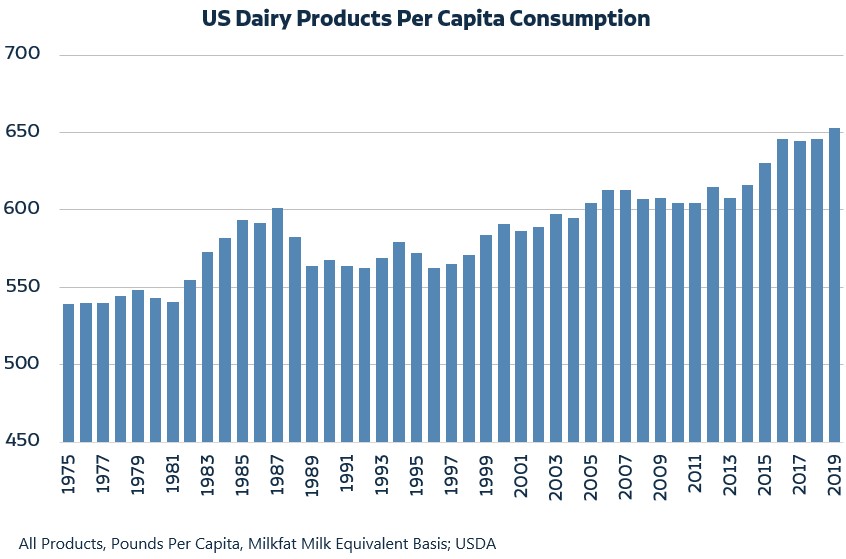
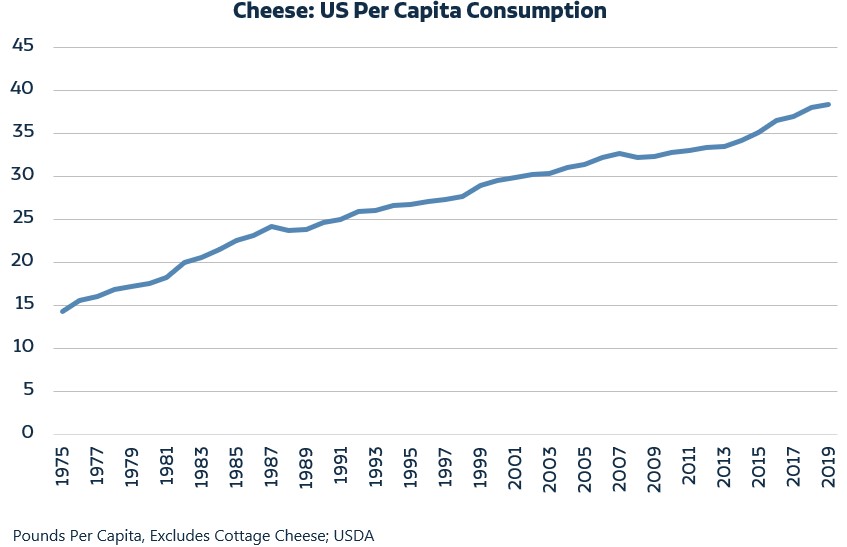
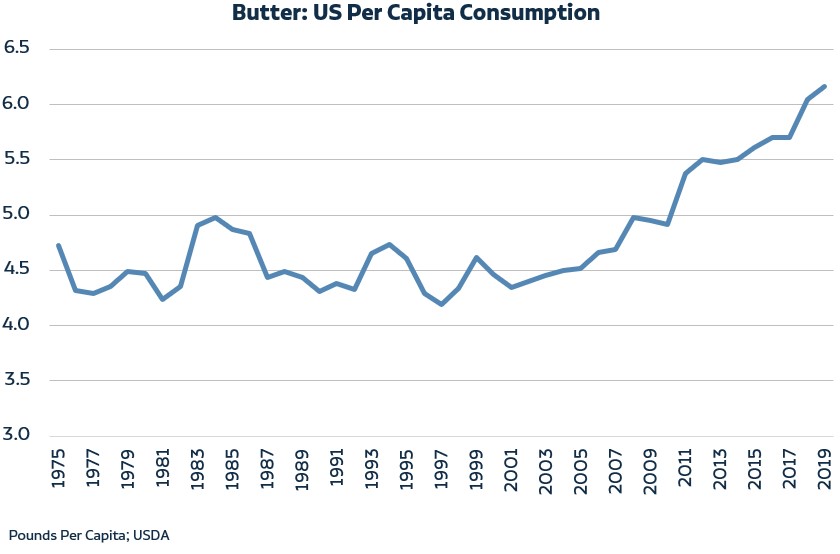
Tell our readers about the reach of the dairy industry, what they might not be aware of in terms of populations served and livelihoods supported?
