How Measurement Errors Cost Dairy Farms $200,000 Annually—And What to Do About It
Executive Summary: Here’s the uncomfortable truth: most dairy operations are losing $200,000 annually to feed shrink they can’t see because traditional measurement methods are off by 15-30%. This hidden crisis came to light when Dean DePestel applied mining industry drone technology to his Minnesota dairy’s silage inventory, discovering discrepancies that are now being confirmed across the industry. While the Statz Brothers’ transformation—cutting shrink from 10% to 2-3% and saving $500,000 yearly—demonstrates the potential, you don’t need their million-dollar infrastructure. Five targeted improvements (face management, scale calibration, ingredient tracking, right-sized bunkers, and refusal optimization) can recover $100,000+ annually for an investment of under $20,000. Drone measurement services at $2,000-5,000 per year deliver quarterly measurements accurate to 1-2%, replacing guesswork with data. Any operation can start with a free 30-day test—tracking mixer output, bunks, and pile faces—to identify their gap. With industry consolidation accelerating and processors demanding sustainability documentation, farms that can’t measure and prove their efficiency won’t just lose money—they’ll lose market access.

I recently spoke with a producer in central Wisconsin who discovered something that made both of us pause. After twenty-five years of dairy farming, he finally measured his silage inventory with precision technology and found he had 23% less feed than his calculations suggested. That’s not a rounding error—that’s planning for April and running out in February.
This builds on what we’ve been seeing across the industry. Recent studies show that drone feed measurements reveal errors ranging from 15% to over 30% between traditional estimation methods and actual silage inventory. The financial implications are substantial, yet many operations haven’t recognized this as a solvable problem.
What’s particularly noteworthy is how this revelation emerged from an unexpected source. Dean DePestel, who farms at Daley Farms in Lewiston, Minnesota, happens to be a mechanical engineer. When he read about mining companies using drone technology to measure tailings piles with remarkable accuracy, he wondered if the same approach could work for silage inventory. As documented in a 2022 Ag Proud article, his curiosity led to discoveries that are reshaping how progressive operations think about feed management.

Understanding Where Traditional Methods Fall Short
The dairy industry has relied on tape measures, wheel measurers, and visual estimates for generations. Derek Wawack from Alltech captured it well in a recent Dairy Herd interview when he described these as “about everything to guess what was in forage piles.” These methods served us adequately when margins were wider and feed costs were lower. Current conditions demand better precision.
Harrison Hobart’s work with Alltech’s Aerial Inventory Program reveals why our traditional approaches struggle. Over two years of measuring corn silage density across multiple operations, he documented variations from 12 pounds to 24 pounds of dry matter per cubic foot within drive-over piles. This aligns with what many nutritionists have suspected but couldn’t quantify.
Consider the economics: A typical 1,000-cow operation today faces daily feed costs of $7 to $8 per cow—roughly $2.5 to $2.9 million annually. When research from land-grant universities, including recent work from Hubbard Feeds and Amelicor, shows shrink rates between 5% and 15% on farms without systematic measurement protocols, the financial exposure becomes clear. At 8% shrink—a conservative estimate for many operations—that represents $204,400 annually on a 1,000-cow dairy.
The Compound Nature of Measurement Errors
Pennsylvania State research offers insight into why single-point measurements mislead us. Their work found bunker density averaging 15.5 pounds of dry matter per cubic foot at the bottom, while the top averaged just 11.2 pounds—a 38% variation within the same structure. When we take one or two core samples and extrapolate, we’re essentially guessing.
This variation extends beyond density. I’ve observed haylage piles where dry matter content ranges from 25% to 55% across different sections. These aren’t poorly managed operations—they’re typical farms dealing with the realities of weather windows, equipment limitations, and labor constraints during harvest.
A Wisconsin Case Study in Transformation
The Statz Brothers operation near Marshall, Wisconsin, offers valuable lessons for the industry. This family has been dairy farming since 1966 and currently manages 4,400 cows across two locations. By any conventional measure, they were successful. Yet they faced a challenge many producers will recognize: feed inventory that seemed to disappear faster than expected.

