180 cows. The threshold that separates dairy tech wins from expensive regrets. Here’s what actually works on each side—and why infrastructure matters more than equipment.
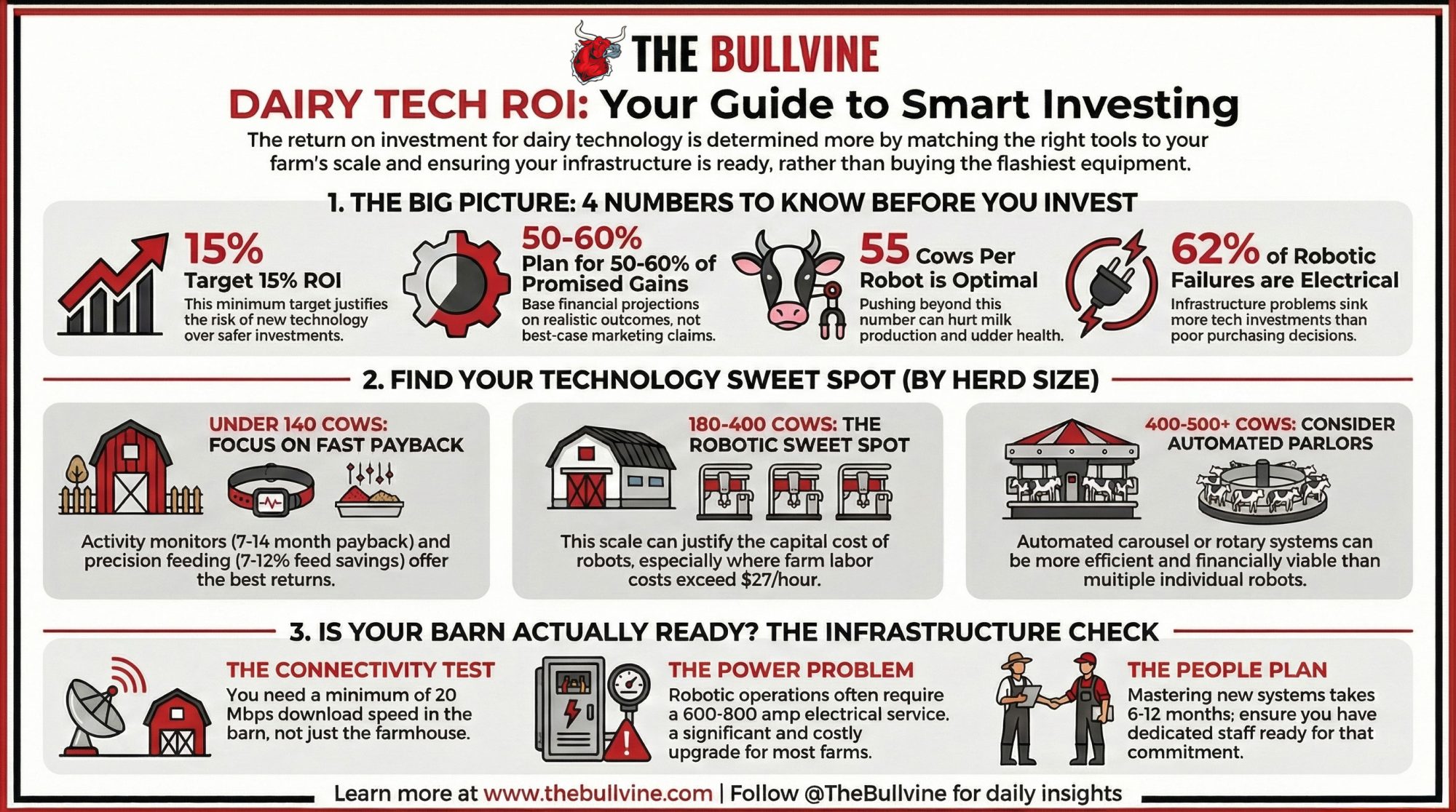
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: The math on dairy technology is simpler than vendors suggest—and more unforgiving than most producers expect. University of Minnesota research shows robotic milking breaks even only when labor costs reach $27.05 per hour, with optimal utilization at 55 cows per robot, according to the University of Wisconsin’s Dairyland Initiative. That reality puts the automation sweet spot squarely between 180 and 400 cows. Below that threshold, activity monitors (7-14 month payback) and precision feeding (7-12% feed savings) consistently deliver stronger returns than robots that can’t justify their capital cost at smaller scales. But infrastructure failures sink more technology investments than poor purchasing decisions ever will—62% of automated milking difficulties trace to electrical inadequacy, and half of US farms lack the connectivity modern systems demand. The producers winning with technology aren’t buying the flashiest equipment; they’re matching capability to scale, fixing infrastructure first, and planning for 50-60% of marketed benefits rather than trade-show promises.

