Although I resolutely hate New Year’s Resolutions, I confess that each turning of the calendar year will find me dreaming up a “project” for the next twelve months. Although I hate resolutions because they just don’t work, nevertheless, I am hooked on projects that that actually do something! Thus, I happily substitute project planning for resolution breaking. However, the project chosen has to have certain features. It must make a difference. It must have a plan. It must have buy in, finances and scheduled action.
Today when I applied those criteria to topics for Bullvine articles, lo-and-behold in the cold dark days of January a light went on!!! Well duh! As I keep an eye on dear hubby’s daily trips to our little barn, I watch to see his progress by looking for the lights in various locations. Lights are also the handy way that my ninety-seven-year-old Mother in Love and I signal that “all’s well!” at her house next door! If the signal light is off after dark, it’s time for a check in. This led me to recall some experiments we implemented during our milking herd days regarding long-day versus short-day lighting on milk production and herd health management.
What’s Light Got to Do With It?
While it would seem simple to simply program dairy facility lighting to turn off and on for the desired amounts of time, there are other considerations that complicate the procedure. For one thing, not all dairy chores are on a predictable schedule. Calvings, maintenance, health issues all require that the human staff can see clearly to carry out their work. Happily, there are studies that allow the necessary dark time for the cattle but allow the necessary light for reading ear tags, medication or other detailed activities.
To measure the level of lighting available, a light measure should be used to measure the foot candles. Fifteen (15) foot candles of light in the housing is the recommended benchmark for benefiting from a long day photoperiod. At the other end of the light manipulation spectrum, darkness also plays an important role. Research shows that cows do not perceive light under five foot candles. This is an important piece of information, particularly for managing 3X operations and anywhere that employees need to be able to continue their work without disrupting the photoperiod being targeted for the herd. One recommended solution is the placing of low-intensity red lights 20 to 30 feet apart and 20 feet off the ground.

You might think the amount of light in your barn doesn’t matter much. Think again. You can improve cow comfort, herd health and productivity by the flick of a light switch.
Working in the Right Light
Studies carried out by Professor Alma Kennedy at the Universities in Canada (Manitoba and Alberta) conclude that dairy cattle can tolerate at least one foot-candle of white light and still experience this as “dark.” This research also showed that exposure to 5 foot-candles at night reduced the normal level of the main nighttime hormone (melatonin) by 50 to 70 percent, a significant interference with the animals’ normal nighttime function.
Based on the present research findings, it is determined that night light in dairy barns can be designed with an intensity of about 1 to 1.5 foot-candles. When this is the case, dim light at 1 to 1.5 foot-candles allows surprisingly precise observation. Literature reports that “a person with normal eyesight can read newsprint with one foot-candle of light. More specifically, dairy farmers report that ear tags can be read, and cows identified at a distance when using this level of dim light.” Some farmers refer to this as “moonlight.” Dual-level fixtures and specially designed fluorescent fixtures are commercially available to meet this purpose.
And the Studies Show…
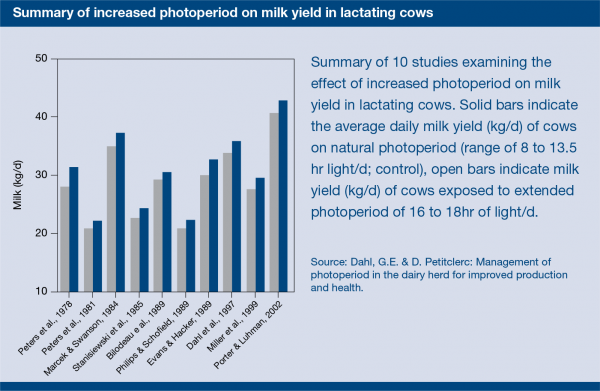
Source: Dahl, G.E. & D. Petitclerc: Management of photoperiod in the dairy herd for improved production and health.