Donald Moore (Executive Director of the Global Dairy Platform, which works to promote the nutrient richness of dairy products, bring balance and research to the role of milk fat in the diet and provide clarity on how dairy is managing its relationship with the environment):
In 2015, Global Dairy Platform (GDP) worked with the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations to determine just how far the dairy sector reaches, the people’s lives we impact. We all knew it was a big industry, but we didn’t know just how big.
They [the FAO] determined that there were 133 million dairy farms in the world. That’s a big number and it also conveys a lot in terms of the families that rely on the industry and the importance behind the nutrition dairy provides.
However, beyond the numbers, let’s talk scale – Based here in the U.S., we tend to think of dairy farms as reasonably large-scale, but in reality, the average dairy farm around the world hosts about three cows. Dairy farms are located in virtually every country in the world, including some small island nations and countries in the Middle East where you would assume the conditions weren’t viable for dairy, yet there they are.
There are some 600 million people living on those dairy farms around the world and if you take into account people who work upstream and downstream from the dairy farm, there’s another 400 million people whose livelihoods depend upon dairy.
We often talk about dairy as being a ‘billion-person community’, so suffice it to say, we support the livelihoods of one billion people, plus.
There are some 240 million full time jobs created by the dairy sector; of those jobs, approximately 80 million are held by women, so it’s a sector that actually has quite a large gender population balance. Of the 133 million dairy farms, 37 million are led by women. One of the things that we like to talk about is the role that dairy can play in bringing gender equality to the global agriculture and livestock sectors.
Jay Waldvogel (Senior Vice President, Strategy- Dairy Farmers of America): Around the world, annually, there are some six billion people who consume dairy. Now obviously, some consume more than others, but six billion people from a consumer perspective are aware of, are touched by, or have some relationship with dairy when it comes to their nutritional intake.
Donald Moore: Roughly ten percent of the world’s protein comes from the dairy sector. In many parts of the world, people lack protein in their diets. One of the things about the dairy sector that I admire is that it provides high-quality protein as well as many other micronutrients that are essential for healthy growth.
Margaret Munene (Co-founder of Palmhouse Dairies and a founding trustee of the Palmhouse Foundation): The Global Dairy Platform ultimately brings the global dairy sector together on a pre-competitive basis, to build evidence on dairy’s impact in a sustainable food system and significant role in the future of food. GDP membership includes more than 95 leading corporations, companies, associations, scientific bodies and other partners. GDP’s members have operations in more than 150 countries around the world and it’s important to note also, that GDP members collectively produce a third of all the world’s milk.
In times of crisis, such as this ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, we often talk about maintaining security by maintaining supply. Tell me about the security of supply pertaining to the dairy industry and its commitment to sustainable food systems…
Donald Moore: Sustainable food systems is a term very much de rigueur at the moment. We’ve been promoting the idea that you need to think about a food system in its totality. Some people started maybe six, seven years ago talking about sustainable diets. Yet diet is just one piece of the food system puzzle.
If you think about agricultural land around the world, approximately 70 percent of agricultural land is regarded as marginal land. In other words, it’s not land where you can plough and plant beans, corn, wheat, or anything else. It’s land that only becomes part of a productive food system when it’s grazed. So, the way we make that a useful contributor to the food system is by grazing it, either with dairy cows or buffalo, goat, sheep, a herd of some form. Those animals then turn that land into nutritious food that humans can consume.
