Week-old beef calf: $1,400. Replacement heifer: $4,000. Still breeding beef? You’re not crazy—you’re doing the math.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: What started as desperate survival in 2018 has become an irreversible trap: beef-cross revenue now provides 16% of dairy farm income, forcing farmers to keep breeding beef at $1,400 per calf even as replacement heifers hit $4,000. This has driven U.S. heifer inventory to 3.9 million—the lowest since 1978—with 800,000 fewer coming before any recovery in 2027. Simultaneously, processors who invested $11 billion expecting 2-3% growth face just 0.4% milk expansion, guaranteeing plant closures and $3-5/cwt regional price swings. The industry is restructuring into three distinct survivors: fortress farms with over 1,500 cows capturing component premiums, strategic operations with 200-500 cows in profitable niches (organic/A2A2/grass-fed), and those exiting now at peak cattle prices. Wisconsin’s 10,000-heifer gain versus Texas’s 10,000-head loss proves that processor relationships and location now matter more than size. Behind the numbers, 2,400-3,700 dairy families face elimination—transforming not just an industry but entire rural communities.

You know something’s off when you’re seeing beef-cross calves bringing $1,000 to $1,400 at a week old while replacement heifers are hitting $4,000 at auction. It doesn’t make sense at first—but then you dig into what’s actually happening out there, and suddenly it all clicks.
We’re not looking at just another market swing here. What we’re seeing is the collision of desperate decisions farmers made back in 2018 and 2019 with billions in processing investments that assumed a completely different future. And if you’re wondering why your neighbor’s still breeding 40% of the herd to beef despite those heifer prices…well, let me walk you through what I’ve been hearing from producers across the country.

Note: Throughout this article, some producers and industry professionals spoke on condition of anonymity to discuss sensitive business details. All financial figures and operational data have been verified against industry benchmarks.
The Numbers Paint a Picture Nobody’s Prepared For
So, CoBank released its latest dairy heifer inventory analysis in August, and the numbers are… honestly, they’re worse than most people realize. According to the USDA’s National Agricultural Statistics Service January 2025 cattle report, the national number of replacement heifers stands at 3.914 million. That’s the lowest since 1978—back when the average herd was what, 30-something cows?