The investment in special lighting is well supported by research trials that provide proof on the effectiveness of long-day lighting as a tool for all dairy operations.
Lactating Cows – More production
There is up to a 10% increase in milk production when cows are given a long day photoperiod. One study reports that cows receiving 16 hours of light a day produce 3.7 pounds more milk a day than cows under a natural lighting scheme. Furthermore, after 20 days, the difference increases to 6.8 pounds per day. Sixteen hour lighting also slowed the decrease in milk production of those cows that originally started with natural lighting.
Lactating Cows – More DMI
Results of studies also supports that cattle exposed to long day lighting take in more dry matter. Compared to cows under a natural photoperiod of 9 to 12 hours of light, the 16-hour exposure can result in up to 6% more dry matter intake. It is interesting that the additional intake did not have a corresponding weight gain. This suggests that long day photoperiod cows are more feed efficient and are capable of converting increased dry matter intake into milk.
Photoperiod Can Affect Reproductive Performance
Dairy herds that provided 24 hours of light to cattle saw negative results. Providing 24 hours of light resulted in longer days between breedings, more days open, and more breedings per cow.
Numerous research studies in North America have clearly demonstrated that when dairy cows are provided summerlike, long days in the winter, they respond with increased milk production. The increase in yield noted in nine such studies average 5 pounds per cow per day. No adverse effects on fertility or health have been reported.
Light Can Mean Lower Age to Puberty
A goal of the industry has been to get heifers into the milking herd as soon as possible. Previous research has indicated that long day photoperiod can lead to leaner growth, greater mammary development, and lower the age to puberty by an average of one month. One study determined that breeding and calving of the heifers in the long day photoperiod occurred earlier than heifers in a short day photoperiod. Even though long day photoperiod heifers had a lower body weight, they did not experience limited skeletal growth. Instead, they had lower body condition scores because they were using the energy that they consumed for skeletal growth. Feed intakes did not differ between the short day photoperiod and long day photoperiod groups and long day photoperiod heifers spent less time at the feed bunk, which would suggest they were more feed efficient. The long day photoperiod heifers also had higher milk production throughout the first 5 DHI tests.
In one of the first studies looking at differences in the growth between heifers with supplemented lighting (16 hours) and natural lighting, heifers in the supplemented lighting group had a larger heart girth size of about 1.6 inches after the 16-week trial. These heifers also averaged 1.9 pounds of daily gain compared to the 1.7 pounds for the heifers in a natural lighting scheme.
Dry Cows Need Less Light
Dry cows have the opposite effect with a long day photoperiod compared to lactating cows and heifers. Providing dry cows with a short day photoperiod leads to higher milk production the next lactation. One study has shown milk production increased 6.8 pounds per day in the next lactation. Milk, fat and protein yields were also higher in the short-day photoperiod cows. A short-day photoperiod also lead to 2.9 lbs more daily dry matter intake during the dry period.
Additional Management Factors
Farmers have many different protocols to increase milk production including manipulating the amount of light available throughout the day. One practice that would yield significant results would be to start managing lighting at a young age. Producers should provide long day photoperiod to their heifers to help increase dry matter intake and make them more feed efficient. Providing a long day photoperiod would also allow them to breed heifers at an earlier age. Dry cows benefit the most from a short day photoperiod, 8 hours of light and 16 hours of dark. Dry matter intake increases when dry cows have shorter lighting periods.
With ever-narrower margins, dairy farmers are always seeking tools that will improve the productivity of their dairy farms.
First make the plan. Modernize and develop lighting on your dairy enterprise.
Then consider the finances. Sure there will be expenses but there will also be proven profitability.
The Bullvine Bottom Line
As we have learned, long-day light is a simple and well-proven technique to increase milk production and profitability.
Don’t make resolutions that you won’t follow through on.
Instead, make sure that you’re seeing your dairy herd in the right light!
Get original “Bullvine” content sent straight to your email inbox for free.