In many parts of the developing world, livestock ownership can be the difference between dietary security / nutritional security and nutritional insecurity. We as a sector remain concerned about some of the discussions that go on at the moment about plants versus animals. We need to leverage all the tools that are available to secure nutrition for future generations. That includes making sure that all of this marginal land is being used as optimally as possible. Food security requires both plants AND animals.
That doesn’t mean that we as a dairy sector have not got our challenges. We recognize our sustainability challenges and have done a lot of work to improve the sustainability performance and the sustainability credentials of the dairy sector.
What is the Global Daily Platform’s approach then to this commitment to sustainability?
Jay Waldvogel: Let’s start at the very beginning when the Global Dairy Platform was created nearly 15 years ago. At that point in time, we were, fairly, being criticized for our environmental footprint. There wasn’t a lot of attention globally on it and it wasn’t that dairy farming necessarily was consciously bad, we just weren’t being as consciously good as we could have been.
Donald Moore: Since GDP’s inception, we’ve been doing a lot of work on how we improve dairy’s sustainability performance.
Together with the global dairy sector, we developed the Dairy Sustainability Framework (DSF) to track 11 strategic criteria to report on the progress dairy is making in areas such as greenhouse gas emissions, animal care, water quality, soil nutrients, among others.
The really good news is that we are seeing continuous improvement in dairy’s sustainability performance. For instance, analysis conducted by FAO found dairy’s emission intensity, or the volume of greenhouse gas emitted per kilogram of product, declined 11% from 2005-2015.
GDP has also been tackling how best we can help the developing world improve similar to, or perhaps even more so than the so-called developed world. If you think about greenhouse gasses, from here in the U.S. or in Europe, we produce roughly 1.2 to 1.4 kilograms of greenhouse gas per kilogram of dairy product produced. In parts of Africa, that’s somewhere between 12 to 18 kilograms of greenhouse gas per kilogram of product produced. So we recognize the opportunity for us to enhance the practices in the developing world and in doing so, reduce the environmental impacts of the dairy sector as a whole while improving farmer livelihoods and farm outcomes.
Margaret Munene: The dairy industry is also truly committed to taking the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) from theory to reality.
Clearly, when farmers have cows, they have milk, which is nutritious and provides them with Vitamin A and protein, among other impactful nutrients. From the milk those farmers sell, they now have the capital to purchase other foods. A cow also, importantly, produces manure which farmers use to fertilize their land, to produce other crops.
So, dairy farmers are often not hungry farmers. I have seen it with the many farmers I work with; they have money in their pockets. They can do many, many things, and actually have better livelihoods. Because they have money, they can take their children to school. Then they have bank accounts and from them, can acquire micro-credit loans. They can improve their herds and therefore, their lives cyclically actually become much better.
I see dairy as a very important sector, driving sustainable development in the developing world and also in the developed world.
Jay Waldvogel: We have an incredible commitment to improving collectively as an industry across numerous metrics. I think if you were to talk to the people at the UN and other agencies about how dairy is pursuing this versus other sectors, you’ll find we’re quite ahead of the curve.
It doesn’t mean we’re perfect at it. It doesn’t mean we’ve got it all solved, but we know our challenges, we know what we need to do, and we’re really actively engaged in measuring and understanding how we can get better.
How has the COVID-19 (coronavirus) pandemic impacted the operations of the global dairy sector?
Donald Moore: In some of the more developed countries, there have been challenges to our value chain because of the amount of dairy product that was previously going into food service; in restaurants, hotels, schools, etc. So, in that channel, the impact has been significant.
On the other side of the coin, however, consumer buying at a retail level had increased quite markedly. It hasn’t made up for losses in the food service area, mind you.
It is difficult for the sector to transition quickly from making 25-kilogram boxes of shredded cheese intended for the foodservice channel, for example, to putting that cheese into consumer-friendly sized packages for retail shelves.