But here’s the kicker that really got my attention: only about 2.5 million of those heifers are expected to actually calve into milking herds this year, based on CoBank’s projections. That’s tracking to be the lowest since the USDA started keeping those specific records in 2001. The ratio’s collapsed, too—USDA’s July calculations show we’re down to 27 heifers per 100 cows. Ten years ago? That was 31 per 100.
And it gets rougher. CoBank’s projects indicate that we’ll lose another 357,490 heifers in 2025, followed by an additional 438,844 in 2026. They’re saying maybe we’ll get back 285,387 or so in 2027, but…that’s still a massive hole. Add it up and we’re talking about 800,000 fewer replacements before any real recovery kicks in.
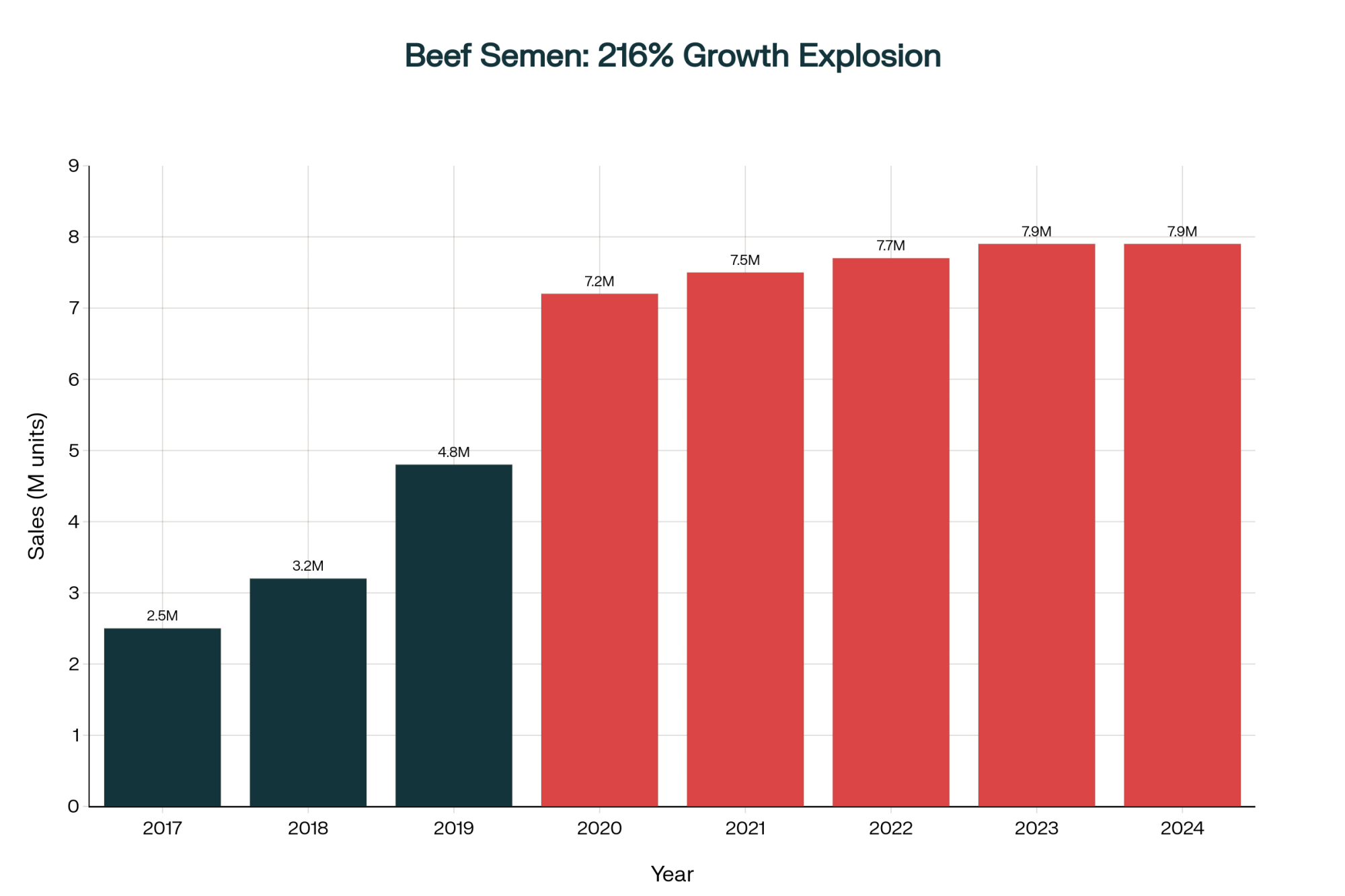
How Seven Years of Survival Mode Created Today’s Crisis
You can trace this whole thing back to that brutal stretch from 2015 through 2021. Class III milk prices averaged below $18 per hundredweight for most of those years—not continuously, but often enough to cause significant harm. University of Illinois dairy economist John Newton documented this period in his 2018 farmdocdaily analysis, calling it an extended period of sustained losses that fundamentally changed the industry.
By April 2019, according to the USDA’s Agricultural Marketing Service reports, replacement heifers that cost $ 2,000 or more to raise were only bringing $1,140 at market. Think about that for a second. You’re losing $860 to $1,360 on every single replacement you raise.
Then the technology all came together at once. Sexed semen finally worked reliably—industry data from Select Sires and other major AI companies shows you can get 90% female calves with 85-95% of conventional conception rates. Genomic testing through companies like Zoetis and Neogen dropped to about $40 per animal. And beef prices? Through the roof. Suddenly, those Holstein bull calves that might bring $200 on a good day were being replaced with Angus crosses worth anywhere from $600 to over $1,400, depending on genetics and your local market.
I mean, what would you have done?
The National Association of Animal Breeders has been tracking this transformation in their annual Semen Sales Reports. Beef semen sales to dairy farms went from about 2.54 million doses in 2017 to over 7.2 million by 2020. That’s nearly triple in three years. Their March 2025 industry update shows we’re now sitting at about 7.9 million units, and it’s just…stuck there. Meanwhile, conventional dairy semen sales have crashed almost 46.5% since 2020.