When Mike Vanbeek installed activity monitors on his Wisconsin dairy, he wasn’t chasing the latest trend. He was solving a specific problem – missed heats were eating into his bottom line, and he knew it. Within months, his 21-day pregnancy rate climbed from 25% to 35%, and he’d cut his synchronization protocol costs by more than half.
That’s a technology success story worth examining. But here’s what makes it interesting: Vanbeek didn’t buy robots. He didn’t automate his milking. He invested in collars and sensors—relatively modest technology that delivered returns he could actually measure against his milk check.
His experience reflects something dairy farmers across North America are discovering as they navigate the flood of precision agriculture tools now available. The question isn’t really “Should I adopt technology?” It’s more nuanced than that: “Which technology fits my operation, my scale, and my specific constraints?”

After Agritechnica 2025 showcased everything from AI-powered weed detection promising 90% herbicide savings to autonomous equipment that seemed lifted from science fiction, that question has become more urgent—and honestly, more complicated—than ever.
The ROI Benchmark That Changes Everything
Let’s start with something practical. Gary Sipiorski, a dairy financial consultant who works with producers across the Midwest, offers a useful framework: compare any technology investment to what you’d earn parking that money in a certificate of deposit. With current CD rates running in the 4-5% range, technology investments should target at least 15% ROI to justify the additional risk and management complexity.
That’s a cold shower for anyone standing in a flashy trade show booth. And it’s where the conversation gets interesting.
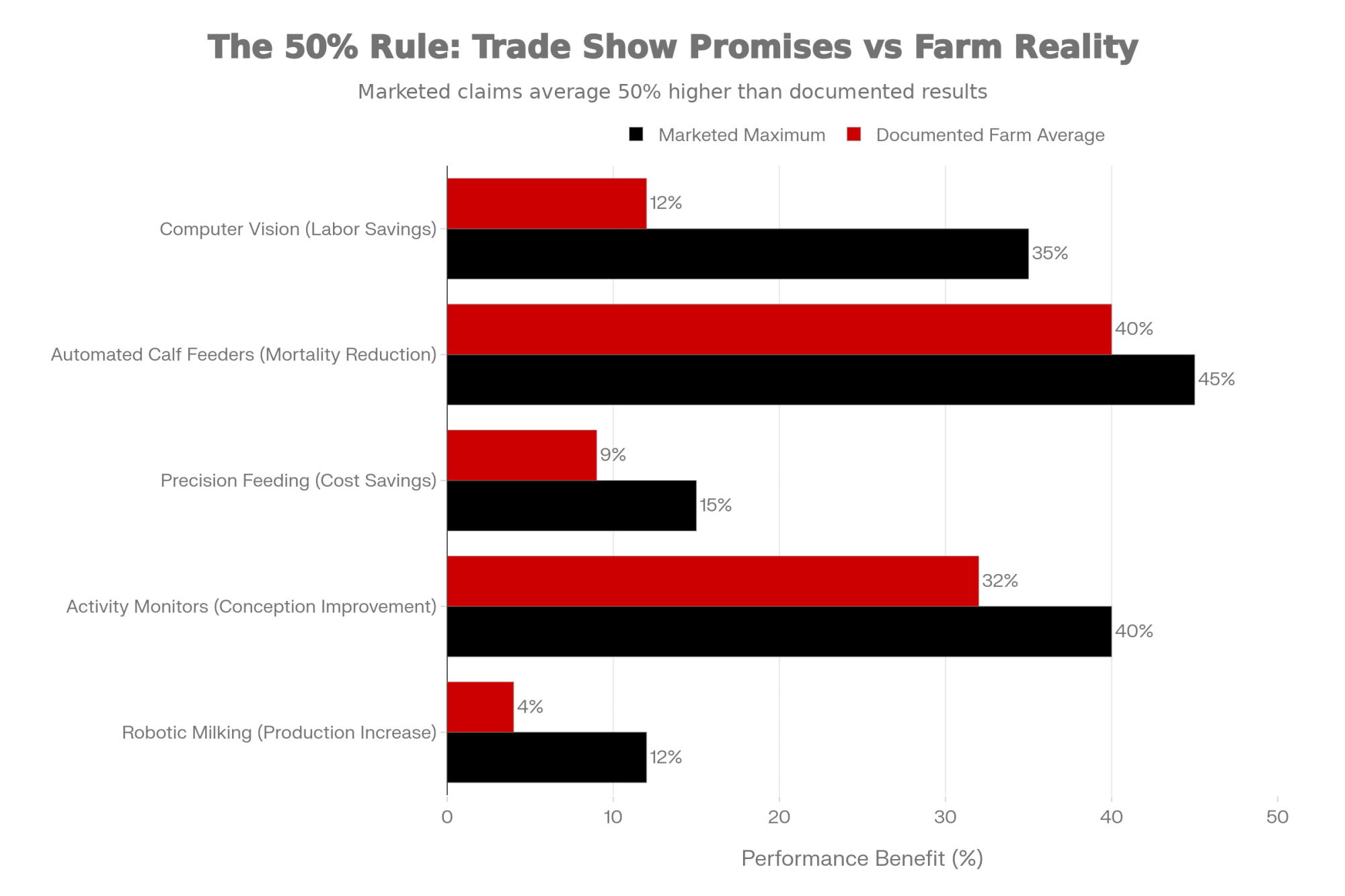
Research on automated milking systems illustrates the challenge nicely. A peer-reviewed study reports that robotic milking has “potential to increase milk production by up to 12%.” By the time that finding works its way through marketing materials, it often becomes “robots increase milk 10-12%.” But the documented average on working farms? Closer to 4%.

