Heat-stressed cows produce 23% more methane per gallon while crushing milk yield—turn cooling into your carbon compliance advantage.
What if the same 90-degree day that’s crushing your 2,040-pound monthly milk yield is also sabotaging your environmental compliance goals—and most dairy operations don’t even realize it’s happening?
Here’s a fact that should stop every strategic planner cold: heat-stressed cows produce up to 23% more methane per gallon of milk while simultaneously tanking your production numbers. This isn’t just about surviving summer anymore—it’s about preventing a double financial disaster that’s hitting the dairy industry, with projected costs of $30 billion globally by 2050, while making environmental regulations nearly impossible to meet at current U.S. milk prices, averaging $21.30 per hundredweight.

You’re facing a hidden crisis that attacks from two angles simultaneously. While you’re focused on maintaining milk production during heatwaves, your operation is unknowingly becoming a methane factory, precisely when you can least afford it. The most productive cows—those genetic investments with superior breeding values that you’ve built your operation around—become your biggest environmental liabilities the moment temperatures push past 68 THI.
The stakes couldn’t be higher. With carbon pricing initiatives spreading across regions and methane regulations tightening, this dual impact threatens to squeeze dairy operations from both revenue and compliance angles. However, cutting-edge research reveals that strategic heat abatement changes everything: it not only protects your milk checks but also serves as your secret weapon for reducing methane emissions while maintaining the productivity that keeps you competitive.
Stop Treating Heat Stress Like Weather—Start Treating It Like the Methane Crisis It Is
Here’s the uncomfortable truth most consultants won’t tell you: the dairy industry’s reactive approach to heat stress is fundamentally flawed and costing you money every single day above 68 THI.
Traditional heat stress management focuses on visible symptoms—such as panting, reduced feed intake, and obvious milk drops—but peer-reviewed research reveals that this reactive approach misses the most expensive damage. By the time you see cows panting, methane intensity has already increased significantly, and rumen efficiency has been compromised for days. It’s like treating a heart attack after the patient collapses instead of monitoring blood pressure proactively.
Most operations still rely on the outdated 80°F threshold for heat stress intervention, but controlled research confirms that metabolic disruption begins at just 68 THI. This 12-degree blind spot costs the average 500-cow operation approximately $15,000-$ 25,000 annually in hidden methane penalties and productivity losses that are not reflected in obvious metrics.
Here’s what the industry doesn’t want you to know about methane and heat stress. Industry literature has long suggested that reduced feed intake during heat stress would naturally lead to a decrease in methane production. However, controlled chamber studies reveal a biphasic response where methane intensity actually increases as heat stress persists, even as absolute emissions initially decline. This means your “low-producing” heat-stressed cows are actually your worst environmental performers per unit of milk.
Challenge Everything: Why Your Genetics Program Might Be Sabotaging Your Climate Goals
Think you’re breeding for the future? Think again. The dairy industry’s obsession with single-trait selection for milk yield has created a genetic time bomb that explodes every time the mercury rises.
The uncomfortable reality is that high-producing animals actually become more susceptible to heat stress due to increased metabolic heat production. We’ve essentially bred cows that are environmental disasters, waiting for the next heatwave. Your highest TPI cows—those $50,000 genetic investments—become methane factories precisely when you need them most productive.
However, here’s where conventional breeding wisdom is turned upside down: genomic research using large-scale datasets reveals that incorporating heat tolerance into selection indices can increase prediction accuracy by up to 10%. This isn’t theoretical—it’s happening right now in operations that are smart enough to challenge the “milk yield at any cost” mentality that has dominated the industry for decades.
Here’s your wake-up call: A recent study found that when exposed to increasing THI levels, cows genetically predisposed to be low methane emitters in comfortable conditions actually increased their methane concentrations under heat stress. Your breeding program for low emissions could be backfiring during hot weather without proper heat abatement.
The Hidden Economic Devastation: What Your Monthly Milk Check Isn’t Telling You
The economic devastation from heat stress extends far beyond production losses—it’s a wealth destroyer that compounds across generations like poorly managed genetics.