Todd Follendorf, their nutritionist from Cornerstone Dairy Nutrition, quantified what they suspected. As he explained to Dairy Global, “Before, we had shrink percentages of around 10% every single day.” For an operation of their size, that translated into over $1.28 million in annual feed losses.
Their response during a 2015 expansion was instructive. Rather than replicating existing infrastructure, they partnered with Mike Greene, a feed management specialist who had developed the TMR Audit system. Together, they designed a 36,600-square-foot fully enclosed feed center—not simply a commodity shed with walls, but a purpose-built facility that protects feed from placement to feeding.
The documented results speak to what’s possible: shrink rates dropped from 10% to 2%-3%. Even conservative calculations suggest annual savings exceeding $500,000, with the investment paying for itself in under three years.
Yet—and this is crucial for most operations—you don’t need their scale of infrastructure to capture significant benefits.
Practical Improvements That Deliver Returns

Through conversations with producers and nutritionists across different regions—from California’s Central Valley to Vermont’s grazing operations—I’ve identified five changes that consistently deliver returns without requiring major capital investment:
1. Optimizing Silage Face Management
Research from UC Davis, widely shared through extension programs, demonstrates that oxygen penetrates up to 3 feet into well-packed silage. When removal rates are too slow—say, 4 inches daily instead of the recommended 6 to 12 inches—that creates an active spoilage zone.
Wisconsin and Penn State extension specialists recommend removing 6 to 12 inches daily in winter, increasing to 10 to 12 inches during warmer months. The technique matters too: scraping from top to bottom rather than digging underneath prevents cracks that increase surface area by 9% or more.
I recently visited a 1,500-cow operation in northeastern Wisconsin that implemented these changes without any equipment purchases. Their estimated savings: $6,000 to $8,000 annually from reduced spoilage alone. A similar operation in California’s San Joaquin Valley reported even higher savings due to the year-round heat stress on exposed faces.
2. Addressing Mixer Scale Accuracy
This issue deserves more attention than it typically receives. Ohio State researchers evaluated mixer wagon scales on 22 dairy farms and found that only half were functioning within acceptable tolerance. A 2% systematic error across all ingredients—easily overlooked in daily operations—costs a 1,000-cow dairy approximately $54,750 annually.
The solution is straightforward: quarterly calibration checks using certified truck scales. The process takes an afternoon, costs $500 to $1,500 for professional calibration if needed, and can identify problems before they compound into significant losses.
3. Ingredient-Specific Shrink Management
Different feedstuffs have dramatically different shrink characteristics, yet many operations apply a uniform percentage across all ingredients. Cornell’s economic analysis and recent coverage in Hoard’s Dairyman highlight this opportunity.
Cottonseed might experience 4% shrink while fine distillers grains can reach 12% to 15%. One documented case at Cornell showed that relocating high-shrink ingredients closer to mixing areas substantially reduced handling losses—a simple change with a meaningful impact.
4. Right-Sizing Face Width to Removal Capacity
Many operations built bunkers for anticipated expansion that hasn’t materialized. An 80-foot-wide bunker makes sense for 2,000 cows, not 1,200. When removal rates are too slow for bunker width, the outer portions essentially compost while you work across.
Penn State’s bunker silo research confirms this is widespread. The solution doesn’t require construction—work bunkers in sections, covering inactive portions. For future construction, consider narrower drive-over piles that match actual removal capacity.
5. Refining Refusal Management
Multiple feeding studies demonstrate that well-managed operations can reduce refusals from 5% to 2% while maintaining or improving intake. On a 1,000-cow dairy, that 3% difference represents $40,000 to $70,000 annually.
This requires discipline: pushing feed every two hours, training someone to read bunks consistently, and finding productive uses for quality refused feed rather than composting it. Yes, labor is challenging, but the returns justify the effort.
The Implementation Journey
When operations begin measuring feed inventory precisely with drone technology or other precision tools, the journey typically follows a predictable pattern. The initial measurement often reveals significantly less inventory than expected—it’s common to discover you’re 15% to 20% short of calculations. This can be unsettling, but it’s also the beginning of improvement.