This isn’t vendor deception. It reflects how many variables influence outcomes—management practices, facility design, cow genetics, transition period protocols, and even how consistently someone responds to system alerts at 2 AM. The farms hitting those top-end numbers are doing a lot of things right simultaneously. They’ve got their fresh cow management dialed in, their nutritionist is optimizing rations for the system, and they’ve committed the time to really learn the technology.
The takeaway for anyone evaluating technology: trade show projections represent best-case scenarios achieved under optimal conditions. Planning around 50-60% of the marketed benefits yields more realistic financial projections. Not pessimistic—just grounded in what the data actually shows.
Where Scale Changes the Math

This is where the research gets genuinely useful for decision-making. University of Wisconsin’s Dairyland Initiative has established a practical guideline that’s reshaping how farmers think about robotic milking: plan for 55 cows per robot for optimal performance.
Vendors might suggest higher numbers—theoretical capacity calculations can make 70 or even 78 cows per robot sound feasible. But cows aren’t machines. They have circadian rhythms. They prefer milking at certain times. Peak voluntary attendance happens around dawn and dusk, with quieter periods in between. Push too many cows through a robot, and milking frequency drops, udder health issues start appearing, and those production gains you were counting on evaporate.
Some producers have learned this the hard way—pushing cow numbers beyond optimal levels, watching bulk tank SCC climb, then scaling back to more manageable ratios. The theoretical capacity on paper doesn’t account for real-world cow behavior.
Finding Your Technology Sweet Spot
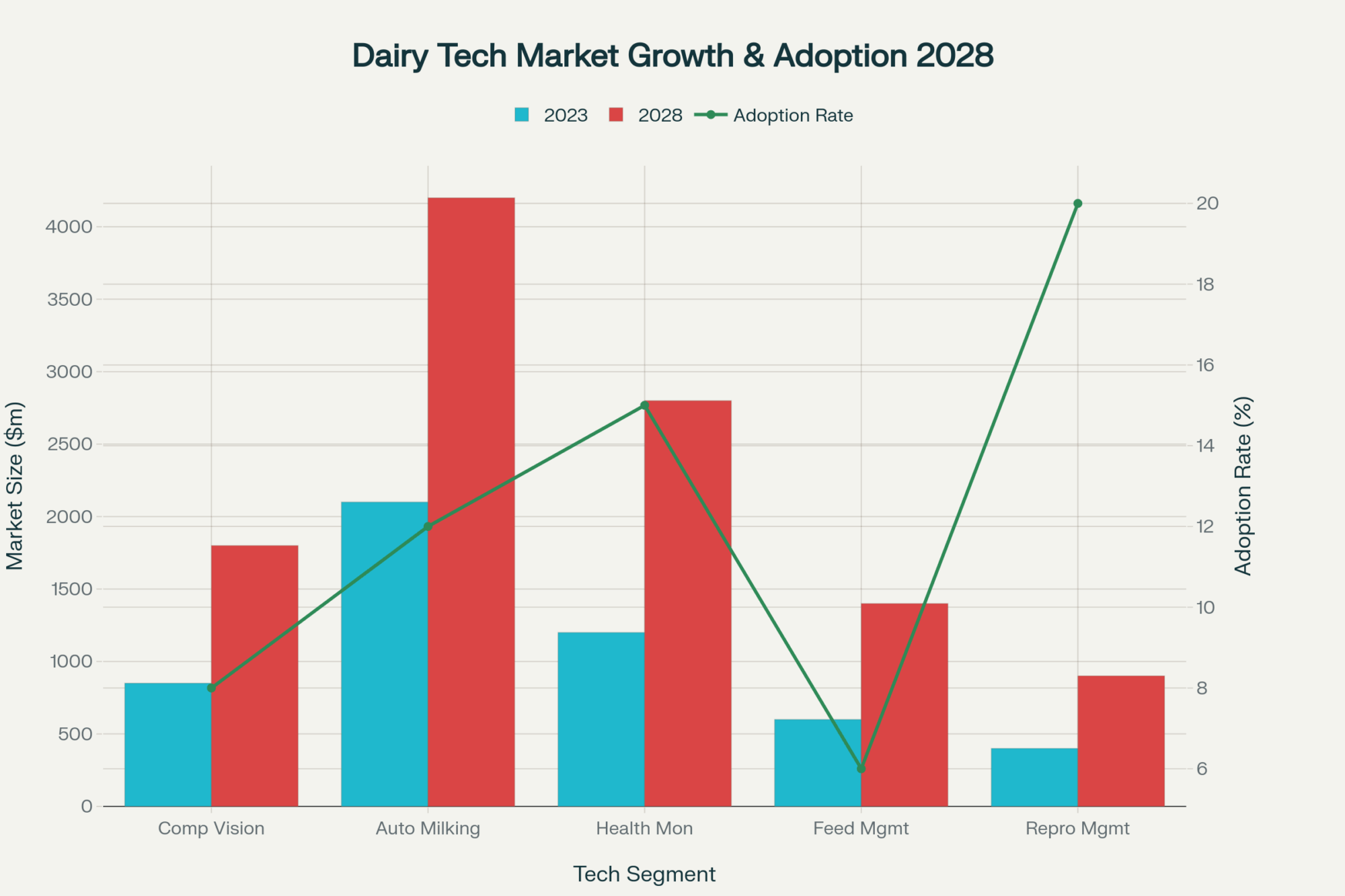
Here’s how the scale economics break down based on current research:
| Herd Size | Optimal Technology Investment | Target ROI Timeline | Primary Barrier | Capital Investment Range |
| Under 140 cows | Activity monitors, precision feeding, automated calf feeders | 7-14 months | High capital cost per cow; labor savings can’t offset robot investment | $10,500 – $35,000 |
| 140-180 cows | Activity monitors, precision feeding, computer vision (emerging) | 12-24 months | Robot ROI marginal; requires $27+ per hour labor costs to break even | $35,000 – $75,000 |
| 180-400 cows | Robotic milking systems (3-4 units), activity monitors | 36-60 months | Electrical capacity, internet latency, training commitment | $600,000 – $1,200,000 |
| 400-500+ cows | Automated parlors, rotary systems with robotic attachments | 48-72 months | Management complexity of multiple individual robot units | $1,200,000 – $2,500,000 |
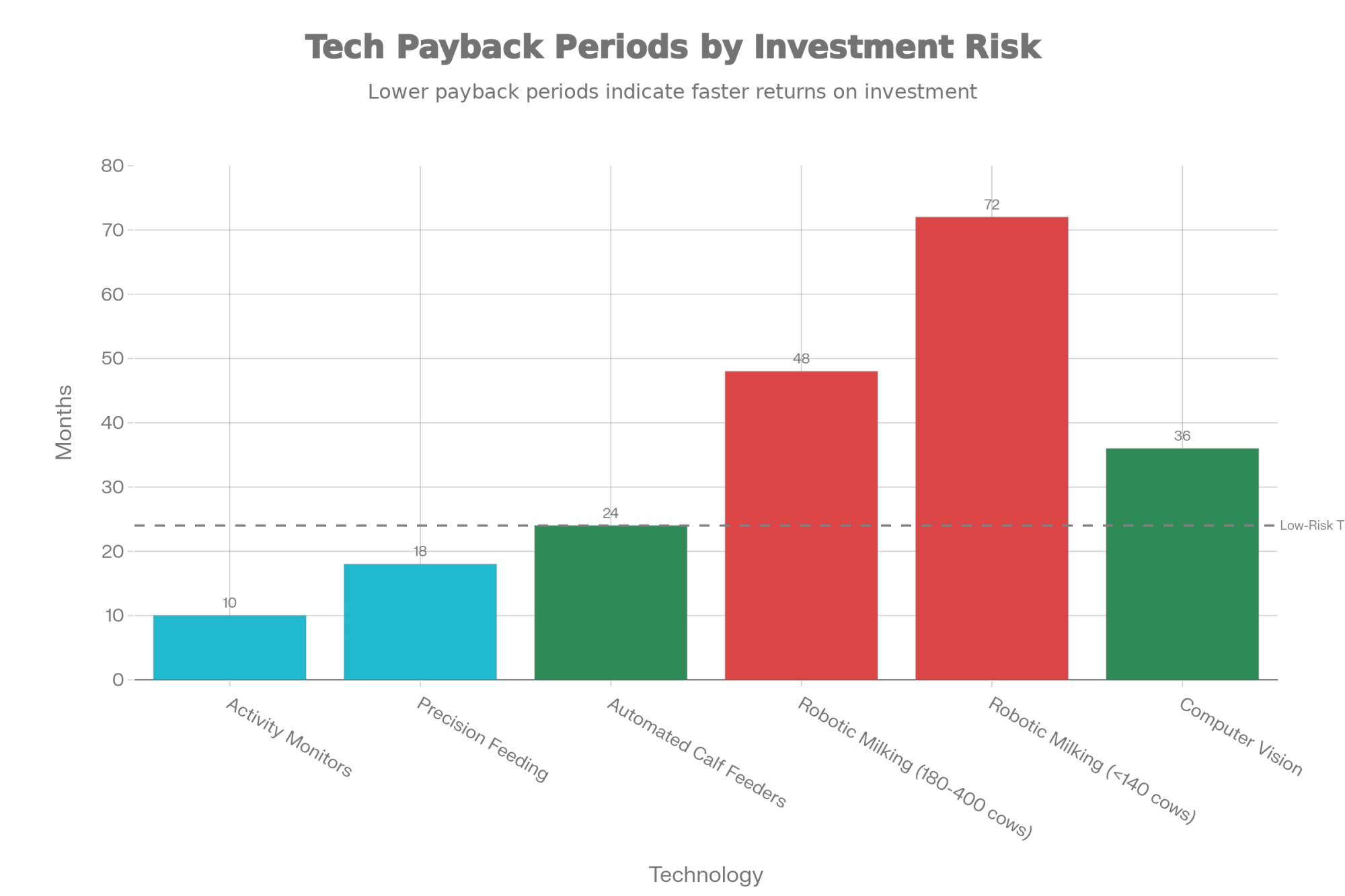
Under 140 cows: The economics of robotic milking get ugly fast. Fixed costs spread across fewer animals, and while labor savings matter, they can’t offset the capital investment. University of Minnesota research found that breaking even on robots requires paying milking labor around $27.05 per hour. If your labor costs are significantly below that, the math doesn’t work.