The developing world didn’t really feel the challenge in the same way that those in the more developed world marketsdid. In the developing world, their challenges were probably more around transporting milk to processing facilities and so on.
Jay Waldvogel: While we had this rather painful moment immediately after COVID-19 broke out here in the U.S., today, we’re actually seeing a forward trajectory that is in fact quite positive, as people are reintroduced to dairy, reintroduced to its flexibility and nutrition and are reintroduced to the fact that there’s an awful lot of dairy products that actually taste quite good!
Margaret Munene: I think for me, COVID-19 has shown us how fragile supply chains can be within the global food system. It has spotlighted that disruption in one link can hurt many other links of the supply chain. And this is not just relegated to the dairy industry. This is, I think, applicable to all sectors for food and nutrition, including meat, fruits, and vegetables.
We run a dairy processing company in rural Kenya, for example. There, we partner with 500 small-scale farmers. Notably, 85% of those farmers are women. We collect milk, process it to make yogurt, and send that yogurt to the very high-end markets of Nairobi. However, at the moment, Nairobi’s five-star hotels and major restaurants have almost come to a standstill. And therefore there has been market disruption throughout, especially for processing companies.
But all is not lost, because we remain adaptive and very innovative. The dairy sector is well-positioned for the future because we are dealing with a product with a high nutritional value and now, more than ever, we need nutritional products like milk to boost our immune systems.
Milk is safe, it is nutritious, it is affordable, and therefore, looking into the future and past COVID-19, though there has been a disruption today, tomorrow still looks bright for the dairy industry.
Where do you envision the global dairy sector in the future?
Donald Moore: I see the dairy sector becoming more effective, more efficient.
From an industry perspective, we really see a bright future for the role that dairy plays. Milk consumption around the world continues to grow at just under two percent per annum. When you consider the size of the dairy sector, two percent is enormous growth in terms of volume.
We’re also actively involved in an initiative we call, “Dairy Nourishes Africa (‘DNA’)”. The idea behind this initiative is to use the dairy sector in such a way that we can tackle the issues of childhood malnutrition.
About 30% of children under the age of five in certain African countries suffer from malnutrition and particularly stunting and wasting. Wasting you can recover from, with appropriate intervention, but stunting is something that has very long-term effects.
Making sure that a child under the age of five has adequate nutrition and high-quality protein in their diet is extremely important to alleviate stunting. We’re looking at how we can use the dairy sector to help tackle those kinds of issues of malnutrition.
We have a series of pilots, which we’ve just literally in the last few weeks signed off on, which will happen in Tanzania and those pilots are intended to enhance the productivity of the sector, make milk more available locally, and for it to then be directed into school nutrition programs.
[To Margaret’s previous point], we are focused on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and how the dairy sector can help to address those key challenges. With regard to our ongoing collaboration with FAO, we [GDP] developed a research paper in conjunction with them 18 months ago about the impact that the dairy sector has on reducing poverty, which is SDG-1. Earlier this year, GDP again collaborated with FAO to publish a paper on SDG-2, emphasizing dairy’s role in ending hunger. And we’re in the process at the moment of preparing a paper on the impact that dairy has on disadvantaged groups; in particular, women and youth, and the role that dairy can [and already] plays in reducing inequalities.
So, there’s quite an active role that we think the dairy sector can take in helping to deliver on some of the key issues that are affecting society at large.
Jay Waldvogel: Dairy will play a lead role going forward. The question is, how big a role?
If dairy continues to improve on its environmental footprint, and I believe it will, if we can help explain to people the holistic impact dairy provides, this food system approach where you take into account, not just the impact you have environmentally, not just the nutritional benefits you bring, but those greater, critical societal issues, those economic issues, then dairy has an opportunity to remain a vital part of society going forward.
Margaret Munene: When you consider all that dairy provides, the nutrition and its health benefits, serving as a driving force for social and economic development in the process and taking into account further the progress that the sector is making in terms of reducing its impact on the planet; for me, I see the future of dairy looking extremely positive.
Dairy is a critically important sector in many ways; I really can’t imagine a future without dairy.