Why $4,000 Heifers Still Can’t Fix the Problem
Examining what doesn’t add up for many people: according to the USDA’s October 2025 Agricultural Prices report, heifers are currently worth a significant amount of money. Wisconsin’s averaging close to $2,860. Vermont’s around $2,930. Premium animals in California and Minnesota are fetching over $4,000, according to recent livestock auction reports. So why isn’t everyone breeding dairy again?
What I’m hearing from nutritionists working with Wisconsin herds is pretty consistent. Consider a typical 500-cow operation that breeds 40% of its cows for beef. They’re bringing in maybe $200,000 a year just from those beef calves. Add in cull cows at current prices, and you’re looking at $350,000 in cattle revenue.
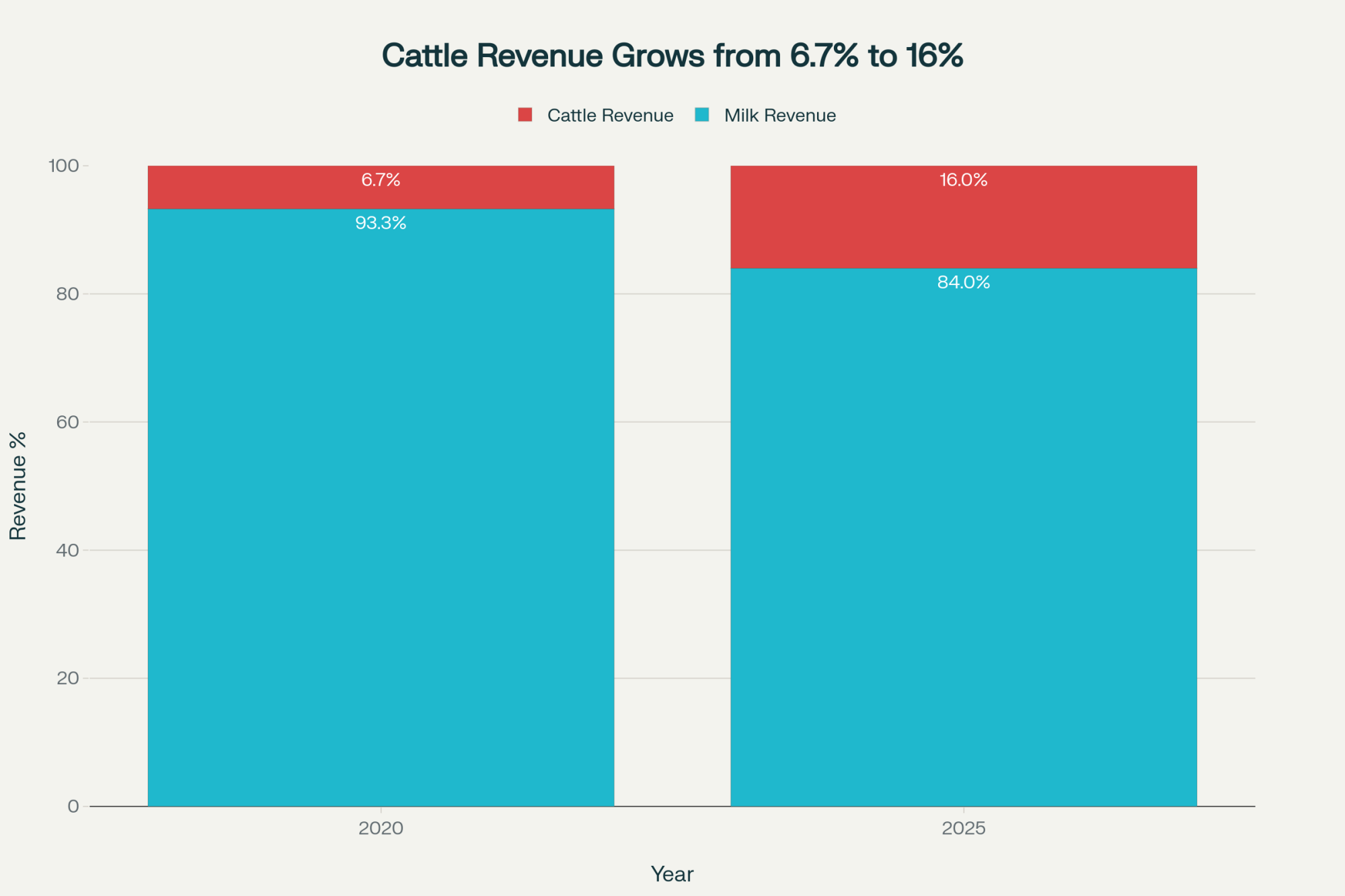
According to USDA Economic Research Service data, that’s approximately 16% of total farm income for many operations now. Back in 2020? Cattle sales were maybe 6.7% of dairy farm revenue.