180-400 cows: This is the sweet spot. With 3-4 robots, farms can eliminate meaningful labor positions while maintaining efficient robot utilization. Research from Australian operations confirms it—farms that pushed their cow-to-robot ratio toward 70 cows (while still managing cow flow effectively) saw measurable profit improvements.
400-500+ cows: Here’s where it gets counterintuitive. Conventional parlor systems with robotic attachment technology may actually outperform multiple individual robot units. DeLaval’s solution managers acknowledge that automated carousel systems become “financially viable for farms with a minimum of 400-500 cows.”
These thresholds shift based on local labor markets and regional conditions. Operations in California’s Central Valley or across the Northeast, where agricultural wages run higher, and labor availability stays tight, may see robots pencil out at smaller scales. Vermont and New York dairies often face economic conditions different from those in the Upper Midwest. Pacific Northwest producers deal with their own labor dynamics, while Texas and Southwest operations factor heat-stress management differently into the equation.
For Canadian producers, the calculation carries an additional wrinkle. Quota value affects how you think about capital allocation—when quota represents a significant asset on your balance sheet, the decision to invest $600,000 in robots versus additional quota becomes a strategic choice about where your capital works hardest. The labor-savings argument still applies, but it competes with a different set of alternatives than US producers face.
Your specific labor market and regional context matter more than any trade show pitch.
What’s Actually Working for Smaller Herds
If robots don’t pencil out at your scale, what does? Turns out, quite a bit. And most of it won’t win any innovation awards—which is exactly why it works.
Activity Monitoring: The Quiet Winner
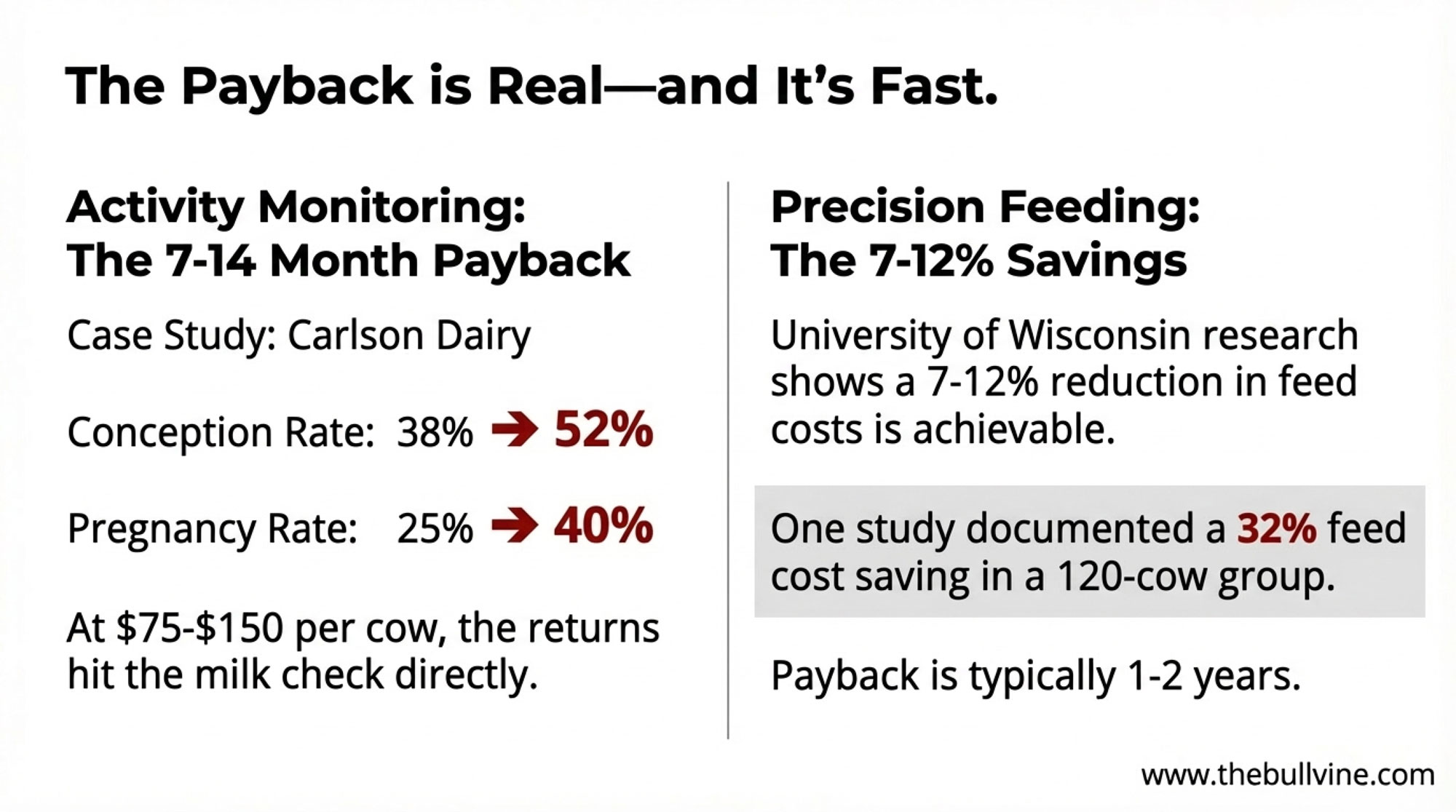
At $75-150 per cow, activity monitors deliver some of the highest returns available to smaller operations. The documented results are consistent: 30-34% improvement in first-service conception rates, meaningful reductions in days open, and earlier illness detection during that critical fresh cow period.
Carlson Dairy’s numbers tell the story. After implementing monitoring, their conception rates rose from 38% to 52%, and pregnancy rates jumped from 25% to 40%. When a single missed heat costs roughly $42 in extended days open—and that compounds across a breeding season—those improvements hit the milk check directly.
Typical payback: 7-14 months. That’s real money, real fast.
Precision Feeding: Where the Real Dollars Hide
Feed represents 50-60% of operating costs on most dairies. Even modest efficiency improvements translate directly to margin—often more directly than technologies that generate more excitement at industry events.