U.S. milk production reached 227.8 billion pounds in 2025, with production per cow averaging 2,040 pounds monthly in major producing states. However, this productivity masks a hidden methane penalty that’s creating measurable compliance costs in regions implementing carbon pricing. When heat stress increases methane intensity by up to 23% at the herd level, operations face direct regulatory exposure that compounds with production losses.
Recent modeling studies tracking high-yielding herds have found that heat stress can decrease herd-level milk yield by up to 8.6% when all effects are combined over extended heat periods. For a 500-cow operation producing at current U.S. averages, this represents potential losses of $25,000 to $ 40,000 during extended heat periods, before accounting for environmental compliance penalties.
Small Farms: The Climate Change Casualties Nobody Talks About
Here’s the brutal truth about climate inequality in dairy: smaller farms are getting crushed while big operations adapt.
Research demonstrates that smaller farms (herds with fewer than 100 cows) suffer disproportionately, experiencing average annual yield losses of 1.6% compared to less than 1% for large herds. Following an extreme heat event, small herds can lose 50% more of a day’s yield than large herds. This disparity is largely attributed to the high capital costs of sophisticated mitigation infrastructure, such as large-scale fan and sprinkler systems, which are often beyond the financial reach of smaller operations.
But the transgenerational damage creates the most insidious economic drain. Heat-stressed dry cows produce calves with permanently reduced productive capacity, creating compounding liabilities that research estimates cost the U.S. dairy industry an additional $595 million annually. These “legacy effects” transform heat stress from a seasonal nuisance into a long-term erosion of genetic investment—and your family farm’s future.