Source: globaltrademag.com








 The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that will establish an interagency process to further support exports of U.S. dairy products. Both agencies play critical roles in facilitating foreign sales of American-made dairy products, which is recognized and appreciated by the U.S. dairy industry. This MOU will draw upon the expertise of FDA as well as USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) and Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) to deepen and streamline their work together on the issues facing dairy exports to the benefit of U.S. dairy farmers and manufacturers.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) that will establish an interagency process to further support exports of U.S. dairy products. Both agencies play critical roles in facilitating foreign sales of American-made dairy products, which is recognized and appreciated by the U.S. dairy industry. This MOU will draw upon the expertise of FDA as well as USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) and Foreign Agricultural Service (FAS) to deepen and streamline their work together on the issues facing dairy exports to the benefit of U.S. dairy farmers and manufacturers. 





 After high school, Calvin Nisly, of Partridge, Kan., wanted to wash his hands of the family dairy. He enjoyed milking cows growing up, but after high school, he did not want to be tied down to a dairy farm. Eventually, his love for cows and living off the land won out.
After high school, Calvin Nisly, of Partridge, Kan., wanted to wash his hands of the family dairy. He enjoyed milking cows growing up, but after high school, he did not want to be tied down to a dairy farm. Eventually, his love for cows and living off the land won out.
 More than 50 milk producers spilled about 200 litres of milk on the road on the Four-Road area in Dharmapuri town on Wednesday to protest certain management decisions of state-run milk co-operative Aavin.
More than 50 milk producers spilled about 200 litres of milk on the road on the Four-Road area in Dharmapuri town on Wednesday to protest certain management decisions of state-run milk co-operative Aavin.

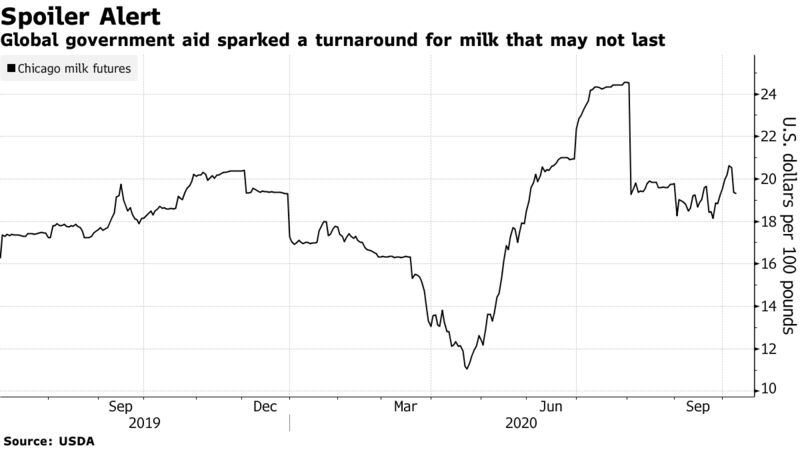
 U.S. milk production volumes had finished higher on a YOY basis over 61 consecutive months from Jan ’14 – Jan ‘19, reaching the longest period of consecutive growth on record, prior to declining by a total of 0.3% from Aug ’19 – Aug ’19. Milk production volumes rebounded throughout more recent months, however, finishing higher over 13 of the past 14 months through Aug ’20. The 12-month rolling average milk production growth rate reached a 28 month high level throughout Aug ’20.
U.S. milk production volumes had finished higher on a YOY basis over 61 consecutive months from Jan ’14 – Jan ‘19, reaching the longest period of consecutive growth on record, prior to declining by a total of 0.3% from Aug ’19 – Aug ’19. Milk production volumes rebounded throughout more recent months, however, finishing higher over 13 of the past 14 months through Aug ’20. The 12-month rolling average milk production growth rate reached a 28 month high level throughout Aug ’20.  YOY increases in production on a percentage basis were led by South Dakota (+10.8%), followed by Texas (+7.1%), Kansas (+6.6%) and Indiana (+6.6%), while production volumes finished most significantly lower YOY on a percentage basis within Vermont (-5.3%), Florida (-3.9%) and Utah (-2.1%). Wisconsin milk production remained lower on a YOY basis for the eighth time in the past ten months, finishing 0.3% below previous year levels. Overall, 16 of the 24 states milk production figures are provided for experienced YOY increases in production throughout the month.