University of Wisconsin research demonstrates what’s possible. Through differentiated concentrate feeding during milking—supplementing high producers with additional concentrates while feeding a more moderate TMR to everyone—farms can achieve 7-12% reductions in feed costs without requiring separate mixer wagons or multiple cow groups.
One study documented a 120-cow group achieving 32% feed cost savings. The principle is simple: feed expensive nutrients to cows that can convert them to milk, not to animals that will deposit them as body condition. We’ve all seen those over-conditioned dry cows heading into calving. This approach prevents that while improving margins.
Payback typically runs one to two years, with returns that continue indefinitely.
Automated Calf Feeders: Investing in Your Future Herd
For operations raising replacement heifers, automated calf feeding offers compelling returns that get overlooked in conversations dominated by milking technology.
The headline number: 40% reduction in calf mortality. But there’s more. These systems detect illness 48 hours before you’d notice visible symptoms during morning chores. With young calves vulnerable to scours and respiratory challenges in their first weeks, catching problems early means the difference between a $50 treatment and a $2,000 dead replacement.
Add 1-2 hours of daily labor savings and improved first-lactation performance from better early nutrition, and the investment typically pays for itself within two years.
One thing worth noting here: if you’re running a beef-on-dairy program with a significant portion of your cows bred to beef sires, the calf feeder ROI calculation shifts. Fewer dairy replacements means fewer calves running through that system, which extends your payback period. It doesn’t kill the investment case, but it changes the math enough that you should run the numbers based on your actual replacement strategy rather than industry averages.
Computer Vision: Promising but Not Proven
You’ll hear buzz about camera-based monitoring as a low-cost alternative to wearable sensors. University research shows a camera setup monitoring a 21-cow pen costs approximately $400 total, compared to $4,200 for wearable sensors covering the same animals.
But let’s be honest about where this technology stands: it’s promising, not proven. The data analysis capabilities are still maturing, accuracy varies significantly across systems, and most commercial offerings aren’t yet delivering the reliability to justify betting your management decisions on them. The technology needs more development before it can match the reliability of proven monitoring systems. Keep watching, but don’t bet your operation on it yet.
The Infrastructure Reality That Kills Technology Dreams

What trade shows won’t tell you: infrastructure readiness determines success more than the technology itself. I’ve seen promising installations fail not because the equipment was flawed, but because the foundation wasn’t ready.

Connectivity: The Deal-Breaker Nobody Discusses
Lely specifies minimum internet requirements for their robotic systems: 20 Mbps download, 5 Mbps upload, less than 100ms latency, and 99%+ uptime. Those are firm requirements, not suggestions.