After the initial surprise, patterns emerge. Operations start connecting measurement data with daily observations. Perhaps loads from one supplier are consistently light, or the mixer has been overfeeding certain pens. By month six, farms implementing systematic changes typically see 2 to 5 percentage points of shrink reduction—not from major investments, but from addressing previously invisible problems.
What I find encouraging is how feed management software integration is evolving to support these efforts. Modern systems can now incorporate drone measurement data directly into inventory tracking, creating real-time dashboards that flag anomalies before they become crises.
The Human Element in Feed Management
Technology alone doesn’t reduce shrink—people using technology systematically do. Successful implementation requires clear ownership and accountability.
The operations achieving the best results designate one person whose primary responsibility (representing 70% to 80% of their time) is feed management. Not someone who feeds when they’re done milking, but someone whose success is measured by feed efficiency and shrink reduction.
Your nutritionist plays a crucial role through weekly or biweekly visits, but they’re designing rations and troubleshooting, not managing daily operations. The distinction matters. Meanwhile, owners or managers need to invest 3 to 5 hours weekly reviewing data and making strategic decisions. This team approach, documented in Michigan State Extension research and Bovine Practitioner guidelines, consistently outperforms fragmented responsibility.
Understanding the Limitations
Professional integrity requires acknowledging the constraints of this technology. Weather presents the primary challenge—most agricultural drones can’t operate in rain or winds exceeding 20 mph. The battery provides 15 to 30 minutes of flight time in good conditions, with less in cold weather.
Since inventory measurement typically occurs quarterly rather than daily, finding suitable flying conditions within a reasonable window is rarely a problem. The 2021 Scientific Reports global drone flyability study confirms this pattern.
Vertical silos present a different challenge—drones can’t see through concrete, so traditional measurement methods remain necessary for these structures. Operations with limited internet connectivity should work with service providers who process data off-farm rather than attempting to manage large file uploads themselves.
Where the Economics Change
Not every operation will benefit equally from precision measurement. A 400-cow grazing operation in Vermont with minimal stored feed faces different economics than a 2,000-cow confinement operation in Wisconsin storing nine months of inventory.
Similarly, Southeast operations practicing rotational grazing might store only 3 to 4 months of silage. For these situations, traditional methods may provide adequate accuracy given the lower total investment in stored feed.
One producer who evaluated but decided against drone measurement made a valid point: “With only 600 cows and buying most of our grain as-needed, the $3,000 service would save us maybe $8,000 annually. That math works, but there are other investments with better returns for our operation right now.” This kind of thoughtful analysis respects that every operation has unique priorities.
Regional Variations and Support Programs
Implementation patterns vary significantly by region. Upper Midwest operations storing 8 to 10 months of feed see the highest returns from precision measurement. California’s large dairies benefit differently—they’re identifying shrink in real time on substantial commodity purchases rather than on stored forage.
What many producers don’t realize is that support exists for adopting these technologies. Multiple states offer cost-share programs through NRCS or state agricultural departments. Wisconsin provides reimbursement for up to 50% of precision agriculture technology costs. Minnesota offers grants for adopting data-driven management systems. These programs, detailed in 2024-2025 announcements from state offices, can significantly improve the economics of adoption.
Looking Ahead: The Strategic Implications
The industry landscape is shifting in ways that make precision feed management increasingly important. Major processors, including Nestlé and Danone, are implementing sustainability documentation requirements. By 2030, operations with 5 years of precision data will have distinct advantages in verifying feed conversion efficiency and optimizing resource use.
These sustainability programs currently offer premiums ranging from $0.50 to $1.50 per hundredweight—significant revenue when applied across annual production. Early adopters are positioning themselves for these opportunities, while others are still evaluating the technology.
