Cheese tanked. Buyers ghosted. Farmers bleeding. Welcome to Monday in dairy.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: You know something’s broken when cheese crashes 10¢ on just TWO trades—that’s exactly what happened today, taking $1/cwt straight out of December milk checks. But here’s what really hurts: the Class III-IV spread hit $3.19, meaning your neighbor shipping Class III is making $45,000 more annually than Class IV shippers on the same-sized farm. We’ve got 9.52 million cows out there—most since 1993—flooding a market where Europe’s selling cheese 37% cheaper and China’s buying less. At $13.90 Class IV against $320/ton feed, even efficient operations are bleeding $2/cwt. The farms that’ll survive are doing three things right now: locking any Class III over $17, cutting cow numbers 15%, and banking six months of operating capital—because this isn’t a correction, it’s a reckoning that’ll last into 2026.

What I’ve found is these aren’t just price moves anymore—they’re survival signals. Here’s what shifted at Chicago today:
| Product | Today’s Close | Change | Farm Impact |
| Cheese Blocks | $1.6650/lb | -10.25¢ | December checks drop ~$1.00/cwt |
| Cheese Barrels | $1.7500/lb | -5.50¢ | Processors drowning in inventory |
| Butter | $1.5775/lb | -3.25¢ | Class IV trapped at breakeven |
| NDM | $1.1300/lb | -0.25¢ | Export competitiveness fading |
| Dry Whey | $0.7100/lb | No change | The only bright spot holding |
Now, what’s really telling here—and you probably noticed this too—is the volume. Or lack thereof, I should say. Nine trades total across all products. Nine! I’ve seen more action at a Tuesday card game in Ellsworth.

When blocks drop a dime on just two trades, it means the price is falling without any real buying support. Those seven offers stacked up? That’s sellers lined up at the door with no buyers in sight. The market isn’t trading; it’s collapsing in a vacuum.
Why This Class Spread Breaks Farms
You know, I’ve been tracking these markets since the ’90s, and this $3.19 gap between Class III at $17.09 and Class IV at $13.90… it’s something else entirely. Three Wisconsin cooperative fieldmen I talked with this morning—all asking to stay anonymous, naturally—painted the same picture: their Class IV shippers are hemorrhaging cash.
“Members are culling anything that looks sideways,” one told me. And at $13.90, even efficient operations lose two bucks per hundred minimum.
Here’s what makes this worse than 2016’s collapse, if you can believe it: feed costs then were 40% lower. The CME futures data shows December corn at $4.3475 a bushel and soybean meal above $320 a ton. You do that math—it doesn’t work.

Regional Pain Points
Wisconsin’s Double Whammy: So Wisconsin’s most recent production data—this is for September, released in October—shows 2.76 billion pounds according to USDA NASS. But here’s the kicker: regional premiums flipped from plus 40¢ in January to minus 15¢ now. That’s a 55-cent swing nobody budgeted for. And meanwhile, local plants are running four-day weeks, while Texas adds 5 million pounds of daily capacity? That’s not a market; it’s a massacre.
Texas Keeps Growing: What’s encouraging for them—not so much for us up north—is that Texas grew 10.6% year-over-year with 50,000 new cows added by April 2025. Their breakeven point is around $14.50, which means they’re still profitable while Upper Midwest farms bleed out. Different labor costs, different feed sourcing… it’s almost like two separate industries now.
California’s H5N1 Factor: Nearly 1,000 confirmed dairy herd cases across 16 states according to USDA APHIS data, with California ground zero. Production down 1.4%—and ironically, that’s the only thing keeping cheese from hitting $1.50.
The Global Picture Nobody Wants to See
Looking at this from 30,000 feet, as they say, we’re seeing convergence of every bearish factor possible. New Zealand’s production is up 2.8% according to Fonterra’s latest data from the Weekly Global Dairy Market Recap. European cheese crashed 37% year-over-year—and when EU product trades at €2,088 per metric ton, why would anyone buy American?