The hard truth? Half of you are trying to run 21st-century tech on a dial-up-era backbone. Research indicates that over 50% of US farmers lack adequate internet service on their farms. And the critical issue isn’t your farmhouse connection—it’s connectivity in the barn, often hundreds of feet from your router through metal buildings and concrete walls.
One farmer put it bluntly: “One of the biggest problems I see is issues with rural internet… If you aren’t able to access the data and actually utilize it, then it’s a waste.”
Before signing any contract for cloud-dependent technology, test your internet speed in the barn during peak household usage—evening hours when everyone’s streaming. That’s your real-world number, not the speed test you run at 2 PM.
Electrical Capacity: The 62% Factor
Here’s a stat that should stop you cold: 62% of automated milking system difficulties trace back to inadequate electrical infrastructure. Not software. Not mechanical failures. Power problems.
The consequences play out predictably. Farms that install robots before addressing electrical capacity often spend months chasing intermittent shutdowns and control board errors that nobody can diagnose. When they finally upgrade—typically $15,000-$25,000 for adequate service—the problems disappear almost overnight. That’s an expensive lesson in doing the infrastructure assessment first.
Most farms operate on 400-amp single-phase service. Robotic operations often require a minimum of 600-800 amps. And keep in mind that these requirements intensify during peak demand periods—summer heat events when cooling systems, ventilation, and robots all run simultaneously, or winter months in northern regions when heating elements and lighting add to the load. Get an electrician who understands agricultural loads to assess your capacity before you commit to anything.
| Infrastructure Category | Minimum Requirement | Assessment Method | Consequence of Failure |
| Internet Connectivity | 20 Mbps download, 5 Mbps upload, <100ms latency, 99%+ uptime | Test speed in barn during peak household usage (7-9 PM) | System can’t access cloud data, alerts fail, remote monitoring impossible |
| Electrical Capacity | 600-800 amp service (minimum) for robotic systems | Professional agricultural electrician assessment of total farm load | 62% of AMS difficulties trace here: intermittent shutdowns, control board failures, months of troubleshooting |
| Facility Layout | 55 cows per robot maximum; clear cow traffic flow paths | Map cow movement patterns; measure fetch distances | Reduced milking frequency, elevated SCC, production gains evaporate |
| Technical Personnel | 2 trained staff members capable of system troubleshooting | Identify backup coverage for vacations, illness, turnover | System underutilized, alerts ignored, data not leveraged for decisions |
| Service Support | Certified technician within 2-hour response radius | Map dealer locations; ask for average response time during peak season | Extended downtime during breakdowns, milk quality issues, lost production |
The Training Gap Nobody Mentions
Vendors typically provide 1-3 days of training for systems that take 6-12 months to master.
One farmer described it honestly: “The robot trainer was here for 3 days… but it took us 6 months to really understand the system.”
Successful adoption requires someone—ideally two people for backup—who can commit to learning the system thoroughly and troubleshooting daily issues. If that person doesn’t exist on your operation, address that before the equipment arrives.
A Framework for Cutting Through Vendor Noise
When evaluating any major technology investment, three questions cut through the sales pitch:
- On support: How many certified technicians are within two hours of your farm? What are the response times when multiple farms need help simultaneously? Agricultural dealerships report they’d hire three to five mechanics immediately if they could find them. Understanding actual support capacity in your region sets realistic expectations.
- On true costs: Request itemized quotes including facility modifications, electrical upgrades, installation, and first-year operating costs. The gap between the quoted price and the all-in cost can reach 50% or more. Better to know upfront than discover it during installation.
- On realistic performance: What percentage of installations achieve the marketed performance? What separates high performers from those that struggle? Any vendor confident in their product can answer this honestly.
For Those Already Invested
Already bought the technology and working to maximize returns? Different conversation, but equally important.
- First 90 days: Expect a learning curve for you and the cows. Production fluctuations during transition are normal. Watch whether production returns to baseline by day 60-90 and whether system issues decrease over time. Trend lines matter more than daily numbers.
- Document everything. Production logs, downtime, service calls, and actual labor hours. You can’t manage what you don’t measure—especially with complex technology where multiple variables interact.
- Focus on controllables. Cow traffic management, feed incentives at the robot, and alert response protocols. These often explain performance gaps between farms running identical equipment. Sometimes it’s not the technology—it’s how you’re managing around it.
- Get outside eyes. Consultants not affiliated with the vendor can spot bottlenecks you’ve stopped noticing after months of daily involvement.
By six months, you’ll have enough data to know if optimization is working or if it’s time to try something different. Trust what the numbers tell you.