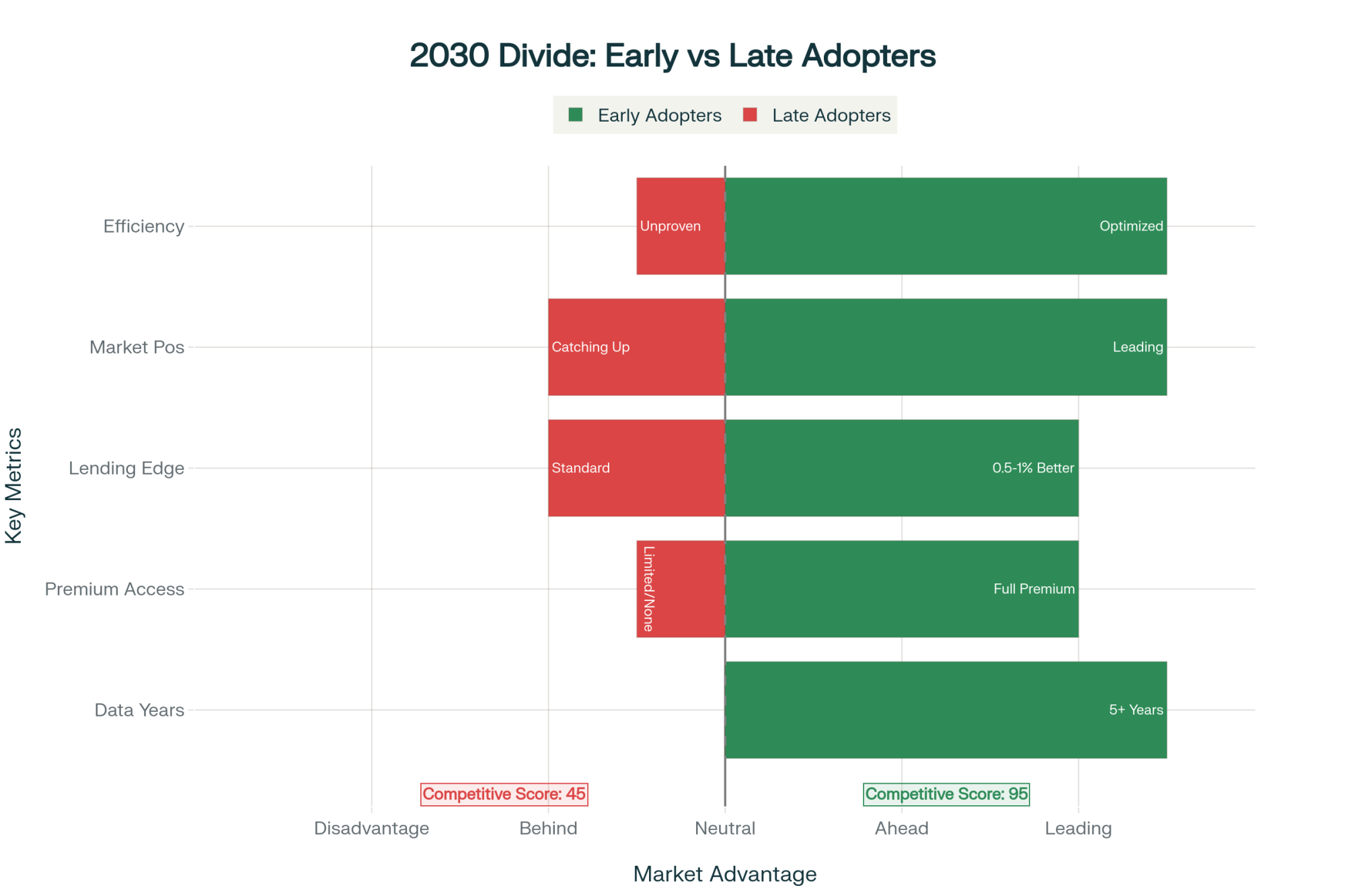
The labor dynamic adds another dimension. Operations reinvesting feed savings into automation report 30% to 40% reductions in labor requirements while maintaining production levels. With quality labor increasingly difficult to find and costing $20 to $25 per hour, these efficiencies matter.