YOY increases in production on a percentage basis were led by South Dakota (+10.8%), followed by Texas (+7.1%), Kansas (+6.6%) and Indiana (+6.6%), while production volumes finished most significantly lower YOY on a percentage basis within Vermont (-5.3%), Florida (-3.9%) and Utah (-2.1%). Wisconsin milk production remained lower on a YOY basis for the eighth time in the past ten months, finishing 0.3% below previous year levels. Overall, 16 of the 24 states milk production figures are provided for experienced YOY increases in production throughout the month.  California milk production volumes increased on a YOY basis for the eighth consecutive month throughout Aug ’20, finishing up 1.8%. California accounted for 18.2% of total U.S. milk production volumes throughout the month, leading all states.
California milk production volumes increased on a YOY basis for the eighth consecutive month throughout Aug ’20, finishing up 1.8%. California accounted for 18.2% of total U.S. milk production volumes throughout the month, leading all states.  Seven of the top ten largest milk producing states experienced YOY increases in production throughout Aug ’20, as milk production within the top ten milk producing states increased by a weighted average of 1.7% throughout the month. The aforementioned states accounted for nearly three quarters of the total U.S. milk production experienced during Aug ’20. Production volumes outside of the top ten largest milk producing states increased 2.3% on a YOY basis throughout the month.
Seven of the top ten largest milk producing states experienced YOY increases in production throughout Aug ’20, as milk production within the top ten milk producing states increased by a weighted average of 1.7% throughout the month. The aforementioned states accounted for nearly three quarters of the total U.S. milk production experienced during Aug ’20. Production volumes outside of the top ten largest milk producing states increased 2.3% on a YOY basis throughout the month.  Aug ’20 YOY increases in milk production on an absolute basis continue to be led by Texas, followed by California and Idaho, while YOY declines in production on an absolute basis were most significant throughout Vermont.
Aug ’20 YOY increases in milk production on an absolute basis continue to be led by Texas, followed by California and Idaho, while YOY declines in production on an absolute basis were most significant throughout Vermont.  The Jul ’20 U.S. milk cow herd was revised 8,000 head higher than levels previous stated while the Aug ’20 figure remained unchanged month-over-month. The U.S. milk cow herd currently stands at 9.36 million head, finishing 42,000 head above the previous year but remaining 78,000 head below the 23 year high level experienced during Jan ’18.
The Jul ’20 U.S. milk cow herd was revised 8,000 head higher than levels previous stated while the Aug ’20 figure remained unchanged month-over-month. The U.S. milk cow herd currently stands at 9.36 million head, finishing 42,000 head above the previous year but remaining 78,000 head below the 23 year high level experienced during Jan ’18.  U.S. milk per cow yields finished 1.4% above previous year levels, finishing higher on a YOY basis for the 57th time in the past 58 months. Yields experienced throughout the Midwestern states of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa and Illinois finished 1.8% higher on a YOY basis while yields experienced throughout the Western states of California, Idaho, Washington and Oregon increased 0.8% YOY.
U.S. milk per cow yields finished 1.4% above previous year levels, finishing higher on a YOY basis for the 57th time in the past 58 months. Yields experienced throughout the Midwestern states of Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa and Illinois finished 1.8% higher on a YOY basis while yields experienced throughout the Western states of California, Idaho, Washington and Oregon increased 0.8% YOY.  A month-over-month increase in the Indiana milk cow herd offset a MOM decline in the Georgia milk cow herd throughout Aug ’20.
