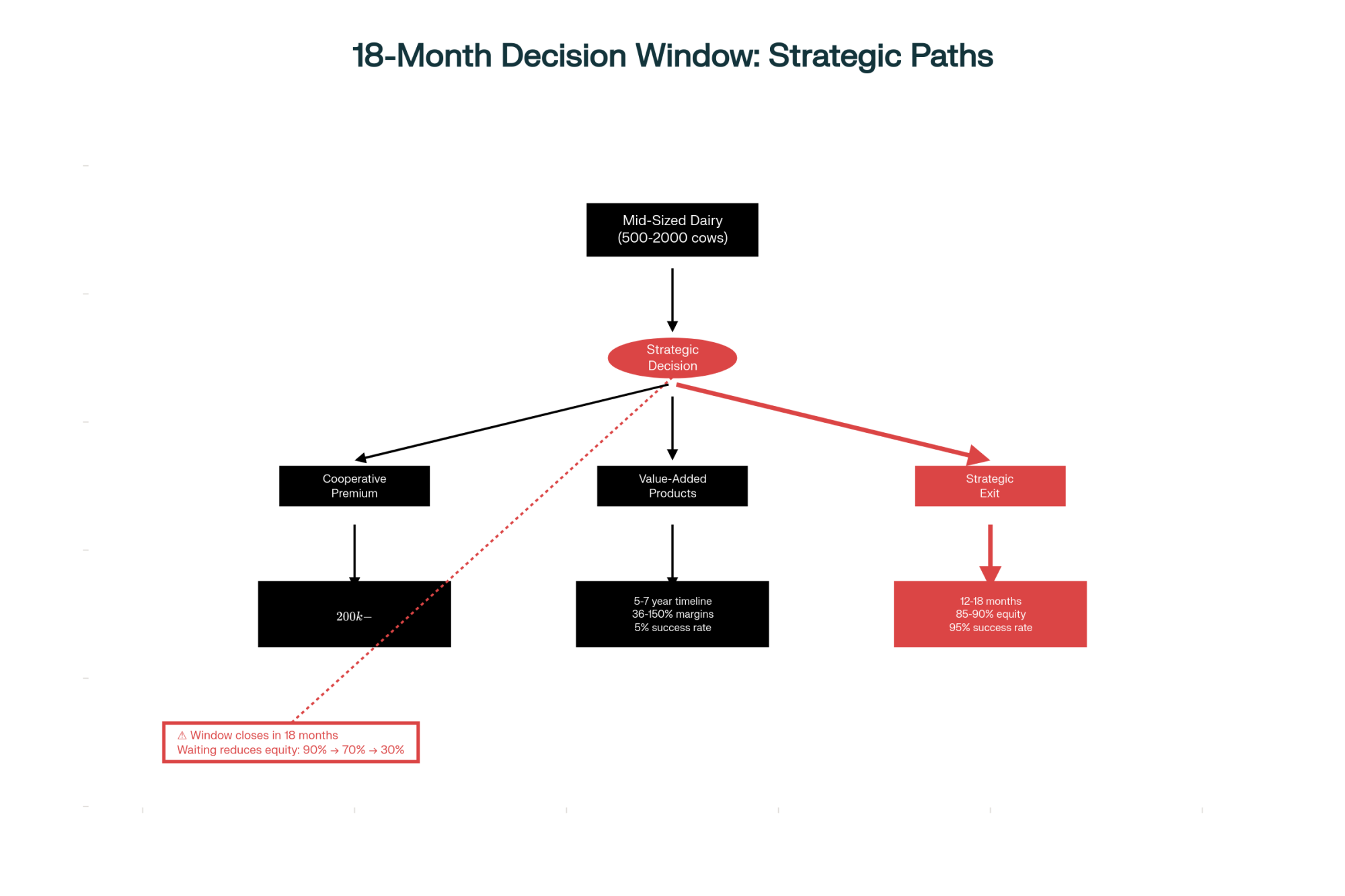
For the 500-2,000 cow operations that form the backbone of American dairy, three strategic paths show promise based on extension research and producer experiences:
Strategic Options for the Mid-Sized Dairy
| Path | Potential Benefit | Timeline / Requirement |
| Cooperative Premium | 8-12% price advantage ($200k-$300k/yr for 1,000 cows) | Requires strong co-op selection & management |
| Value-Added Path | 36-150% margin improvement (cheese, yogurt, direct sales) | 5-7 year development; high marketing & business skill |
| Strategic Exit | Preserve 85-90% of farm equity | Requires proactive timing before major losses |
Maximizing Cooperative Benefits
Cornell’s Dyson School research from 2023, led by agricultural economist Dr. Andrew Novakovic, demonstrates that well-managed cooperatives deliver 8-12% price premiums through collective bargaining compared to independent sales to investor-owned processors. For a 1,000-cow operation, this represents $200,000 to $300,000 in additional annual revenue.