Financial institutions are also taking notice. Lenders recognize that operations with precision management systems demonstrate better margins and lower default risk, translating to more favorable terms and rates.
USDA projections suggest the U.S. dairy industry will consolidate from approximately 35,000 farms today to between 24,000 and 28,000 by 2030. The operations that thrive won’t necessarily be the largest—they’ll be those that combine appropriate scale with operational efficiency.
A Practical Test for Your Operation
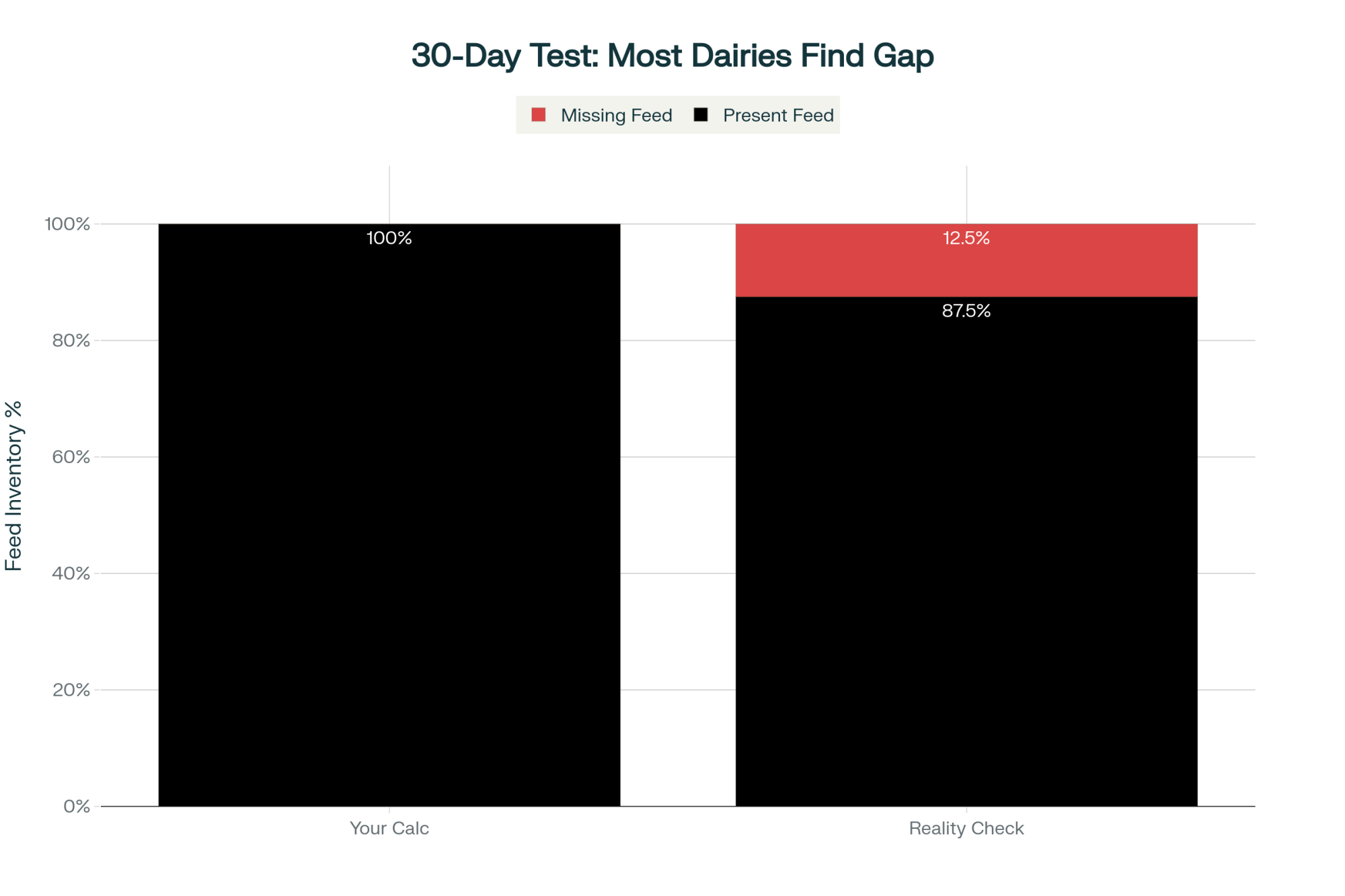
For producers interested but not yet convinced, I suggest a simple 30-day evaluation. Track three metrics daily: what your mixer scale indicates you fed, bunk appearance before the next feeding, and visual assessment of pile face movement.