As one nutritionist put it to me, “It’s not just extra money anymore. It’s structural. These guys can’t just flip a switch and go back. Walking away from that revenue would mean completely restructuring the operation.”

The Processing Overcapacity Challenge Coming in 2027
And here’s where it gets really messy. According to the International Dairy Foods Association’s industry investment tracking, the processing sector has invested more than $10 billion in new facilities over the past three years—some estimates put the total closer to $11 billion. New York’s Department of Agriculture reports that the state alone has $3 billion in processing investments that require an additional 10 to 12 million pounds of milk per day.
These plants were all designed assuming we would continue to grow milk production at a rate of 2-3% annually, as we have for decades, based on USDA historical data from 1995 to 2020. Instead? USDA’s October 2025 World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates project just 0.4% growth next year. That’s not a typo—zero point four percent.
Mike North from Ever.Ag’s Risk Management division put it bluntly at the September 2025 Milk Business Conference: “We don’t have enough cows to fill all these plants.” He thinks we’ll see inefficient plants close, and others running way under capacity. That’s billions in stranded investment.
What’s worth noting here is that we’re already seeing some policy discussions emerging. The National Milk Producers Federation has formed working groups to study the situation, though no concrete proposals have emerged. Meanwhile, some state agriculture departments are exploring incentive programs for heifer retention, but the scale of these initiatives remains small compared to the challenge.
Three Different Worlds Emerging
What’s really interesting—and I’ve been watching this develop over the past year or so—is how the industry’s basically splitting into three completely different business models.
The Big Operations (Your “Fortress Farms”)
These 1,500 to 5,000-cow dairies have basically built moats around their businesses. They’re conducting genomic testing on every single heifer through programs like Zoetis’ CLARIFIDE Plus, utilizing AI-powered systems like DairyComp for informed decision-making. According to the Penn State Extension’s 2025 component premium tracking, they’re achieving component premiums that add $1.50 to $2.50 per hundredweight.
Large Midwest operations I’ve talked with are reporting revenue per cow that’s approaching $6,000 to $7,000—numbers that would’ve been fantasy five years ago. They’re generating base milk revenue in the millions, plus substantial component premiums, and nearly a million dollars from beef calves in some cases.
What’s interesting here is something I noticed visiting a couple of these operations recently: they’re not just bigger—they’re fundamentally different businesses. One manager showed me their real-time component monitoring system. “We know within 0.1% what our butterfat’s gonna test every single day,” he said. “That consistency is worth an extra $750,000 a year to us.”
It’s worth noting that these operations are also exploring emerging technologies. Embryo transfer programs, automated calf feeding systems, precision nutrition through AI…they’re positioning themselves for whatever comes next. Some are even experimenting with automated milking systems that can handle 500-plus cows, completely changing labor dynamics.
The Strategic Middle
This is where it gets interesting for those with 200-500 cows. According to the USDA’s organic dairy market reporting, they’re finding ways to make it work through specific niches. Organic products typically sell for $7-12 more than conventional ones. University of Wisconsin extension studies on pasture-based dairy show grazing systems are cutting costs by 30-50%. Some are going direct-to-consumer and getting $4 more per gallon.
I visited an organic operation in Vermont last month, which had transitioned to organic in 2022, with 280 cows. The producer told me she’s actually more profitable now than when she had 350 conventional. The premium’s real—she’s averaging about $9.50 over conventional—and her vet bills dropped 40%.