Quick Reference: The Numbers That Matter

| Critical Benchmark | Number | Decision Application |
| Robot viability threshold | 180 cows minimum | Below this, activity monitors + precision feeding deliver better risk-adjusted returns |
| Optimal cows per robot | 55 cows | Push toward 65-70 only with excellent cow traffic; vendor claims of 78 ignore cow behavior |
| Labor cost breakeven | $27.05/hour | If your milking labor costs less, robots won’t generate positive ROI at typical scales |
| Minimum ROI target | 15% annually | Technology must beat low-risk alternatives (5% CD rate) by 3x to justify complexity and risk |
| Realistic benefit planning | 50-60% of marketed claims | Vendors quote best-case scenarios; farm averages run half that across all technology categories |
| Infrastructure failure rate | 62% of AMS problems | Most difficulties trace to electrical/connectivity, not equipment—audit before purchase |
| Electrical requirement | 600-800 amps minimum | Most farms operate on 400-amp service; upgrade costs $15K-$25K but prevents months of issues |
| Internet minimum | 20 Mbps down / 5 Mbps up | Test in barn during peak usage, not farmhouse during off-hours—real-world connectivity matters |
| Activity monitor payback | 7-14 months | Fastest proven ROI in dairy technology; $75-$150 per cow consistently delivers |
| Automated parlor threshold | 400-500+ cows | Above this scale, consider automated parlors vs. multiple robot units for reduced complexity |
Before your next technology conversation, know these benchmarks:
- 55 cows per robot — Optimal utilization target (University of Wisconsin)
- $27.05/hour — Breakeven labor cost for robot ROI (University of Minnesota)
- 15% ROI — Minimum target to justify technology risk over safer investments
- 50-60% — Realistic benefit assumption vs. marketed claims
- 62% — AMS difficulties traced to electrical infrastructure
- 600-800 amps — Typical electrical requirement for robotic operations
- 20 Mbps download — Minimum internet for cloud-dependent systems
- 7-14 months — Typical activity monitor payback period
- $15,000-$25,000 — Common electrical upgrade cost range
The Bottom Line
The technology landscape in dairy keeps evolving, and the opportunities are real for operations positioned to capture them. But success depends less on buying the most advanced equipment and more on matching the right technology to your scale, infrastructure, and management capacity.
For smaller herds, that usually means activity monitors and precision feeding—technologies that deliver strong returns without massive capital or infrastructure overhaul. For mid-sized operations in that 180-400 cow range, robotic milking can transform profitability—if the foundation supports it. For larger operations, automated parlors might actually outperform multiple robot units while reducing complexity.
The farmers navigating this best share a common approach: they evaluate innovations based on fit rather than flash, and they’re brutally honest about their infrastructure, skills, and scale before signing anything.
As one industry advisor put it: “Think from the farm’s needs backward, rather than picking a technology and projecting it onto the farm.”
So here’s the question you need to answer before your next equipment conversation: Is your barn actually ready for the technology you’re considering, or are you just buying a shiny ornament for an outdated foundation?
The math doesn’t care about your enthusiasm. It only cares whether the numbers work.
Keep in mind that technology economics shift over time as equipment costs change and labor markets evolve. These frameworks should guide your thinking, but revisit the calculations periodically—what didn’t pencil out three years ago might look different today, and vice versa.
Key Takeaways
- Match technology to scale. Activity monitors and precision feeding often deliver stronger returns for smaller operations than robots. Sometimes the unglamorous stuff pays best.
- The 180-400 cow range is the robotic sweet spot. Below 140 cows, the math rarely works. Above 500, automated parlors deserve serious consideration.
- Infrastructure comes first. Test barn internet, assess electrical capacity, identify dedicated personnel—before signing anything. Expensive technology on inadequate infrastructure is a recipe for frustration.
- Plan around 50-60% of the marketed benefits and target 15% ROI to justify the risk.
- Already invested? The first 90 days are a learning curve. By six months, trust what the data tells you—not what you hoped would happen.
We’d love to hear how these frameworks apply to your operation. Share your technology experiences—successes and struggles alike—in the comments below or reach out directly. Your real-world insights help the entire dairy community make better decisions. Which of these numbers surprised you most? Or better yet, which one have you proven wrong on your own farm?
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More
- Tech Reality Check: The Farm Technologies That Delivered ROI in 2024 (And Those That Failed) – This field-tested breakdown exposes why 34% of tech installs fail due to infrastructure gaps. It delivers verified payback timelines for health sensors and robotic pushers, arming you with the data to avoid the industry’s most expensive “shiny toy” traps.
- 2800 Dairy Farms Will Close This Year—Here’s the 3-Path Survival Guide for the Rest – Rabobank’s data reveals a brutal 9% annual farm closure rate through 2027. This strategy guide breaks down the three specific paths left for mid-sized operations, helping you position your balance sheet to survive the industry’s “middle ground” collapse.
- 5 Technologies That Will Make or Break Your Dairy Farm in 2025 – AI and “Youngstock” sensors are no longer science fiction. This report reveals how self-powered monitoring and visual AI are slashing fresh cow treatments by 40%, delivering a competitive advantage that moves far beyond basic activity tracking.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.






 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!