The key lies in cooperative selection. Strong downstream market positioning and professional management make the difference. Cornell’s pricing analysis found some underperforming cooperatives actually paying 3.5% less than investor-owned processors, underscoring the importance of due diligence.
Value-Added Diversification
European research examining 265 dairy farm diversification efforts, published in the Agricultural Systems journal, found compelling margins: cheese production generated €0.688 per liter more than fluid milk, while yogurt generated €1.518 more. Direct sales improved margins by an average of 36%.
These numbers look attractive, but Ireland’s Nuffield scholarship research from Tom Dinneen provides important context: approximately 95% of dairy farmers lack the marketing and business skills needed for successful value-added transitions. The typical path to profitability takes 5-7 years—requiring substantial patience and capital reserves.
Strategic Transition Planning

Wisconsin Extension’s 2024 farm financial analyses, compiled by agricultural economist Dr. Paul Mitchell, reveal the importance of timing. Producers making strategic exit decisions while maintaining strong equity positions typically preserve 85-90% of their farm’s value. Waiting 12-18 months reduces this to 70-80%. Those forced to exit after several years of losses might retain only 20-30% of their equity.
Extension specialists share examples of successful transitions. One documented case from southern Wisconsin involved a producer with $850,000 in equity who transitioned strategically, preserving over $700,000 for retirement and new ventures. These aren’t failure stories—they’re examples of astute business management in changing markets.
The Precision Fermentation Revolution

While consolidation reshapes current production, precision fermentation represents a potentially transformative disruption. The Good Food Institute’s 2025 market analysis tracks growth from $5.02 billion currently toward projected valuations of $36.31 billion by 2030—representing 48.6% annual growth.
Companies like Perfect Day already produce commercial-scale whey and casein proteins identical to dairy-derived versions. Consumers are purchasing products containing these proteins—Brave Robot ice cream, California Performance Co. protein powders, and even Nestlé’s new plant-based cheese line using precision fermentation proteins—often without realizing the proteins come from fermentation rather than cows.
Investment tracking from PitchBook and Crunchbase shows over $840 million from major investors, including Bill Gates’ Breakthrough Energy Ventures, flowing into these technologies, with $50+ billion projected across the sector by 2030. Cost curves suggest price parity with conventional dairy proteins by 2027-2028, potentially capturing 25% of commodity protein markets by 2035.
This doesn’t spell immediate doom for traditional dairy, but when you’re planning infrastructure investments with 20-30 year depreciation schedules, these technology trends deserve serious evaluation. I’ve noticed that younger producers are particularly attuned to these disruption risks when making expansion decisions.
International Regulatory Pressures
European developments offer insights into potential regulatory futures—and they’re moving faster than many realize. The EU’s Farm to Fork Strategy targets 25% organic production by 2030, while nitrate directives and evolving welfare requirements fundamentally alter production economics.
The Netherlands allocated €25 billion for livestock farm buyouts near environmentally sensitive areas—a scale of intervention that would have seemed impossible just years ago. German regulations now require specific space allocations (6 square meters indoor plus 4.5 square meters outdoor per cow) for certain certifications, fundamentally changing the economics of the confinement system.
These aren’t just European issues. Similar discussions around environmental impact, animal welfare, and production intensity are emerging across North America. California’s evolving regulations often preview broader U.S. trends. Whether through regulation or market pressure, these factors will likely influence future production systems globally.