Here’s How Smart Operations Turn Heat Management into Competitive Advantage
Stop thinking about heat abatement as a cost center. Start thinking about it as the most profitable investment you’ll make this decade.
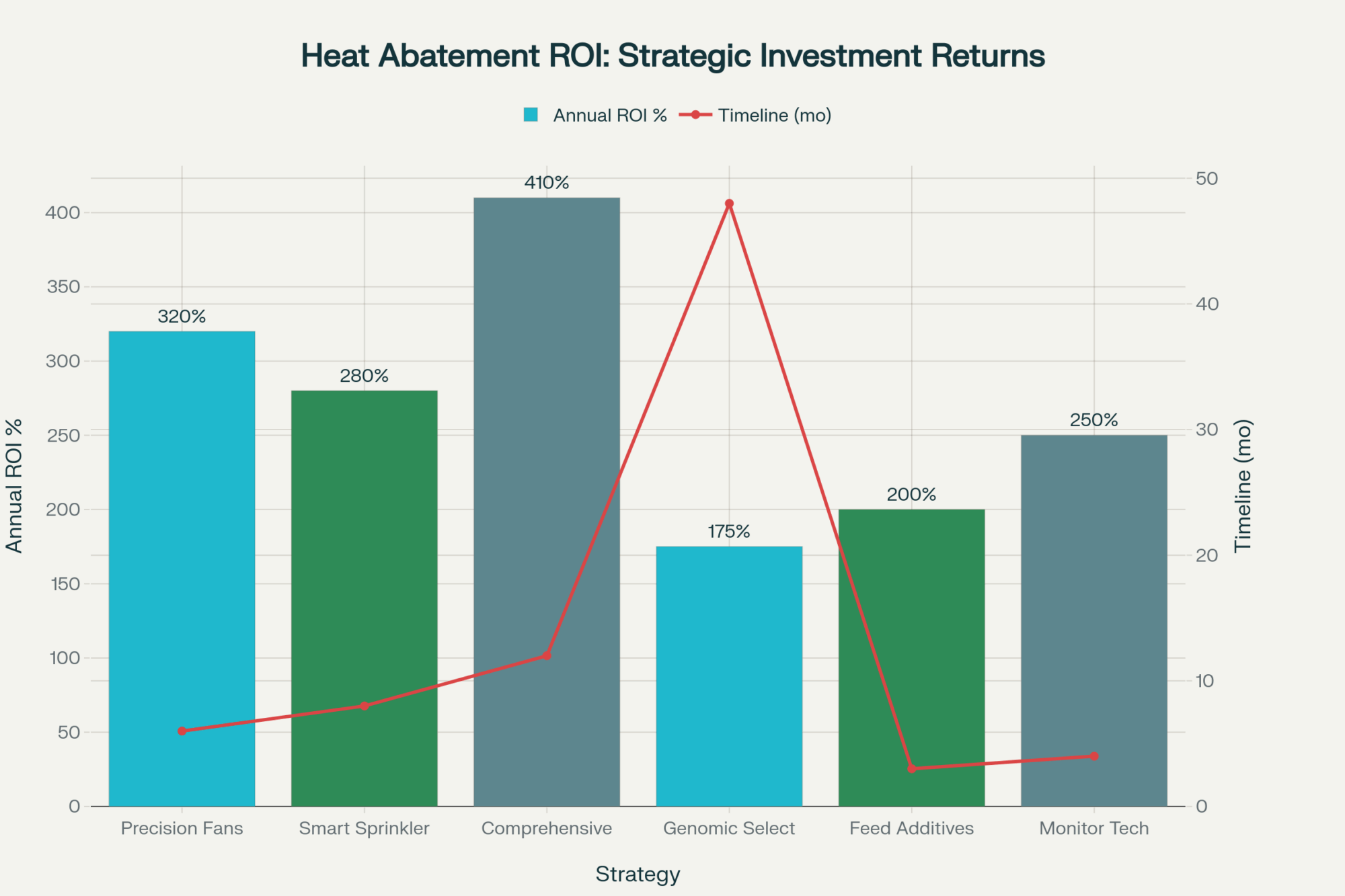
Research consistently demonstrates that every dollar invested in effective heat abatement returns $3 to $ 5 in avoided production, reproductive, and health losses annually. However, what most operations overlook is that the environmental benefits generate additional value streams, which could be worth thousands in carbon credits and regulatory compliance advantages.
Precision cooling systems that maintain consistent airflow prevent the rumen disruptions responsible for increased methane intensity. Unlike basic shade structures that most farms still rely on, engineered ventilation systems maintain normal rumination patterns and digestive efficiency even during periods of thermal stress, thereby preventing the microbial dysbiosis that drives methane inefficiency.
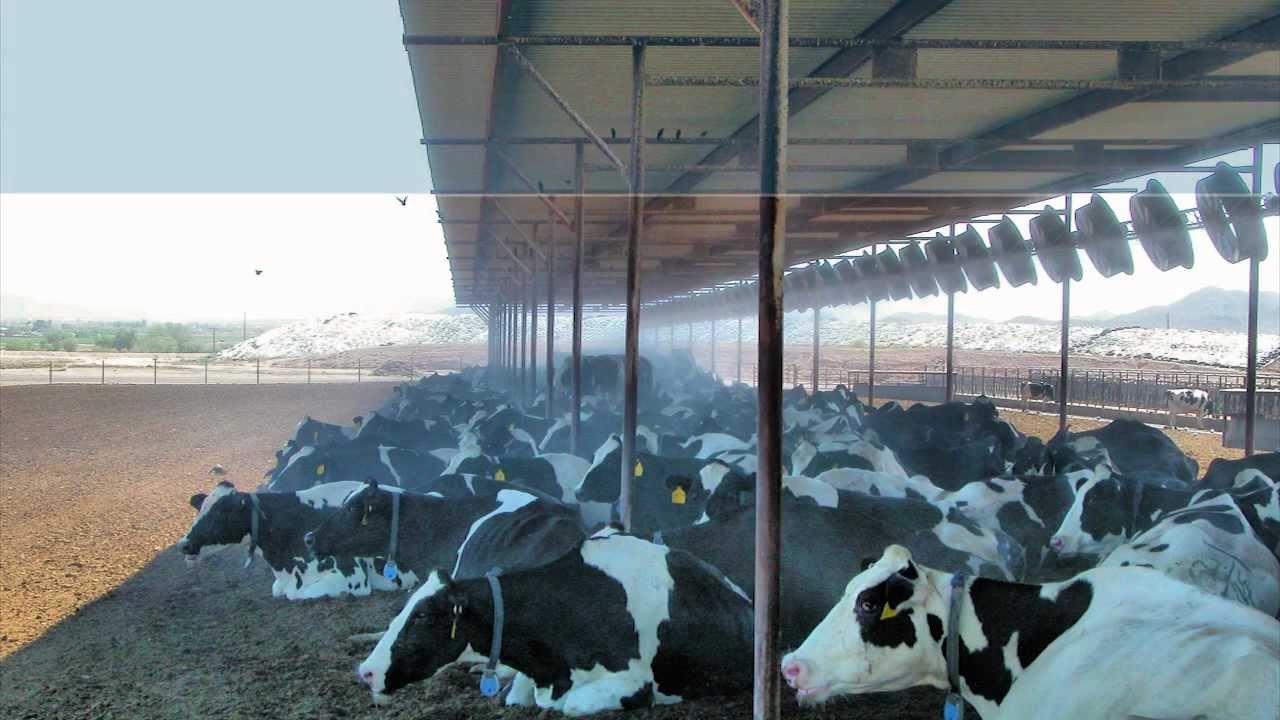

The Technology Revolution: Why Precision Monitoring Beats Gut Feel Every Time
Modern heat stress management leverages the same precision agriculture principles, transforming crop production, and the ROI is extraordinary.
Real-time reticulorumen pH and temperature monitoring systems can detect the impacts of heat stress on methane production before visible symptoms appear. This allows proactive intervention rather than reactive damage control. Think of it as the difference between having a cardiac monitor versus waiting for chest pains.
Activity monitoring and data analytics track individual cow responses to thermal stress, providing early detection capabilities that prevent productivity losses before they occur. Operations utilizing these technologies capture market advantages by maintaining stable production and environmental performance, even as competitors struggle.