A month-over-month increase in the Indiana milk cow herd offset a MOM decline in the Georgia milk cow herd throughout Aug ’20.  YOY increases in milk cow herds continued to be led by Texas, followed by Idaho and South Dakota, while Wisconsin experienced the largest YOY decline in their milk cow herds throughout the month
YOY increases in milk cow herds continued to be led by Texas, followed by Idaho and South Dakota, while Wisconsin experienced the largest YOY decline in their milk cow herds throughout the month
 The Aug ’20 YOY increase in New Zealand milk production volumes was the fourth experienced in a row and the largest experienced throughout the past 14 months a on percentage basis. New Zealand milk production volumes have reached record high seasonal levels over each of the past four months. ’19-’20 annual milk production volumes declined 0.7% on a YOY basis however production on a milk-solids basis increased 0.3% YOY throughout the period. Drought conditions impacted the milk supply throughout the ’19-’20 production season. ‘20-’21 YTD New Zealand milk production volumes have rebounded by 4.7% on a YOY basis throughout the first quarter of the production season.
The Aug ’20 YOY increase in New Zealand milk production volumes was the fourth experienced in a row and the largest experienced throughout the past 14 months a on percentage basis. New Zealand milk production volumes have reached record high seasonal levels over each of the past four months. ’19-’20 annual milk production volumes declined 0.7% on a YOY basis however production on a milk-solids basis increased 0.3% YOY throughout the period. Drought conditions impacted the milk supply throughout the ’19-’20 production season. ‘20-’21 YTD New Zealand milk production volumes have rebounded by 4.7% on a YOY basis throughout the first quarter of the production season.  Farmgate Milk Prices Fonterra finalized their ’19-’20 farmgate milk price at a value of $7.14/kgMS, reaching a six year high level. Fonterra’s ’20-’21 farmgate milk price forecast was unchanged from the previous month through Sep ’20, remaining at a range of $5.90-$6.90/kgMS. Fonterra’s ’20-’21 farmgate milk price forecast range remains historically wide as significant uncertainties remain surrounding the impact of COVID-19 on global demand.
Farmgate Milk Prices Fonterra finalized their ’19-’20 farmgate milk price at a value of $7.14/kgMS, reaching a six year high level. Fonterra’s ’20-’21 farmgate milk price forecast was unchanged from the previous month through Sep ’20, remaining at a range of $5.90-$6.90/kgMS. Fonterra’s ’20-’21 farmgate milk price forecast range remains historically wide as significant uncertainties remain surrounding the impact of COVID-19 on global demand.  Cow & Heifer Slaughter New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates increased 14.0% on a YOY basis during Jul ’20 when normalizing for slaughter days, reaching a 34 year high seasonal level. The YOY increase in New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates was the second experienced in a row. Jul ’20 dairy cow & heifer slaughter, which has more limited historical data available, also increased on a YOY basis for the second consecutive month, finishing up 7.0%. ’19-’20 annual New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates rebounded 2.7% from the previous year, reaching a four year high level. ’20-’21 YTD New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates have increased by an additional 9.6% on a YOY basis throughout the first two months of the production season.
Cow & Heifer Slaughter New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates increased 14.0% on a YOY basis during Jul ’20 when normalizing for slaughter days, reaching a 34 year high seasonal level. The YOY increase in New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates was the second experienced in a row. Jul ’20 dairy cow & heifer slaughter, which has more limited historical data available, also increased on a YOY basis for the second consecutive month, finishing up 7.0%. ’19-’20 annual New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates rebounded 2.7% from the previous year, reaching a four year high level. ’20-’21 YTD New Zealand cow & heifer slaughter rates have increased by an additional 9.6% on a YOY basis throughout the first two months of the production season.  New Zealand milk production volumes increased at a compound annual growth rate of 4.2% over the ten year period ending during the ’14-’15 record production season but have trended flat-to-lower over the four most recent production seasons as farmgate milk prices declined from the ’13-’14 record high levels and the New Zealand milk cow herd was reduced. USDA is projecting the New Zealand milk cow herd will decline slightly on a YOY basis throughout 2020 but remain above the six year low level experienced throughout 2017.