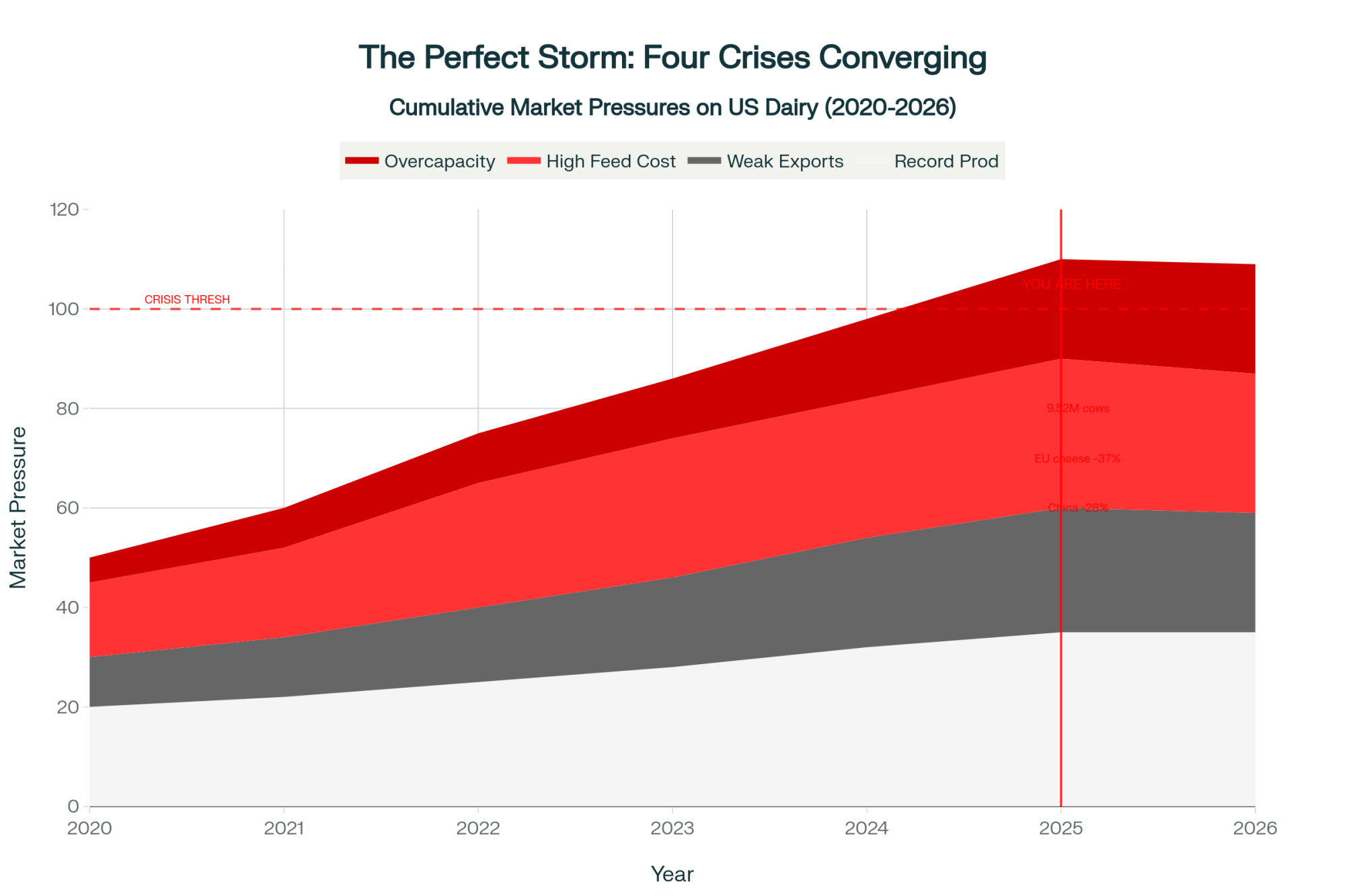
China’s pulling back too—total imports up just 6% through July, but that’s still 28% below their 2021 peaks. They’re cherry-picking what they need: whey up, everything else sideways or down. And Mexico, our biggest customer? They’ve been discussing dairy self-sufficiency targets for 2030. That could mean 230,000 metric tons of powder exports are potentially gone.
A StoneX trader told me Friday—and I think he nailed it—”The U.S. is the Cadillac in a world shopping for Chevys.”
Feed Markets: The Other Shoe Dropping
The milk-to-feed ratio tells the whole story: 1.48 right now. You need 2.0 for decent margins, generally speaking, and 1.8 to break even.