Out in California, there’s a different approach. One Jersey producer with about 450 cows is locked into a specialized cheese contract. Between base and components, he’s getting close to $24.50 when commodity milk’s at $21. On 10 million pounds, that $3.50 spread is…well, you can do the math.
Down in Georgia—and this is something you don’t hear much about—a 300-cow operation switched to A2A2 milk production exclusively. They’re selling direct to Atlanta-area health food stores at premium prices. “It’s niche as hell,” the owner admits, “but it works for us.”
The Ones Choosing to Exit
Then there are the operations using these high cattle prices as their exit opportunity. After a decade of barely hanging on, they’re done—and honestly, who can blame them?
I caught up with a couple who recently sold their 185-cow place in Wisconsin. After accounting for debt service, living expenses, and reinvestment, they were netting maybe $18,000 a year for 70-hour weeks. Now they’ve got a solar lease on the land, bringing in $52,000 with zero labor. Can’t really argue with that decision.

Global Perspective: How Other Countries Face Similar Dynamics
What’s fascinating is seeing how this isn’t just a U.S. problem. The European Union’s dealing with their own version of this crisis, though for different reasons. Environmental regulations and nitrogen limits are forcing Dutch and German producers to reduce herd sizes, just as their processing sector has expanded to meet export market demands. According to European Dairy Association reports, EU milk production is expected to decline 1.5% annually through 2027.
New Zealand’s taking a different approach. Fonterra’s latest annual report shows they’re actually encouraging farmers to reduce production intensity and focus on value-added products. Their winter milk premiums now exceed NZ$11 per kilogram milk solids—that’s roughly equivalent to a $7/cwt premium in U.S. terms—specifically to maintain year-round supply for their specialty ingredient plants.
Brazil and India, meanwhile, are ramping up production. Brazil’s domestic consumption is growing at a rate of 3% annually, and the country is investing heavily in genetics and infrastructure. India’s cooperative model—completely different from ours—is actually expanding smallholder participation. It’s a reminder that there’s more than one way to structure a dairy industry.
What’s interesting is watching how other countries handled similar situations. Dairy Australia’s market analysis shows that in 2023, when their production hit 30-year lows, processors like Goulburn Valley Creamery started paying AUS$9.70 per kilogram milk solids—equivalent to about $28 per hundredweight U.S.—just to keep smaller farms from shutting down. We’re starting to see hints of that in the Upper Midwest—smaller co-ops offering bonuses that weren’t on the table two years ago.
Why Some Regions Are Winning While Others Lose
The shortage’s not hitting everywhere the same. USDA’s January 2025 cattle report shows Wisconsin actually added 10,000 replacement heifers last year. Meanwhile, Kansas dropped 35,000, Idaho lost 30,000, and Texas shed 10,000.
Why the difference? Extension specialists at UW-Madison point to several factors. It’s partly infrastructure, partly processor relationships, but mostly it’s about positioning. Wisconsin cheese plants require consistent, high-quality milk, and they’re willing to pay for it. They’re offering retention bonuses, multi-year contracts—things that make raising heifers actually pencil out.
Down in Texas, it’s brutal. One producer recently told me that he paid $4,200 per head for bred heifers from Wisconsin, plus an additional $380 each for trucking. “It hurt,” he said, “but dropping our ship volume would’ve cost us our quality premiums. That’s $140,000 gone.”
Out in the Mountain West states—Colorado, Wyoming, parts of Montana—they’re dealing with different challenges. Water rights, urban expansion, and feed costs… it’s pushing many smaller operations out. One Colorado producer told me, “Between Denver sprawl and water restrictions, we’re done in five years regardless of heifer prices.”
The “Obvious” Solution That’s Actually a Trap
You’d think with heifers at $4,000, somebody would be raising extras to cash in. Spend $2,400 raising them, pocket $1,600 profit. Simple, right?
Not really. The heifer management experts at UW-Madison have thoroughly reviewed this. First problem: mortality. The USDA’s 2022 Dairy Cattle Management Practices study shows you lose about 21% of heifers from birth to freshening when you factor in all causes of mortality and culling. So that $2,400 cost becomes over $3,000 per surviving heifer.