Benchmark Your Vulnerability: The 5-Minute Heat Stress Audit
Want to know if you’re losing money right now? Answer these questions:
- Airflow Test: Can you measure 200+ feet per minute airflow at cow resting height in your three highest-traffic areas? If not, you’re losing money every day above 68 THI.
- THI Monitoring: Do you have real-time THI monitoring with alerts at 68 (not 80)? Most operations are flying blind with outdated thresholds.
- Water Capacity: Can your system deliver 50+ gallons per cow per day during peak demand? Water limitation amplifies every other heat stress factor.
- Methane Baseline: Do you know your current methane intensity (g CH4/kg milk)? Without baseline data, it is impossible to measure improvement.
| Heat Abatement Strategy | Initial Investment | Annual ROI | Methane Reduction | Implementation Timeline | External Validation |
| Precision Fan Systems | $200-400/cow | 3.2:1 | 15-20% intensity | 4-6 weeks | Journal of Dairy Science |
| Smart Sprinkler Systems | $150-300/cow | 2.8:1 | 12-18% intensity | 6-8 weeks | Animal Science Research |
| Comprehensive Cooling | $400-800/cow | 4.1:1 | 20-25% intensity | 8-12 weeks | Multiple Studies |
| Genomic Selection | $60/animal testing | 150-200% | 8-15% intensity | 3-5 years | Nature Scientific Reports |
The Genomic Revolution: Stop Breeding for Yesterday’s Climate
Here’s the paradigm shift that separates industry leaders from followers: selecting for heat tolerance isn’t about sacrificing productivity—it’s about protecting your genetic investments from climate volatility.
Heritability estimates for heat tolerance traits range from 0.13 to 0.17, sufficient for meaningful genetic progress. The “SLICK” haplotype, resulting in short, sleek hair coats, dramatically improves heat dissipation and can be incorporated into Holstein populations without compromising milk production potential.