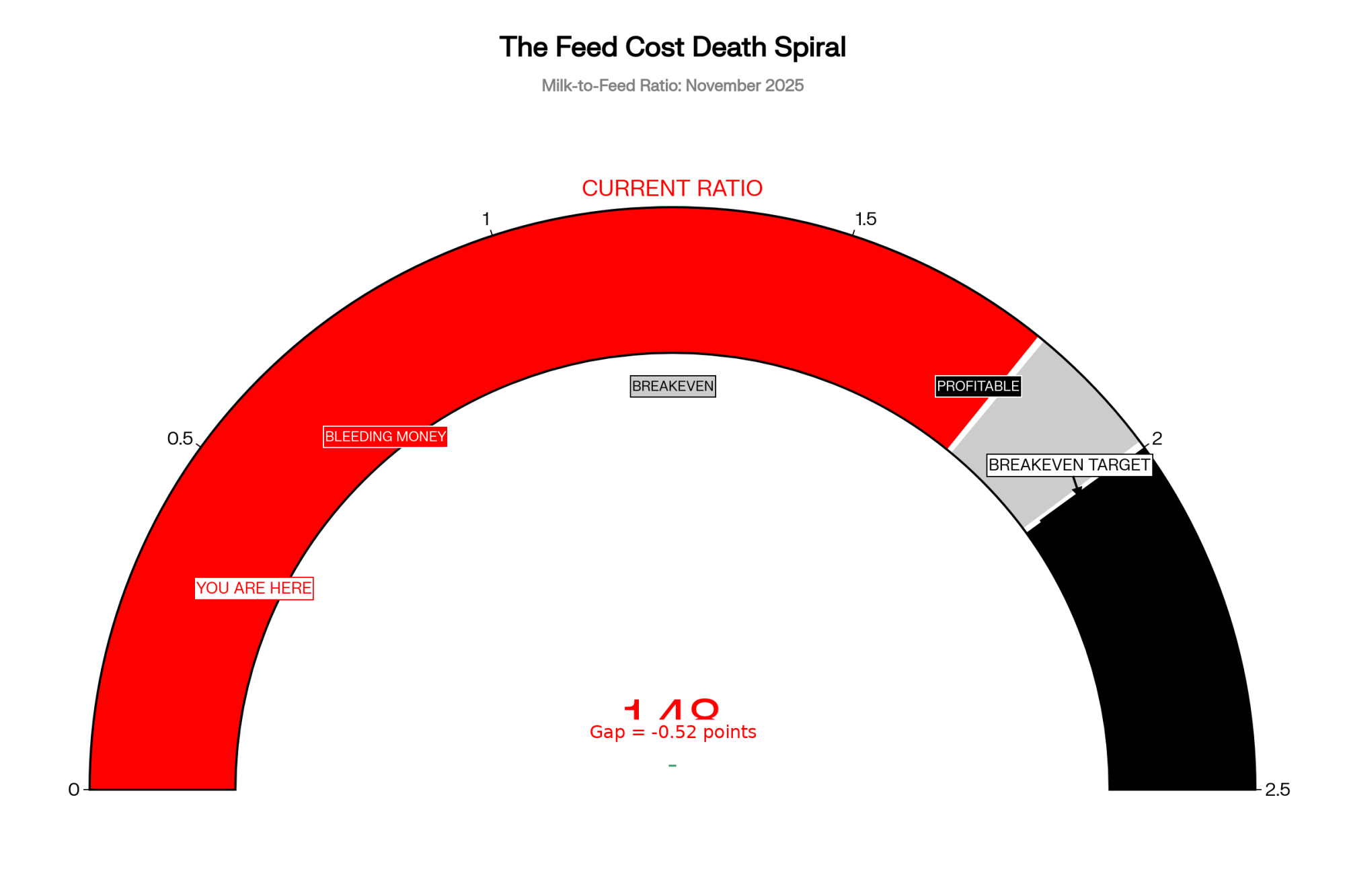
December corn at $4.3475 offers no relief. Western Wisconsin hay dealers? They want $280 a ton delivered for decent mixed—if they’ll even quote you. The latest WASDE Report mentions the U.S.-China trade deal promising 25 million tonnes annually, but you know, that’s maybe next year, not this month’s certain.
Processing Plants Playing Different Games
So here’s what really gets me: three cheese plants just announced 400 million pounds of new capacity for 2026. Hilmar’s Texas facility cranks up in January—5 million pounds daily. Meanwhile, Wisconsin plants run four-day weeks, managing inventory.
How’s that make sense? Well, it doesn’t—unless you realize processors profit on volume, not price. They don’t really care if cheese is $1.60 or $2.10. They care about throughput. More milk equals more margin dollars even at lower percentages. But farmers? We need price, not volume. That fundamental disconnect… that’s what’s killing us.
What Smart Operations Do Now
Here’s what the survivors are telling me, and it’s worth noting these aren’t the guys complaining at the coffee shop—these are the ones actually making it work:
Lock anything over $17 for Class III immediately. One large Wisconsin producer locked 40% of his Q1 production last week at $17.20. As he put it, “I’m not swinging for fences anymore. Singles keep you in the game.”
Cull deep, cull strategically. With springers at $2,100, that third-lactation cow with feet issues? She’s worth more as beef. Several nutritionists report their clients running 15% lower numbers—on purpose.