Then add labor—extension economists calculate $400-600 per head through freshening. Feed costs can fluctuate by $400 based solely on corn prices—we’ve seen a variation of $2.80 per bushel over the past 18 months. And you’re making a 24-month bet with no way to hedge the price risk.
As one extension specialist explained, “The only people successfully raising heifers for sale have paid-off facilities, family labor, and grow their own feed. That’s not a business model most can replicate.”
Industry Response: Fragmented Approaches to a Systemic Challenge
You’d think there’d be some coordinated response, but…not really. The National Milk Producers Federation has been discussing the situation, but they’re mostly focused on data collection and suggesting best practices. No real market intervention, though they are exploring potential policy recommendations for the next Farm Bill discussions.
Some cooperatives are exploring different approaches to help members finance replacement raising, though the details vary significantly by region. But as one board member mentioned in a recent meeting, the scale of what’s needed versus what’s being offered is pretty mismatched. We need hundreds of thousands, not tens of thousands, of additional heifers.
What’s encouraging is seeing some innovation at the regional level. A group of farms in Minnesota formed what they’re calling a “heifer pool”—basically sharing genetics and breeding decisions to optimize replacement production across multiple operations. It’s early days, but the concept’s interesting.
Meanwhile, some states are getting creative. Pennsylvania’s Department of Agriculture is piloting a heifer retention incentive program, offering $200 per head for farms that increase replacement numbers. It’s small—only $2 million allocated—but it’s something.
2027: The Year Everything Changes
Based on everything I’m hearing from processors, economists, and producers—plus what we’re seeing in reports from CoBank and Rabobank’s latest dairy quarterly analysis—here’s what’s probably coming:
Milk prices will diverge significantly regionally—possibly $3-5 per hundredweight between shortage and surplus areas. I’m already seeing it start. Some cooperatives in Texas are offering $2.40 location premiums for new farms near their plants.
Industry analysts suggest that processing plants will operate at 72-76% capacity, rather than the 85-90% required for profitability. Smaller regional processors will either close or get bought for significantly less than their construction cost. As one former cheese plant executive explained to me, “The consolidation is coming, it just hasn’t started yet.”
Heifer prices are likely to peak around $4,200-$4,800 in early 2027, based on historical price patterns from similar periods of shortage. They will then moderate back to $3,800-$ 4,200 as more sexed semen is used and the supply improves slightly.
According to NAAB’s projections, beef-on-dairy sales are expected to decline slightly—possibly to 6.5-7 million unitsfrom the current 7.9 million—but they are unlikely to return to pre-2020 levels. As one large-herd manager put it, “Once you’ve built those calf buyer relationships and you’re getting $1,000 to $1,400 per head, you don’t just walk away.”
The Human Cost We’re Not Calculating
What gets lost in all these numbers is what this means for actual people. Back in 2018, Agri-Mark started including suicide prevention hotline numbers with milk checks after losing three members to suicide, as documented in their member communications. The CDC’s 2020 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report shows farmers have the highest occupational suicide rate in America—43.7 per 100,000 workers, over 3 times the general population.
When 10-15% of dairy operations close over the next decade—that’s 2,400 to 3,700 families based on current USDA numbers—we’re not just losing businesses. These are communities that have been built around dairy farming for generations.
Researchers studying farmer mental health, such as those at the University of Illinois’ Agricultural Safety and Health Program, have found that after a decade of financial stress, decision-making processes undergo fundamental changes. As one researcher explained, “These aren’t people making strategic business decisions anymore. They’re making survival decisions from a place of chronic stress.”
I see it visiting farms. The producer who won’t look you in the eye when money comes up. The couple who stopped talking about succession because their kids made it clear they’re not coming back. The neighbor who sold out and now won’t answer calls because the shame’s too heavy.
That’s the real cost we’re not calculating.
Your Survival Playbook for the Next 18 Months
Look, every operation’s different, but here’s what seems to make sense based on what I’m seeing:
If You’re Under 200 Cows
Be honest about whether this still works for you. I know that’s hard, but extension economists have shown pretty clearly that the economics are brutal at this scale unless you’ve got a real niche.