After 30 days, compare purchase records with calculated usage. Most operations discover an 8% to 15% gap that they cannot explain. For a 1,200-cow dairy, that gap represents $72,000 to $135,000 in annual costs at current feed prices.
This evaluation costs nothing but time and reveals whether precision measurement would benefit your operation. If your numbers align within 3% to 5%, this may not be urgent. But if you discover a significant gap—as most do—the investment case becomes clear.
Practical Perspectives for Decision-Making
After examining data from operations across the country and discussing experiences with producers who’ve implemented these changes, several principles emerge:
First, determine whether you have a problem worth solving. The 30-day tracking exercise provides that answer without requiring any investment.
Second, you don’t need to revolutionize your entire feeding system. The five operational improvements outlined earlier can deliver $100,000 or more in annual savings for less than $20,000 in total investment.
Third, for most operations, service arrangements make more sense than equipment ownership. At $2,000 to $5,000 annually for drone measurement services, you access the technology benefits without the complexity.
Fourth, assign clear responsibility. Feed management as a secondary responsibility inevitably underperforms dedicated oversight.
Finally, consider the compound benefits. Early adopters are building advantages in sustainability documentation, labor efficiency, and capital access that extend well beyond immediate feed savings.
The discovery we’re making across the industry is that our traditional “good enough” approach has been far more expensive than we realized. Once operations identify where losses are occurring, they can’t return to the previous level of uncertainty.
For an industry facing continued margin pressure and evolving market demands, the ability to measure and manage precisely may determine who remains competitive. The question isn’t whether perfect measurement exists—it doesn’t. The question is whether three to four accurate measurements annually provide better decision-making than twelve months of estimation.
From my perspective, having watched operations transform their economics through systematic measurement, there’s a substantial opportunity hiding in plain sight on many dairy farms. The challenge—and opportunity—is deciding whether to pursue it.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- You’re losing $200,000 annually—and don’t know it – Traditional feed measurements are off by 15-30%, hiding massive shrink on typical 1,000-cow dairies
- Test yourself free in 30 days – Track three numbers daily (mixer output, bunk status, pile face movement); most farms discover 8-15% gaps worth $72-135K yearly
- Five simple fixes deliver $100K+ – Face management ($6-8K), scale calibration ($25-55K), ingredient placement ($30-40K), bunker sizing ($6-8K), refusal optimization ($40-70K)—total investment under $20K
- Rent accuracy, don’t buy it – Drone services at $2-5K/year provide quarterly measurements within 1-2% (versus 20-40% error with traditional methods)
- The 2030 divide is forming now – Early adopters secure sustainability premiums ($0.50-1.50/cwt), better lending rates, and processor partnerships, while others scramble to catch up
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Death of ‘Get Big or Get Out’? Why Tech-Savvy 500-Cow Dairies Are Outperforming Mega-Farms – This article explores how other technologies, like robotics and precision feeding, create highly profitable, mid-sized dairies, proving that efficiency and smart investment—not just scale—define success.
- The $11 Billion Gap: Where Processing Investment Meets Producer Reality – This strategic analysis details how new processor investments and updated FMMO component rules are changing milk checks. It shows why the feed efficiency gained from better measurement translates directly into capturing valuable component premiums.
- The $43800 Hidden in Your Water: How Top Dairies Gain 6 Pounds More Milk Daily – This piece expands the “hidden profit” concept from feed to water. It provides a tactical guide to water testing and treatment, revealing how another overlooked input can unlock significant production gains.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!