Envisioning 2035: A Transformed Industry
Based on IFCN projections, FAO’s 2024 agricultural outlook, and technology trends, the 2035 dairy landscape will likely differ dramatically from today. Current projections suggest that approximately 40% of global production will come from 300-500 industrial mega-dairies, concentrated in the U.S., China, and the Middle East. Another 35% would come from South Asian smallholders—primarily the millions of households in India and Pakistan that maintain 2-5 animals. Precision fermentation might capture 25% of commodity protein production, with less than 5% from premium niche operations serving specialty markets.
The “missing middle”—operations between 500-2,000 cows—faces the greatest pressure in this scenario, unable to achieve mega-dairy economies or premium market positioning. This isn’t predetermined, but current trends point strongly in this direction.
Practical Considerations for Today’s Decisions
Looking at all this data and these trends, what should producers consider?
For operations under 500 cows, differentiation becomes essential. Whether through premium market positioning, exceptional management within strong cooperatives, or direct marketing, competing in commodity markets against mega-dairies appears increasingly challenging. I’ve seen success with A2 milk premiums (30-50% price advantage), grass-fed certification (40-60% premiums), and local brand development—but each requires commitment beyond production alone.
Operations in the 500-2,000 cow range face time-sensitive decisions. The window for strategic transitions that preserve equity is narrowing—probably 12-18 months based on current market dynamics. Waiting for ideal conditions that may never materialize risks substantial equity erosion.
Those considering expansion should carefully evaluate whether achieving a 2,500+ cow scale is realistic given capital and management resources. Partial expansions that don’t achieve efficient scale often compound problems rather than solving them. I’ve watched too many 1,500-cow expansions create more debt without solving the fundamental economic problems.
Everyone should monitor precision fermentation developments. This technology will impact commodity markets within the decade, requiring strategic adaptation across the industry.
Key Takeaways
- The 82% productivity gap proves scale doesn’t guarantee success: Saudi Arabia’s desert dairies outperform China’s mega-farms—it’s management and technology integration, not cow count, that wins
- Mid-sized farms (500-2,000 cows) have three options, not four: Scale to 2,500+, find a $300K premium niche, or exit strategically—”staying the course” is slow-motion bankruptcy
- Your equity has an expiration date: Exit now, preserving 85%, wait 18 months for 70%, or lose 60-80% fighting the inevitable—the clock started when you opened this article
- Lab-grown milk isn’t a future threat—it’s a current reality: $840M invested, identical proteins in stores now, price parity by 2027—plan infrastructure accordingly
- Winners already chose their lane: 300 mega-dairies will dominate commodities, 2,000 niche farms will own premiums, everyone else disappears—which are you?
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY:
- China’s Modern Dairy runs 472,480 cows, while Silicon Valley grows identical milk proteins without cows—your 800-cow operation is caught between these extremes. Mid-sized farms (500-2,000 cows) now face $9.77/cwt cost disadvantages that excellent management cannot overcome, translating to nearly $1 million in annual structural penalties. Three proven escape routes remain: joining strong cooperatives for immediate 8-12% premiums, developing value-added products for 36-150% margin improvements, or executing strategic exits that preserve 85% of equity versus 20% after prolonged losses. With precision fermentation achieving price parity by 2027 and China eliminating import markets, the decision window has narrowed to 18 months. The industry will split into 300 mega-dairies, 2,000 premium niche operations, and precision fermentation facilities—the 15,000 farms in between will vanish.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Unlock Hidden Dairy Profits Through Lifetime Efficiency: How Modern Genetics and Strategic Nutrition Can Cut Feed Costs by $251 Per Cow – This tactical guide provides a direct alternative to scaling, showing how to generate $100,000+ in new margins by implementing precision nutrition and genetic strategies that transform cost centers into profit drivers.
- Global Dairy Market Dynamics: Navigating Volatility and Strategic Opportunities in 2025 – This market analysis provides the immediate economic context for the main article’s strategic threats, detailing current GDT volatility, new US pricing formulas, and European production shifts that producers must navigate right now.
- How AI is Banking Dairy Farmers an Extra $400 Per Cow – While the main article details long-term tech threats, this case study reveals the immediate ROI of technology you can adopt today, demonstrating how AI-driven health and feed monitoring is already delivering $400/cow in proven profit.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.






 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!