If you’re staying, pick your lane now. Organic certification takes three years, but it adds significant premiums, according to USDA data. Grass-fed certification is faster. Direct sales need the right location. However, you have to pick one and commit to it completely. Half-measures don’t work anymore.
Consider teaming up with neighbors. I’m seeing more informal cooperatives forming—sharing equipment, coordinating breeding, even pooling milk for better bargaining power. It’s worth exploring.
If You’re 200-500 Cows
This is your moment to choose. The middle ground’s gone.
Invest smart. Extension research indicates that testing the top 30% of animals genomically costs approximately $3,000-$ 4,000 per year, but can significantly advance your genetics. Activity monitors from companies like SCR by Allflex run $150-200 per cow, but their field data shows conception rate improvements of 8-12%.
Build relationships with your processor now. The farms that’ll get premiums when things get crazy in 2027 are the ones building trust today. Consistent quality, reliable volume, good communication—that’s what processors are looking for.
And keep beef breeding at a maximum of 35-40%. Yeah, those $1,000-plus checks are nice, but you need flexibility when markets shift.
If You’re Over 500 Cows
Focus on component consistency. Penn State’s data show that farms with less than 2% daily variation are earning significant premiums—$375,000 to $750,000 annually on 50 million pounds of product.
Test everything genomically. University research consistently shows that herds testing all their females make genetic progress over twice as fast. At $40 per test, it pays for itself quickly through increased production efficiency.
Be ready to expand strategically when neighbors exit. But like one Idaho dairyman told me, “Don’t expand just because you can. Expand because it makes your operation better.”
What This All Really Means
We’re sitting at 3.914 million heifers—the lowest since 1978, according to the USDA—with 800,000 fewer expected to arrive before anything improves, based on CoBank’s modeling. We’re not going back to the dairy industry we knew.
What started as desperate survival with beef-on-dairy has triggered a complete restructuring. When cattle revenue reaches 16% of farm income, according to USDA ERS data, and large operations capture premiums that smaller farms cannot match, when $10 billion in processing investment faces milk shortages nobody predicted—this is creative destruction happening in real-time.
What’s emerging isn’t necessarily better or worse; What’s emerging isn’t necessarily better or worse. It’s fundamentally different.. The broad middle that defined dairy for generations is disappearing, replaced by high-tech large operations and strategic niche players.
The decisions you make in the next 18-24 months about breeding, technology, and positioning will determine not just profitability but survival. There’s opportunity in this chaos, but only if you recognize the game has completely changed.
The heifer shortage isn’t the crisis. It’s the catalyst exposing a transformation that was always coming. The question now is whether you’re positioned for what’s next or still trying to preserve what was.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- The Numbers: 3.9 million heifers (lowest since 1978) with 800,000 fewer coming by 2027—yet farmers won’t stop breeding beef because it’s now 16% of revenue vs 6.7% in 2020
- The Collision: $11 billion in new processing capacity built for 2-3% growth will get 0.4%—expect plant closures and $3-5/cwt regional price swings by 2027
- Your 18-Month Strategy: Scale to 1,500+ cows for premiums | Find your niche at 200-500 (organic/A2A2/grass-fed) | Exit under 200 while cattle prices are high
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- 2025 Dairy Market Reality Check: Why Everything You Think You Know About This Year’s Outlook is Wrong– This strategic analysis reveals why traditional market forecasts are failing. It provides a crucial framework for understanding how component economics, processing relationships, and volatile trade policies are fundamentally reshaping dairy profitability beyond the heifer shortage.
- AI and Precision Tech: What’s Actually Changing the Game for Dairy Farms in 2025? – For producers aiming to build a “Fortress Farm,” this article details the specific technologies creating separation. It breaks down the ROI on AI-driven health monitoring, precision feeding, and robotics, demonstrating how to achieve quantifiable cost savings and yield gains.
- The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration – While the main article explains why beef-on-dairy is a structural necessity, this tactical guide explains how to execute it for maximum profit. It provides actionable strategies on sire selection, calf care, and marketing to optimize your beef-cross revenue stream.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.






 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!