New Zealand milk production volumes increased at a compound annual growth rate of 4.2% over the ten year period ending during the ’14-’15 record production season but have trended flat-to-lower over the four most recent production seasons as farmgate milk prices declined from the ’13-’14 record high levels and the New Zealand milk cow herd was reduced. USDA is projecting the New Zealand milk cow herd will decline slightly on a YOY basis throughout 2020 but remain above the six year low level experienced throughout 2017. 
 The USDA is projecting Argentine milk production will increase by 4.3% on a YOY basis throughout the 2020 calendar year as a positive margin environment, coupled with positive weather conditions, is expected to incentivize production expansion. USDA noted inflation and currency devaluation will begin to cut into profitability as the year goes on, however, while domestic demand is expected is fall due to a contraction in GDP related to COVID-19. 2020 YTD milk production is up 8.0% on a YOY basis throughout the first two thirds of the calendar year.
The USDA is projecting Argentine milk production will increase by 4.3% on a YOY basis throughout the 2020 calendar year as a positive margin environment, coupled with positive weather conditions, is expected to incentivize production expansion. USDA noted inflation and currency devaluation will begin to cut into profitability as the year goes on, however, while domestic demand is expected is fall due to a contraction in GDP related to COVID-19. 2020 YTD milk production is up 8.0% on a YOY basis throughout the first two thirds of the calendar year.  Recently experienced adverse conditions contributed to the Argentine dairy cow herd declining to a long-term record low level throughout 2019, finishing lower for the seventh consecutive year. USDA is projecting the Argentine dairy cow herd will rebound by 0.8% throughout 2020, however. Recent declines in the Argentine dairy cow herd resulted in a consolidation of operations along with a culling of the lowest producing cows.
Recently experienced adverse conditions contributed to the Argentine dairy cow herd declining to a long-term record low level throughout 2019, finishing lower for the seventh consecutive year. USDA is projecting the Argentine dairy cow herd will rebound by 0.8% throughout 2020, however. Recent declines in the Argentine dairy cow herd resulted in a consolidation of operations along with a culling of the lowest producing cows.  Argentina is the second largest milk producing country in South America, trailing only Brazil, and the fifth largest global dairy exporter, trailing only New Zealand, the EU-28, the U.S. and Australia. Of the aforementioned major dairy exporting regions, Argentina accounted for 3.6% of total combined milk production and 2.8% of combined butter, cheese, nonfat dry milk (NFDM) and whole milk powder (WMP) export volumes throughout 2019.
Argentina is the second largest milk producing country in South America, trailing only Brazil, and the fifth largest global dairy exporter, trailing only New Zealand, the EU-28, the U.S. and Australia. Of the aforementioned major dairy exporting regions, Argentina accounted for 3.6% of total combined milk production and 2.8% of combined butter, cheese, nonfat dry milk (NFDM) and whole milk powder (WMP) export volumes throughout 2019.  The bulk of Argentine dairy exports are in the form of WMP and cheese. Argentina was the third largest exporter of WMP throughout 2019, trailing only New Zealand and the EU-28, accounting for 4.7% of global WMP export volumes. From a global perspective, WMP markets Aug be most affected by a continued rebound in Argentine milk production.
The bulk of Argentine dairy exports are in the form of WMP and cheese. Argentina was the third largest exporter of WMP throughout 2019, trailing only New Zealand and the EU-28, accounting for 4.7% of global WMP export volumes. From a global perspective, WMP markets Aug be most affected by a continued rebound in Argentine milk production. 



 President Donald Trump trails in the polls in Wisconsin and Minnesota, but he is banking on the support of one group whose fortunes have improved somewhat in the past year: dairy farmers.
President Donald Trump trails in the polls in Wisconsin and Minnesota, but he is banking on the support of one group whose fortunes have improved somewhat in the past year: dairy farmers. THIS WEEK marked the closure of Defra’s 12-week long consultation on contractual relationships in the UK dairy industry.
THIS WEEK marked the closure of Defra’s 12-week long consultation on contractual relationships in the UK dairy industry.