Genomic research indicates that cows predicted to be heat-tolerant through genomic breeding values exhibit less decline in milk output and fewer increases in core body temperature during controlled heat stress events. This isn’t theoretical breeding—it’s practical risk management for operations planning beyond the next lactation.
Why This Matters for Your Operation’s 2030 Planning
With genomic testing costs having dropped below $60 per animal and a documented ROI ranging from 150-200%, the data exist to accelerate genetic selection for climate resilience. However, most operations continue using breeding strategies designed for yesterday’s climate patterns, leaving money on the table that forward-thinking competitors are already capturing.
Recent advances in multi-trait selection indices that balance productivity, heat tolerance, and methane emissions are becoming commercially viable. Operations implementing these strategies today position themselves for regulatory compliance advantages and market premiums as environmental standards become increasingly stringent.
Future-Proofing Your Operation: The Climate Adaptation Imperative
Climate projections make early adoption crucial for long-term strategic positioning rather than short-term comfort.
Models predict that 90% of the Canadian national dairy herd will experience large increases in heat stress frequency, severity, and duration under most climate scenarios. For U.S. operations, climate projections indicate that extreme heat days will become more frequent, resulting in a 30% increase in milk yield losses by 2050.
The competitive advantage extends beyond individual operations. While heat stress affects all dairy farms, those with effective abatement maintain stable production and environmental performance during peak stress periods when competitors struggle. This consistency in both milk delivery and carbon footprint creates market differentiation in an increasingly sustainability-conscious industry.
Three Critical Questions Every Strategic Planner Must Answer Today
Are you prepared for the regulatory reality that methane pricing is no longer theoretical? Several regions have already implemented carbon fees, and methane regulations continue to expand across agricultural sectors. Operations with documented heat stress mitigation can demonstrate measurable emission reductions that translate to compliance value.
Can your current genetic program deliver productivity under 2030 climate conditions? If you’re still selecting purely for milk yield without considering thermal resilience, you’re building vulnerabilities into your herd that will become expensive liabilities within this decade.
Do you have real-time data on the impacts of heat stress, or are you managing by gut feel and reactive intervention? Precision monitoring systems that detect problems before they become visible provide the competitive intelligence necessary for proactive management in an increasingly volatile climate.
The Bottom Line: Your Strategic Imperative Is Now
That 90-degree day scenario isn’t a future threat—it’s happening right now, and it’s costing you money while sabotaging your environmental goals every time temperatures climb above 68 THI.
The research is unequivocal: heat stress creates a devastating double impact where cows produce up to 23% more methane per gallon while making significantly less milk. This isn’t just a summer comfort issue—it’s a year-round threat to both profitability and environmental compliance that will only intensify as climate change accelerates.
Strategic heat abatement solves both problems simultaneously. Cooling investments deliver a 3-to-1 return by maintaining rumen efficiency, which keeps methane intensity low while protecting milk production. Whether through precision airflow systems, intelligent sprinkler cycles, or genomic selection strategies, effective heat management prevents digestive disruptions that drive both productivity losses and increased emissions.
Climate regulations and carbon pricing aren’t going away—they’re expanding. The documented reduction in methane intensity achieved through proper heat abatement creates a measurable compliance value while protecting your operation from significant annual losses that unmitigated heat stress can inflict.
Your 72-Hour Action Plan
Your strategic imperative demands immediate action:
This Week: Audit your current heat abatement systems using the 5-minute vulnerability assessment above. Measure airflow at cow resting height in your three highest-traffic areas—if you’re not consistently hitting 200+ feet per minute, you’re losing money and increasing emissions every day above 68 THI.
This Month: Install real-time THI monitoring with 68-degree alerts (not 80). Contact your genetic supplier to discuss incorporating heat tolerance breeding values into your selection program. Request genomic heat tolerance scores for your current sire lineup.
This Quarter: Calculate your current methane baseline and heat stress economic impact using the ROI framework provided. Develop a 3-year cooling infrastructure plan that qualifies for USDA cost-share programs.