Component premiums still matter. Dry whey holding at 71¢ means protein still pays. Farms maximizing components—and you know who you are—they’re seeing 30-40¢ more per hundredweight. Not huge, but it’s something.
Rethink expansion completely. Pete Johnson, who ships direct to a cheese plant, told me something interesting: “My neighbor’s co-op pays $1.40 more in premiums, but after deductions, we net about the same. Difference is, I can walk if needed.”
Cooperatives Scrambling for Answers
You know, DFA’s base-excess programs start December 1st, cutting deliveries 5% from last year. Land O’Lakes is paying 25¢ per somatic cell under 100,000—quality over quantity, finally.
What’s interesting is Cornell research shows non-co-op handlers paying 37% quality premiums versus co-ops at 29%. But co-ops counter with competitive premiums, keeping members from jumping. Mixed signals everywhere you look.
The Six-Month Survival Test
Let me be straight with you: if you’re shipping Class IV milk right now, you need at least 6 months of cash reserves. December checks—and I hate to be the bearer of bad news—will drop $1.00 to $1.50 per hundredweight from November based on current futures.
The Federal Order reform coming January 1st? It’ll shift maybe 30¢ from Class I to manufacturing. That’s like putting a Band-Aid on an amputation, honestly.
California’s methane rules adding 45¢ per hundredweight compliance costs starting July… USDA projecting 230 billion pounds production for 2025 in their October forecast… We don’t need more milk, folks. We need less.
The Bottom Line
You know, standing here looking at these numbers, I keep remembering what my dad used to say: “The cure for low prices is low prices.” Eventually, enough producers quit, supply tightens, and prices recover. But how many good families lose everything getting there?
Today’s 10¢ cheese crash wasn’t a correction—it was capitulation. Blocks at $1.67 with seven offers stacked and two lonely bids? That’s not a market; it’s a distress sale. The funds have bailed, end users are covered, and producers… well, we’re holding the bag.
If you’re planning an expansion, stop. Those new parlor dreams? Shelve them. With 9.52 million cows out there—the highest since 1993, according to USDA data—we’re looking at 6 to 12 months before any real relief.
The farms that’ll make it through are the ones acting now: cutting costs aggressively, optimizing components over volume, maintaining working capital for the storm ahead. Everyone else? Well, auction barns are busy again for a reason.
Your November milk check just got lighter—that’s the reality. Tomorrow morning in the parlor, before dawn breaks and that first cup kicks in, ask yourself this: Am I farming to live, or living to farm?
Because at these prices, you better know the answer.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Ghost Town Trading: Cheese crashed 10¢ on just TWO trades today—when seven sellers can’t find buyers, your December check loses $1/cwt
- Tale of Two Farms: Identical 200-cow operations, but Class III shippers bank $45,000 more annually than Class IV neighbors—same work, vastly different pay
- Perfect Storm Brewing: Record 9.52M U.S. cows flooding markets while EU cheese trades 37% cheaper and Mexico eyes dairy independence by 2030
- The $2/cwt Bleed: At $13.90 Class IV milk vs $320/ton feed, even top-tier operations lose money before paying labor, vet, or utilities
- Survival Playbook: Winners are doing three things NOW—locking any Class III over $17, strategically culling 15% of herds, and banking 6+ months operating capital for the long winter ahead
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- December 1 Deadline: How Cutting 15% of Your Herd Could Add $40,000 to Your Bottom Line – This provides the exact 90-day playbook for the “cull strategically” advice in the main report, revealing how to identify underperformers and use beef-on-dairy genetics to immediately cut costs and capture new revenue streams.
- Why Dairy Markets Can’t Self-Correct Anymore: The Hidden Forces Reshaping the Dairy Industry’s Future – This strategic analysis directly challenges the “cure for low prices is low prices” mentality by exposing the structural forces, from EU co-op rules to U.S. digester contracts, that lock in oversupply even when prices crash.
- Unlock Hidden Dairy Profits Through Lifetime Efficiency: How Modern Genetics and Strategic Nutrition Can Cut Feed Costs by $251 Per Cow – While the main report outlines the feed cost crisis, this article delivers an innovative solution. It demonstrates how to leverage genetic selection for feed efficiency (RFI) to achieve specific, measurable cost savings of $251 per cow.
 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
Every week, thousands of producers, breeders, and industry insiders open Bullvine Weekly for genetics insights, market shifts, and profit strategies they won’t find anywhere else. One email. Five minutes. Smarter decisions all week.






 The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.
The Sunday Read Dairy Professionals Don’t Skip.