But don’t stop with infrastructure. The operations implementing comprehensive climate adaptation today will capture the market advantages that determine industry leadership in the decade ahead. With U.S. milk production at 227.8 billion pounds annually and rising global demand, the opportunity for decisive action has never been greater.
The dairy operations thriving in 2030 won’t be those that survived climate change—they’ll be those that turned thermal management into a competitive advantage by solving productivity and environmental challenges with strategic, data-driven approaches. Your competitors are already making these investments. The question is: will you lead or follow?
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Challenge the 80°F Comfort Zone Myth: Research confirms metabolic disruption begins at 68 THI, not 80°F, creating a 12-degree blind spot that costs average 500-cow operations $15,000-25,000 annually in hidden methane penalties and productivity losses that never show up in obvious metrics.
- Precision Cooling Delivers Carbon Compliance Value: Strategic cooling investments that maintain 200+ feet per minute airflow at cow resting height prevent rumen disruptions responsible for increased methane intensity while delivering 3-to-1 ROI through avoided production, reproductive, and health losses. With carbon pricing expanding, documented 20-25% methane intensity reductions create measurable compliance value.
- Genomic Selection for Heat Tolerance Protects Genetic Investments: The “SLICK” haplotype and heat tolerance breeding values (heritability 0.13-0.17) can be incorporated into Holstein populations without compromising milk production potential, while genomic testing costs below $60 per animal deliver 150-200% ROI by protecting productivity under 2030 climate conditions.
- Small Farm Climate Inequality Demands Immediate Action: Operations with fewer than 100 cows experience 50% higher daily yield losses during extreme heat events compared to large herds, with USDA EQIP funding covering up to 75% of qualified cooling improvements making adaptation accessible for strategic implementation.
- Future-Proof Through Proactive Management: Climate models predict increasing heat stress frequency with some regions facing 100-300 annual heat stress days by 2050, making thermal resilience essential for maintaining competitive positioning as global dairy production faces potential 4% reduction without comprehensive adaptation strategies.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Stop treating heat stress like weather and start treating it like the methane crisis it is—because your “comfortable” cows are becoming environmental disasters every day above 68 THI. Recent controlled research reveals that heat-stressed dairy cattle produce up to 23% more methane per gallon of milk while simultaneously reducing production by 8.6% when all effects combine over extended periods. This double economic hit costs the U.S. dairy industry $900 million to $1.5 billion annually, with individual operations losing an average of $264 per cow per year from unmitigated heat stress. Small farms suffer disproportionately, experiencing 1.6% annual yield losses compared to less than 1% for large herds, creating a climate-driven consolidation crisis that threatens family operations. While current cooling technologies can offset about 40% of productivity losses during extreme heat, strategic heat abatement delivers 3-to-1 ROI by maintaining rumen efficiency that keeps methane intensity low while protecting milk production. Global projections show dairy production could crash by 4% by 2050 unless operations implement comprehensive climate adaptation strategies that turn thermal management into competitive advantage. Audit your heat abatement systems now and calculate methane reductions using documented improvement factors—your competitors are already making these investments.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Heat Stress Isn’t Coming – It’s Already Robbing Your Milk Check. Here’s How Elite Dairies Are Fighting Back – Reveals specific cooling protocols and infrastructure strategies elite operations use to achieve 3:1 ROI on heat abatement while protecting generational genetic investments from thermal damage.
- USDA’s 2025 Dairy Outlook: Market Shifts and Strategic Opportunities for Producers – Demonstrates how tightening milk supplies and revised price forecasts create strategic positioning opportunities for climate-resilient operations in an evolving competitive landscape.
- 5 Technologies That Will Make or Break Your Dairy Farm in 2025 – Explores cutting-edge monitoring systems and AI-driven analytics that enable precision heat stress detection 48 hours before visible symptoms, maximizing both productivity and environmental compliance.
 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
Every week, thousands of producers, breeders, and industry insiders open Bullvine Weekly for genetics insights, market shifts, and profit strategies they won’t find anywhere else. One email. Five minutes. Smarter decisions all week.






 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.